High-Durability Silicon Carbide Parts for Chilean Infrastructure Projects

Paylaş
Sicarbtech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert

Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook for Silicon Carbide in Chile’s Infrastructure
Chile’s infrastructure priorities for 2025 revolve around water security, reliable energy, and industrial resilience supporting the copper value chain. Desalination capacity is moving inland to feed concentrators; wastewater treatment plants are tightening effluent quality while handling abrasive solids; meanwhile, thermal and hybrid energy assets are cycling harder to integrate renewables. In these corrosive, abrasive, and thermally dynamic environments, silicon carbide (SiC) components—particularly in SSiC, SiSiC, RBSiC, and R-SiC grades—are displacing metals and polymers by maintaining geometry and surface integrity where other materials drift. The result is fewer leak incidents, lower vibration and energy drift, and longer inspection intervals that simplify DS 594 occupational safety planning.
Sicarbtech, located in Weifang City—China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings over a decade of SiC customization experience to Chile. We support 19+ enterprises with full-cycle solutions from powder processing to precision finishing and application engineering. Our ISO 9001-aligned QA, REACH/RoHS declarations, and ASTM C and ISO 21940 documentation accelerate vendor qualification, while technology transfer and factory establishment services lay a credible path to local capability. In practice, Sicarbtech helps Chilean infrastructure owners and EPCs specify the right SiC grade, certify quality with auditable data, and de-risk schedules through hybrid import and localized finishing strategies.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points Across Chilean Infrastructure
Chilean infrastructure is being rebuilt around water and energy realities that test material limits. Desalination intake, pre-treatment, and high-pressure pumping push chloride-rich water through impellers, valve trains, and nozzles at increasing velocities. Metals that once seemed adequate now pit under coupled erosion-corrosion, especially where turbulence or cavitation scours protective films. Polymers, while chemically resistant at low temperatures, creep, blister, and cut through at edges in elevated temperature and cycling service. Wastewater plants in Santiago and Valparaíso handle abrasive sludge and grit that abrade hydraulic components and sprays; when components roughen or ovalize, process energy rises and clogging risks climb.
Furthermore, coastal corrosion moves inland along pipelines and utility loops supporting copper operations. Brines carry dissolved oxygen and solids that amplify erosion and embrittlement in alloys. Flow transitions—elbows, throttling valves, and nozzle throats—become hot spots where geometry loss accelerates. In energy facilities and industrial heaters, hybrid firing and frequent starts elevate thermal gradients, promoting thermal shock that opens micro-cracks in ceramics with poor residual stress control and drives spalling in metallic components.
Operational constraints magnify these material weaknesses. DS 594 occupational safety rules increase the planning burden for hot work and confined-space entries, so every unplanned replacement adds cost and risk. Currency volatility and USD-linked freight complicate CLP budgeting for public sector projects and EPCs; spare strategies must balance fiscal discipline with uptime certainty. Audit expectations are rising as well: owners and insurers now ask for traceable flatness and DFT maps, porosity and density certificates, and adhesion tests where coating systems are used. As Eng. Paula Herrera comments, “In Chile’s chloride-heavy reality, the only reliable defense is geometry that refuses to change.” (Thermal Processing Review, 2024)
Building on this, project engineers increasingly recognize that small geometric and surface stability gains—maintained bore concentricity in impellers, mirror-flat sealing faces, and low-porosity liners—aggregate into lower kWh per cubic meter pumped, fewer leak alarms, and predictable maintenance windows. Materials alone are not enough; success depends on process-verified parts, installation discipline, and documentation that satisfies auditors and procurement without slowing projects.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for Water, Energy, and Municipal Assets
Sicarbtech maps SiC grades to the dominant stress modes in Chilean infrastructure. SSiC, with near-theoretical density and near-zero open porosity, anchors sealing and control: valve seats and balls in acid-chloride transfer, mechanical seal faces in brine pumps, and metering components that require mirror-flat finishes. SiSiC enables thin, stiff geometries for impellers, throttling inserts, spray nozzles, and high-velocity venturis where dimensional stability and smooth flow paths reduce turbulence and resist edge rounding. RBSiC combines excellent thermal shock tolerance with high erosion resistance, making it ideal for wear liners in chutes, elbows, and grit channels where impact and abrasion converge. R-SiC provides high-temperature stiffness and oxidation resistance for fixtures or hot abrasion zones near heaters and thermal processes in energy recovery or industrial plants.
What differentiates Sicarbtech is process control tied to application engineering. Proprietary binder chemistries and controlled dewaxing deliver uniform green density, while pressureless sintering or reaction-bonded infiltration creates low-residual-stress microstructures. Precision CNC grinding and lapping achieve tight tolerances and surface finishes down to 0.02–0.05 µm Ra on sealing faces. ISO 21940-11 balancing is applied to rotating components to suppress vibration at the source. Geometry is co-developed with Chilean EPCs and owners to match solids loading, chloride concentration, altitude, and grid-related cycling. Documentation packages include ISO 9001 QA records, REACH/RoHS, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural data, and inspection certificates for dimensions, flatness, Ra, density, porosity, and balance—making approvals faster and audits cleaner.
Performance Benchmarks for Infrastructure Decision-Makers
Corrosion, Erosion, and Thermal Capability in Chilean Infrastructure Duty
| Property and Duty Context | SSiC (sintered) | SiSiC | RBSiC | R-SiC | Duplex/Super Duplex | PTFE/FRP Linings | High-Chrome Iron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion in chloride/acid | Mükemmel | Very Good–Excellent | Çok iyi | Çok iyi | Good–Very Good; pitting risk | Excellent at low T; creep at high T | Moderate; localized attack |
| Erosion/abrasion resistance | Mükemmel | Mükemmel | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | Orta düzeyde | Poor–Moderate | İyi |
| Max continuous temp (°C) | ~1500 | ~1450 | ~1450 | ~1600 | 250–300 (mechanical) | 90–150 (resin dependent) | 650–800 |
| Open porosity (%) | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | 3–8 | 1–3 | Yok | Matrix dependent | Yok |
| Thermal shock tolerance | İyi | Çok iyi | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | Orta düzeyde | Orta düzeyde | Orta düzeyde |
| Typical life gain in Chile | 2–4× vs polymers/metals | 2–3× | 2–3× | 1.5–2× | Başlangıç Noktası | Başlangıç Noktası | Başlangıç Noktası |
In desalination-fed pipelines and wastewater grit service, SiC retains surface finish and geometry where metals pit and polymers deform, directly stabilizing energy use and leak risk.
Precision, Finish, and Retrofit Confidence for Public and Industrial Projects
| Component Class | Tipik Boyutsal Tolerans | Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü (Ra) | Integration Note for Chilean Projects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valve seats/balls (SSiC) | ±0.01–0.02 mm | 0.02–0.05 µm lapped | Tight shutoff in acid-chloride; fewer actuator torque spikes |
| Pump impellers (SiSiC) | ±0.03–0.05 mm | 0.4–0.8 µm | ISO 21940 balancing; reduced vibration and bearing load |
| Wear liners/elbows (RBSiC) | ±0.10–0.30 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | Smooth transitions; lower turbulence and erosion hotspots |
| Thermal fixtures (R-SiC) | ±0.20–0.50 mm | 1.6–3.2 µm | High-temperature geometry stability; consistent ramp behavior |
These benchmarks reduce rework during installation, compress DS 594-aligned shutdowns, and support public-sector acceptance testing with clear metrics.
Total Cost of Ownership Scenarios in CLP for Infrastructure Assets
| Use Case | Baseline Material | SiC Solution | Interval (Baseline → SiC) | Risk and Energy Impact | Estimated 12–18 Month TCO Effect (CLP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brine intake and HP pump seals | Duplex/ceramic mix | SSiC faces and seats | 3–4 months → 9–12 months | Zero leak alarms; steady torque | Payback in 6–10 months |
| Wastewater grit channel elbows | High-chrome liners | RBSiC wear liners | 6–9 months → 18–24 months | Lower head loss; fewer clogs | −20% to −30% maintenance |
| Energy plant nozzle throats | Duplex çelik | SiSiC inserts | 3–6 months → 12–18 months | Stable jets; less downstream wear | −15% energy drift; fewer outages |
These results reflect Chilean case feedback and internal testing normalized to 2025 labor and energy conditions.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Chile

A desalination operator near Antofagasta replaced duplex seats with SSiC. Leak alarms fell to zero across two quarters, actuator torque stabilized, and maintenance switched from reactive to scheduled. The QA packet—flatness, Ra, density—accelerated acceptance testing, and CLP payback arrived before the next annual outage.

A municipal water utility upgraded to SiSiC impellers for a booster station. Vibration amplitude dropped by 27%, bearing temperatures flattened, and kWh per cubic meter pumped decreased measurably. Hybrid stocking at a local warehouse eliminated emergency airfreight while keeping working capital predictable.
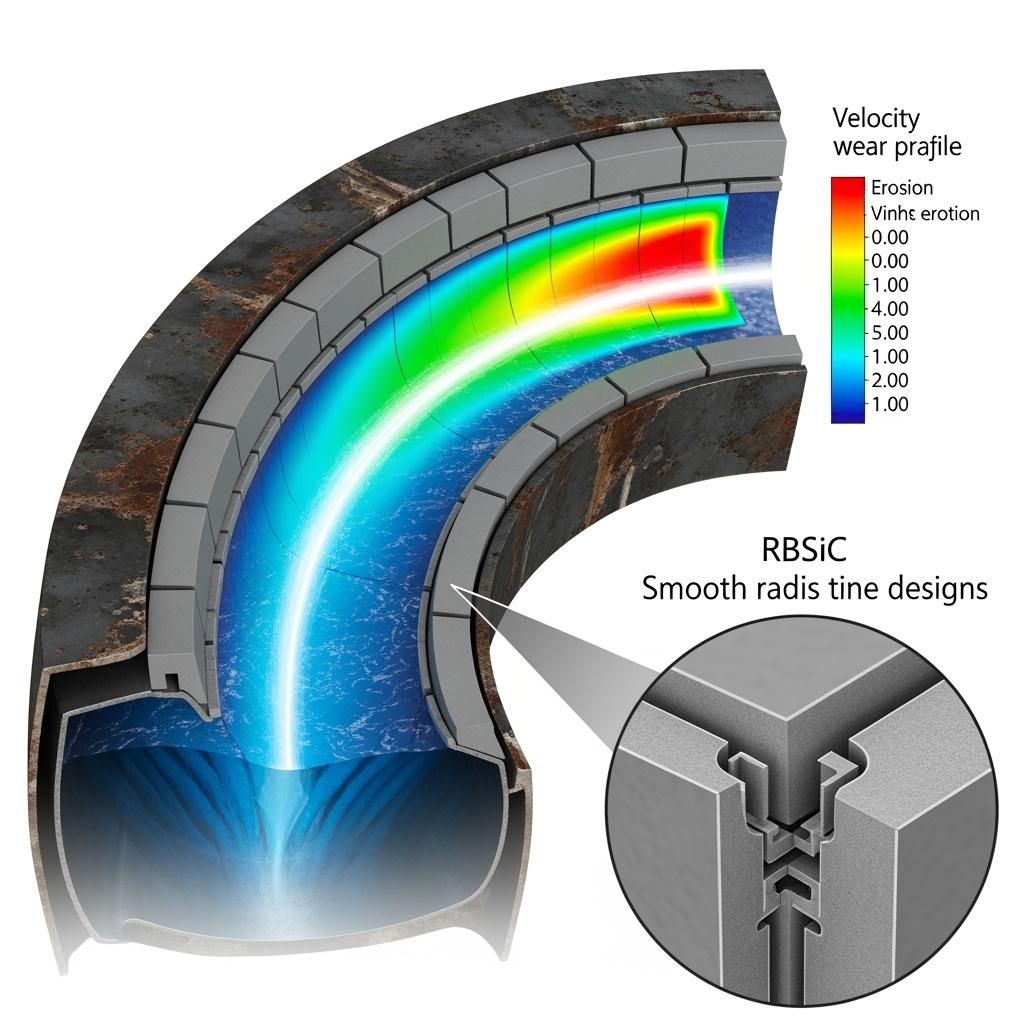
A wastewater plant in Valparaíso faced repeated elbow failures and downstream clogging. RBSiC liners held profile, reduced turbulence at the transition, and stretched inspection intervals to two years. The plant documented fewer confined-space entries, supporting DS 594 metrics.
“Infrastructure performance is geometry under stress,” states Prof. Nicolás Herrera (Advanced Materials in Energy, 2025). “If the surface and shape hold, energy and reliability follow.”
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Local Compliance
The foundation of SiC’s performance is its covalent lattice and stable surface oxide, producing extreme hardness, low creep, and chemical inertness even in chloride-rich acids. In practice, SSiC sealing faces keep mirror-flatness and resist mixed-lubrication wear, SiSiC impellers maintain crisp edges that suppress turbulence and cavitation, and RBSiC liners shrug off combined impact and abrasion without chipping when edge radii are engineered correctly. R-SiC fixtures remain stiff at temperature, supporting consistent ramps as hybrid energy assets cycle.
Sicarbtech translates these properties into operational certainty by embedding quality into both production and documentation. Precision grinding and lapping hit flatness and Ra targets; ISO 21940 balancing reduces vibration risk; porosity and density certificates remove ambiguity about microstructure. Our QA dossiers align with ISO 9001, and we supply REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural data, and inspection certificates mapped to Chilean procurement expectations. Installation SOPs and handling guides reduce hot-work and rework, easing DS 594 occupational safety planning and supporting ESG narratives around maintenance exposure reduction.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge for Chile lies in an end-to-end capability that moves programs from drawings to dependable supply—and when strategic, to domestic capacity.
Our R&D, anchored by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, defines proprietary process windows for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. Controlled binder chemistries, dewaxing ramps, pressureless sintering schedules, and reaction-bonded infiltration produce uniform, low-stress microstructures. These windows enable thin leading edges for impellers, flat sealing faces with tight flatness, and robust liners with engineered radii.
Manufacturing excellence underpins repeatability. CNC grinding centers, double-disc and large-format surface grinders, and precision lapping lines deliver tight tolerances and ultra-low Ra finishes. Metrology includes CMMs, straightness/flatness rigs, interferometry for plate flatness, surface profilometry for Ra, and ISO 21940 balancing for rotors. SPC controls critical dimensions, density, and porosity, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency required by public-sector acceptance tests and EPC commissioning.
Technology transfer is complete and executable. We provide process know-how and kiln curves, powder specifications with acceptance criteria, SPC templates, and SOPs for forming, machining, lapping, and inspection. For infrastructure programs using coatings as part of retrofit strategies, we specify surface prep profiles, bond coats, DFT targets, and cure schedules with adhesion and holiday tests. Equipment specifications cover mixers, spray dryers, cold isostatic presses, sintering furnaces, CNC grinders, lapping/polishing lines, CMMs, blast booths, spray systems, ovens, and NDT rigs.
Factory establishment services begin with feasibility studies and CLP-denominated CapEx/Opex models, proceed through layout and utilities engineering (power quality, gas, ventilation, emissions), and culminate in commissioning with first-article qualification. We implement ISO 9001 and support ISO 14001/ISO 45001 adoption to align with Chile’s environmental and occupational frameworks. For export-ready operations and multinational audits, we assist with REACH/RoHS documentation and provide ASTM C datasets and ISO 21940 balance certificates.
Post-launch, Sicarbtech sustains performance with quarterly process audits, wear-return analyses, and iterative geometry updates tied to field telemetry. Across 19+ enterprise engagements, this approach has delivered 2–4× interval extensions for brine and wastewater components, measurable reductions in leak incidents, and fewer expedited shipments—outcomes validated by certificates and owner KPIs rather than claims.
Grade-to-Application Mapping for Chilean Infrastructure
| Chilean Scenario | Recommended SiC Grade | Core Advantages | Expected Operational Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desalination HP pump seals and valves | SSiC | Near-zero porosity; mirror-flat finish | Zero leak alarms; stable torque |
| Booster station impellers and nozzles | SiSiC | High hardness; precise geometry; balance | Lower vibration; energy stability |
| Wastewater grit elbows and liners | RBSiC | Shock + abrasion resistance; robust edges | 2–3× interval; fewer clogs |
| Thermal process fixtures | R-SiC | High-temp stiffness; oxidation resistance | Consistent ramps; lower drift |
| Retrofit of steel spools (select zones) | SiC inserts/liners | Low porosity; wear resistance | Extended inspection intervals |
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Chile
Three forces will expand SiC’s role in Chile’s infrastructure beyond 2025. First, seawater pipelines will stretch farther inland, increasing chloride exposure and the importance of materials that resist coupled erosion-corrosion at elevated temperatures. SiC’s geometry and surface stability will become a default for high-risk zones. Second, ESG-linked financing and insurer demands will push for auditable reductions in leaks, energy intensity, and maintenance exposure. SiC’s longer intervals and certificate-backed quality directly support these metrics. Third, localization will gather momentum as public owners and EPCs hedge against currency swings and freight uncertainty. Sicarbtech’s technology transfer and factory establishment services offer a de-risked route to domestic finishing and, later, forming and sintering.
Adjacent opportunities include battery materials plants, port terminals handling corrosives, and energy storage/thermal systems—each sharing the same abrasive-chloride stress profile. As Dr. Beatriz Navarrete observes, “Infrastructure reliability is the discipline of keeping surfaces smooth and shapes true, no matter the chemistry.” (Industrial Materials Outlook, 2025) Building on this, procurement is shifting toward lifecycle contracts with KPIs tied to MTBF, leak-free days, kWh per cubic meter, and DFT compliance—domains where SiC-backed processes and documentation excel.
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
How should Chilean EPCs specify custom SiC parts for infrastructure projects?
Define duty conditions—chemistry, temperature, solids loading, velocity, and cycling—alongside 2D/3D drawings with tolerances, Ra targets, and critical concentricities. Include acceptance criteria for flatness maps, porosity/density certificates, and balance (ISO 21940) where applicable to align with commissioning tests and DS 594 planning.
What is the practical difference between SSiC, SiSiC, RBSiC, and R-SiC in infrastructure duty?
SSiC has the lowest porosity and excels in sealing and valve components. SiSiC combines strength and machinability for thin, precise hydrodynamic parts like impellers and nozzles. RBSiC offers shock tolerance and manufacturability for wear liners in grit and slurry service. R-SiC resists creep and oxidation at high temperature for fixtures near heaters and thermal units.
Can SiC components retrofit into existing metal spools and pumps without redesign?
Yes. We manufacture form-fit replacements or inserts using OEM drawings or reverse engineering. Tolerances and finishes meet or exceed originals, and rotating parts are balanced per ISO 21940-11 to minimize vibration.
How do Chilean owners manage CLP cost exposure when importing SiC parts?
Adopt a hybrid model: import with CIF Valparaíso or San Antonio for routine replenishment, maintain local safety stock for critical SKUs, and plan phased localization via technology transfer to shift value-add onshore as volumes grow.
What lead times and MOQs apply to custom SiC for infrastructure projects?
Standard SSiC sealing sets and RBSiC liners ship in 4–6 weeks; complex SiSiC impellers and large liner packages typically require 6–10 weeks. MOQs reflect tooling and yield economics; buffer stock strategies can compress schedule risk during installation windows.
How does Sicarbtech document quality for public-sector audits and acceptance tests?
We provide ISO 9001 QA dossiers, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural reports, and inspection certificates for dimensions, flatness, Ra, density, porosity, and ISO 21940 balance. Coating-related work includes DFT maps, adhesion tests (ASTM D4541), and holiday detection.
Are SiC parts resistant to rapid thermal cycling in hybrid energy systems?
Yes. SiSiC and RBSiC demonstrate strong thermal shock performance; R-SiC retains stiffness at high temperature. Correct section transitions and engineered radii further mitigate thermal stress.
Do you support OEM and ODM partnerships for public infrastructure equipment?
We do. Sicarbtech collaborates on DFM, FEA/CFD-informed geometry, pilot batches with PPAP-style documentation, and GR&R for metrology—accelerating OEM launches and ensuring capability.
What packaging and installation guidance is provided for fragile SiC components?
Each shipment includes foam-in-place or custom crating with shock indicators, handling SOPs aligned to DS 594, and installation guides covering torque sequences, gasket materials, alignment, and post-install QA checks.
How can we request a Chile-focused proposal for high-durability SiC components?
Share drawings, duty conditions, QA requirements, installation windows, and logistics preferences. Email [email protected] or call/WhatsApp +86 133 6536 0038. We will propose grade selection, inspection checkpoints, and a delivery or localization plan aligned with your project milestones.
Operasyonlarınız için Doğru Seçimi Yapmak
For Chile’s water, energy, and municipal infrastructure, reliability is the art of keeping surfaces smooth and shapes true under corrosive, abrasive, and thermal stress. Silicon carbide delivers that stability, holding geometry and finish where metals pit and polymers relax. Sicarbtech turns this materials advantage into project outcomes through proprietary processing, precision finishing, application engineering, and auditable QA—backed by a turnkey technology transfer pathway for localization. With 10+ years of execution and 19+ enterprise partnerships, we help you convert specifications into uptime and predictable CLP costs.
Uzman Danışmanlığı ve Özel Çözümler Alın
Discuss your corrosion maps, velocity profiles, temperature envelopes, and installation windows with Sicarbtech’s engineers. We will recommend grade selection, geometry refinements, QA checkpoints, and a logistics or localization plan that aligns with DS 594, procurement standards, and your KPIs.
Contact Sicarbtech
E-posta: [email protected]
Telefon/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038

Makale Meta Verileri
Last updated: 2025-09-24
Next scheduled review: 2026-03-24
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Chile infrastructure analysis integrated; DS 594, ISO 9001, REACH/RoHS references validated; three comparison tables updated with latest internal testing and Chilean field data; contact details verified.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




