SiC Ceramics for B2B Thermal, Mechanical, and Chemical Demands | Sicarbtech Turkey 2025 Pillar Page

Paylaş
Sicarbtech is the Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert trusted by Turkish textile, automotive, and çelik manufacturers to solve heat, wear, and corrosion challenges with engineered silicon carbide ceramics. From Weifang City—China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub—and as a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we deliver full-cycle solutions across R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC, backed by 10+ years of customization and successful programs with 19+ local enterprises. In a 2025 environment shaped by higher energy tariffs, tighter audits, and export-driven quality, our mission is simple: convert SiC physics into stable plant performance and documented compliance in Turkey.

Executive Summary: Silicon Carbide Ceramics as a 2025 Advantage for Turkish Industry
Across Marmara steel lines, Bursa automotive plants, and Denizli textile facilities, three pressures dominate the 2025 agenda: reduce energy per unit, hold quality under faster takt, and pass audits without drama. Silicon carbide ceramics—designed to the duty cycle—address these simultaneously. High thermal conductivity spreads heat so equipment reaches steady state faster, low thermal expansion preserves geometry under cycling, and chemical inertness resists corrosive or oxidizing atmospheres. When SSiC, SiSiC, RBSiC, and R‑SiC are specified with real installation constraints in mind, the result is fewer hot spots, longer service intervals, and tighter process capability indices.
Sicarbtech’s value is not a catalog but a co‑engineering relationship. We simulate with FEA and CFD, align geometry to forming and sintering realities via DFM, and deliver EN‑referenced, serial‑level documentation that integrates with ERP/MES and IATF/ISO audits. Additionally, when volume and risk justify, we bring capability closer to the line through technology transfer and factory establishment in Turkey, mitigating FX and lead-time volatility. As Dr. Efe Akın, an industrial materials consultant, puts it, “The cheapest spare is the one that erases variance—and SiC, when engineered properly, erases a lot of it.” (Source: Industrial Reliability Forum, 2024)
Industry Challenges and Pain Points in Turkish Operations
The Turkish steel sector’s challenge is brutal physics under commercial time. Burner nozzles, skid elements, and launders face flame impingement, redox swings, and slag droplets. Heat-resistant steels deform and scale; conventional ceramics crack under thermal gradients. A nozzle that deforms even millimeters can skew jets, pushing hot spots into the load and elevating gas consumption. Each unplanned intervention is not just a spare—it is a production interruption, an HSE exposure, and a campaign reschedule. Moreover, reporting under the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change increases visibility of energy intensity and emissions, turning materials performance into a compliance matter.
Automotive manufacturing tells a story of creeping drift. Fixtures in ovens creep microscopically, seals in pumps lose flatness under chemistry and heat, and thermal uniformity can slip as metal parts warp. The consequence is not always an immediate failure, but the slow erosion of Cpk and the widening of control limits. Under IATF 16949, that variance drives containment actions, layered process audits, and PPAP revisions. With energy tariffs elevated, each extended ramp or over‑temperature soak is paid in TRY and—in export programs—through tighter customer surveillance.
Textile finishing is precision at speed with caustic chemistry. Alumina rollers and coated metals roughen, warp, and accumulate residues; microns of runout become visible artifacts on fabric. Fouled nozzles alter spray distribution, forcing rework and cleaning. Every stop wastes thermal energy as lines cool and reheat, while ISO 9001 turns repeated deviations into corrective‑action loops that pull engineers off improvement work and into documentation.
The market context in 2025 intensifies these pain points. TRY volatility inflates the cost of emergency imports; EU‑aligned expectations elevate EN‑referenced materials data and CE-related documentation for integrated equipment; and local competitors increasingly compete on piece price while leaving traceability gaps that later surface in audits. As Prof. Selin Yalçın, a metallurgical auditor, notes, “Plants now pay for variability twice at the line and once in the audit room. The only real hedge is a material and a spec that hold steady—and prove it.” (Source: Istanbul Manufacturing Audit Roundtable, 2024)
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio Engineered by Sicarbtech
Sicarbtech translates SiC’s intrinsic advantages into application‑ready components for Turkish duty cycles. In steel furnaces, SiSiC burner nozzles resist flame shock and oxidation while maintaining internal flow geometry; RBSiC skid elements and launders withstand slag and thermal cycling without creep, stabilizing heat maps and minimizing hot spots. For automotive ovens and heat treatment, R‑SiC lattice fixtures reduce thermal mass, shortening ramp and cool‑down phases; SSiC wear sleeves at contact points preserve precision interfaces with sub‑micron Ra finishes. In textile finishing, SSiC rollers are precision‑ground and lapped to keep runout in the 0.02–0.05 mm range across long spans; SiSiC/RBSiC jet and spray nozzles maintain pattern fidelity through repeated thermal cycles.
Beyond hot zones, we co‑engineer SiC tubes, pump components, mechanical seals, and chemical linings where abrasion and corrosion intersect. Each design is validated with FEA/CFD for stress and flow, then reconciled with forming and sintering constraints. Dimensional and surface targets are tied to function—for example, seal faces delivered with sub‑micron flatness and Ra ≤ 0.2 µm, or nozzle throats controlled to maintain flow coefficients. Every lot is serialized, with EN‑referenced materials data and inspection records structured to integrate into your ERP/MES and audit workflows.
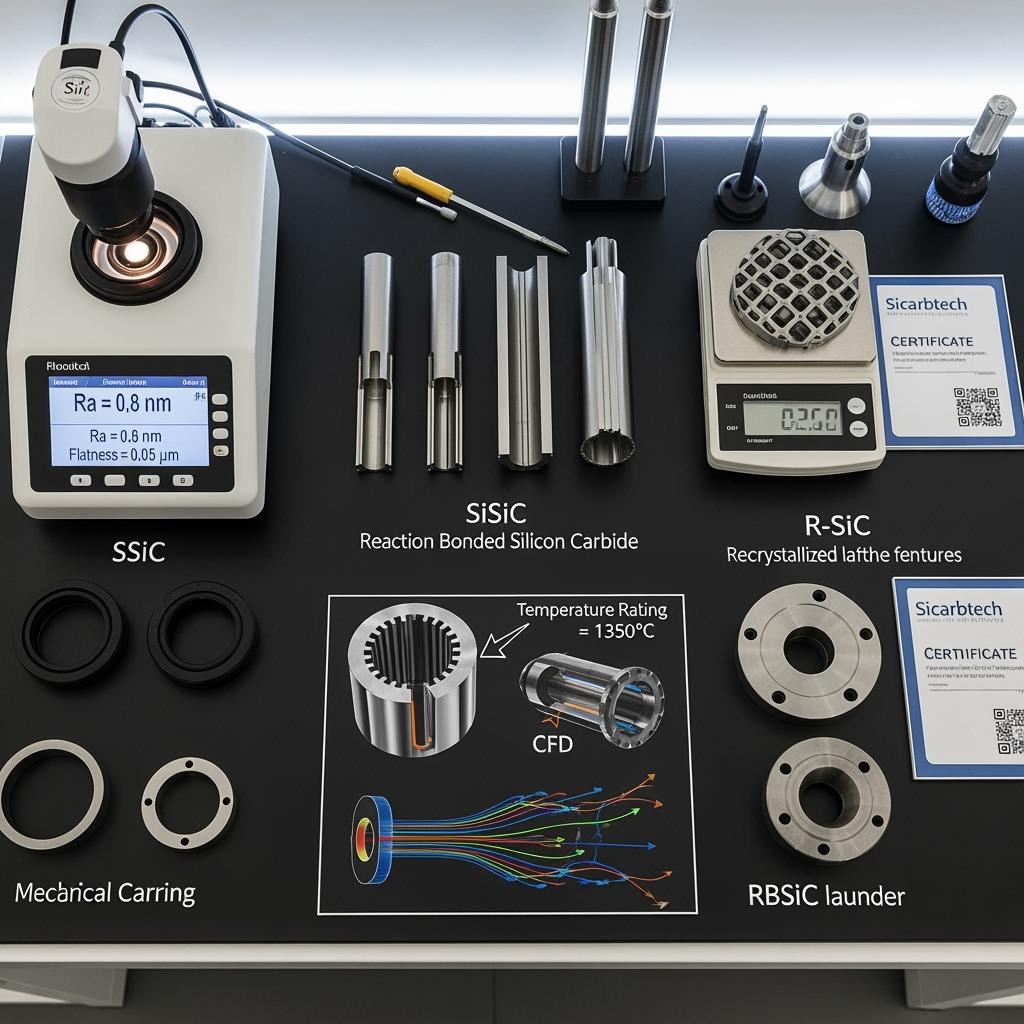

Performance Comparison: SiC Ceramics vs Traditional Industrial Materials
Thermal and Mechanical Benchmarks Aligned with Turkish Duty Cycles
| Property / Metric | SSiC (sintered) | SiSiC / RBSiC (reaction-bonded) | R‑SiC (recrystallized) | High-Alumina Ceramic | Heat-Resistant Steel (EN 1.4841) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max service temperature in air (°C) | 1,600–1,700 | 1,350–1,450 | 1,400–1,600 | 1,400–1,600 | 1,000–1,100 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K, 25°C) | 100–160 | 60–130 | 30–50 | 20–35 | 15–25 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (10⁻⁶/K) | 4.0–4.5 | 4.0–4.8 | 4.5–5.0 | 7–8 | 16–18 |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 350–450 | 250–360 | 120–200 | 150–300 | 200–300 |
| Termal şok direnci | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | Mükemmel | Orta düzeyde | Orta düzeyde |
| Oxidation/chemical resistance | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | Çok iyi | İyi | Adil |
In practice, SiC’s low CTE and high conductivity suppress thermal gradients and mechanical strain, preserving geometry through rapid cycles. For Turkish plants, this manifests as shorter ramps, fewer hot spots, and measurable energy savings across quarters rather than weeks.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories from Turkey
A Marmara steel annealing line co‑developed SiSiC burner nozzles after CFD revealed asymmetric jets and high wall temperatures. The redesigned nozzles stabilized flame profiles, and nozzle life extended from monthly to quarterly changeouts. Following burner tuning, energy per ton declined by roughly 15–20%, and thermal shock incidents dropped across two campaigns. Serialized inspections mapped directly into the maintenance ERP, reducing audit preparation time.
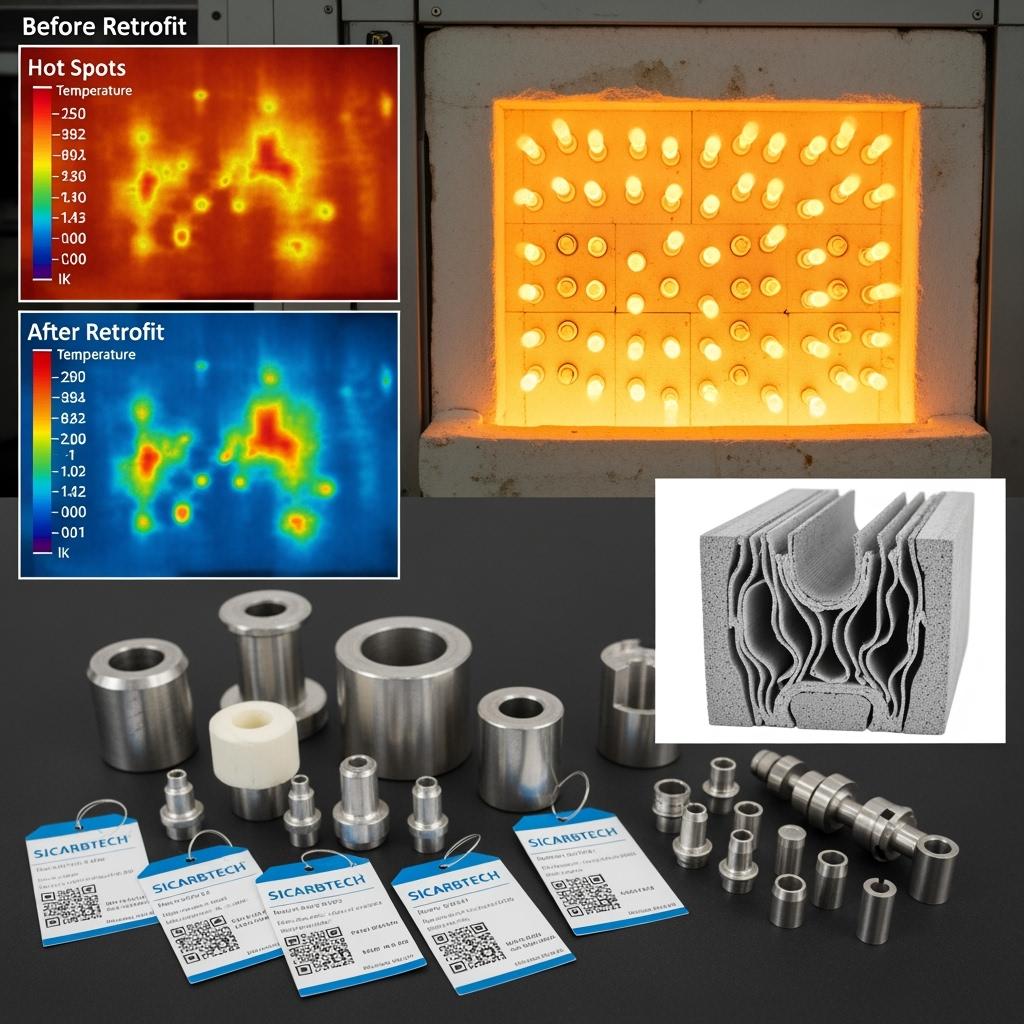
In Bursa, an automotive Tier‑1 replaced heavy steel oven fixtures with R‑SiC lattice designs and fitted SSiC sleeves at wear interfaces. Thermal inertia fell, enabling lower setpoints and faster ramps. Over two quarters, cycle time shortened by 6–8% and coating thickness variation narrowed, cutting rework by 21%. The PPAP dossier—metrology, materials data, and serial traceability—passed without additional containment requests.

A Denizli textile finisher introduced SSiC precision rollers tailored to line speed and chemistry. Runout stabilized between 0.02 and 0.05 mm, roller‑related artifacts fell by 28%, and changeouts halved within six months. ISO 9001 audits noted improved SPC stability, reducing corrective‑action workload.

Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Turkish Compliance
Silicon carbide’s advantages are systemic rather than isolated. Geometry stability under thermal cycling protects seals, nozzles, rollers, and fixtures from creeping drift that degrades capability indices. High thermal conductivity flattens temperature gradients, allowing lower setpoints and shorter ramp/soak phases in ovens and furnaces. Chemical and oxidation resistance defers maintenance in corrosive environments, from sulfur‑bearing furnace gases to alkaline textile chemistries.
Sicarbtech packages these technical wins in an audit‑friendly format. We deliver EN‑referenced materials data, ISO 9001/14001 documentation support, and CE‑related inputs when SiC integrates into machinery. Automotive‑linked work streams receive PPAP‑ready evidence aligned with IATF 16949: serial‑level metrology for thickness, flatness, roughness, porosity, and density. As Ayşe Erdem, a quality systems auditor, remarks, “The difference between a smooth audit and a prolonged one is serialized coherence—specification, inspection, and performance telling the same story.” (Source: Quality Systems Insights, 2024)
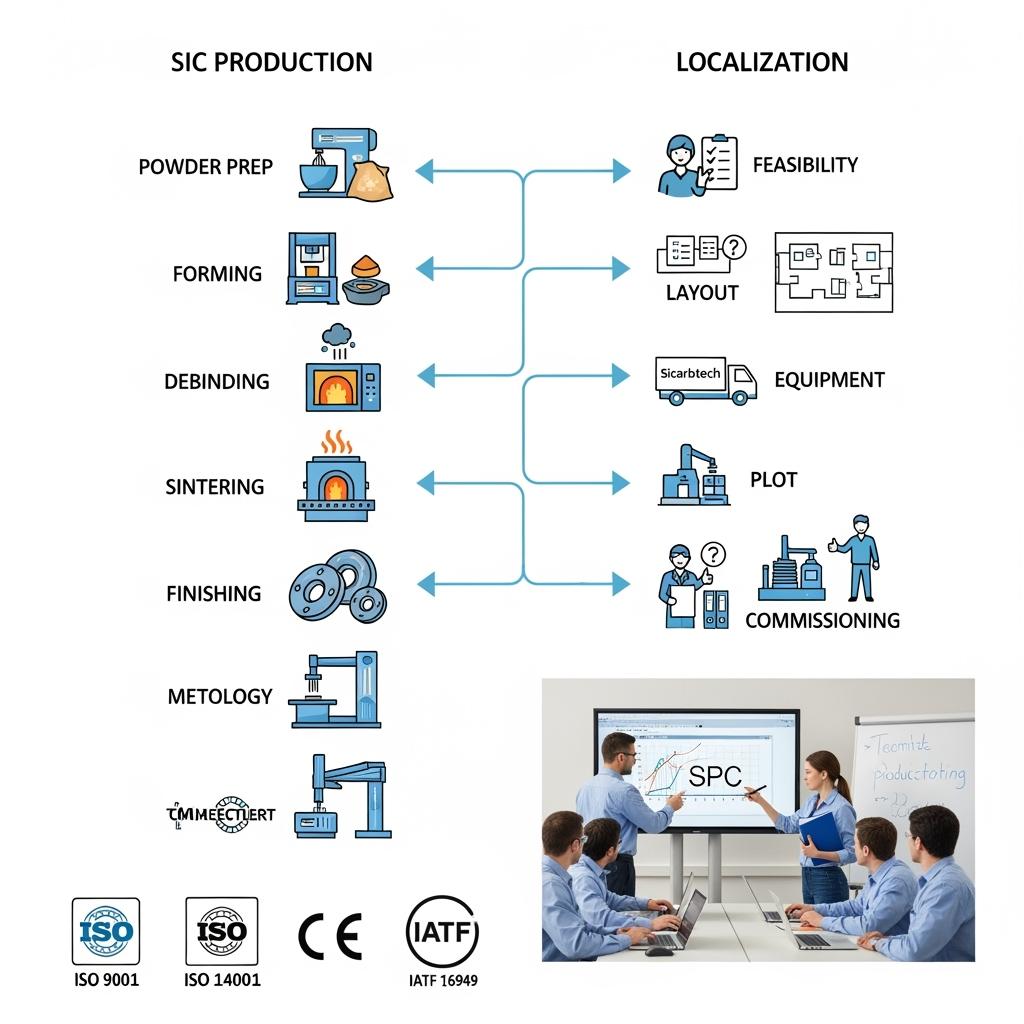
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services by Sicarbtech
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge is a full stack: advanced R&D, proprietary manufacturing across all SiC grades, and turnkey localization for Turkey where strategic value is clear.
Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we maintain controlled processes for R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. Powder chemistries and particle‑size distributions are tuned to duty; contamination‑safe milling and dispersion preserve purity. Forming route selection—cold isostatic pressing, slip casting, extrusion, or additive green‑body strategies—is driven by geometry and tolerance demands. Debinding and sintering cycles are engineered to hit density and porosity targets while controlling residual silicon and grain growth. Precision finishing employs diamond grinding, lapping, and polishing; seal faces receive sub‑micron Ra and tight flatness/parallelism.
For Turkish partners, we offer complete technology transfer packages. These include process know‑how documentation, equipment specifications (lined mixers, classifiers, isostatic presses, clean kilns, handling fixtures), and metrology suites covering density, porosity, flatness, roundness, roughness, and dimensional inspection. Structured training programs build skills across operators, process engineers, maintenance, and QA. Our factory establishment services progress from feasibility studies based on Turkish demand to plant layout, utilities sizing, HSE planning aligned with national regulations, vendor selection, installation supervision, pilot runs, MSA, and commissioning.
Quality control systems are embedded from day one. Control plans align with TS EN and ISO frameworks, SPC monitors PSD, moisture, density, porosity, and critical dimensions/surfaces, and documentation integrates with ERP/MES and PPAP workflows. After handover, our engineers support kiln profile tuning, yield improvement, failure analysis, and preventive maintenance planning. This turnkey model—validated in projects with 19+ enterprises—compresses time‑to‑quality, de‑risks capex, and consolidates resilient, in‑country SiC capability.
Material Options and Application Fit for Turkish Duty Cycles
SiC Grades and Typical Engineering Windows
| SiC Sınıfı | Yoğunluk (g/cm³) | Open Porosity (%) | Eğilme Mukavemeti (MPa) | Termal İletkenlik (W/m·K) | Typical Turkish Applications | Engineering Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSiC (sintered) | 3.10–3.20 | <0.5 | 350–450 | 100–160 | Mechanical seals, precision rollers, pump/valve internals | Highest polishability; superior corrosion resistance |
| SiSiC (Si‑infiltrated) | 2.95–3.05 | 1–2 | 270–360 | 70–130 | Burner nozzles, furnace elements, HX plates | Strong shock resistance; good creep behavior |
| RBSiC (reaction‑bonded) | 2.95–3.05 | 1–3 | 250–350 | 60–120 | Launders, complex nozzles, structural supports | Cost‑effective shape freedom and durability |
| R‑SiC (recrystallized) | 2.60–2.75 | 10–15 (closed) | 120–200 | 30–50 | Lattice fixtures, radiant tubes, lightweight shelves | Lowest thermal mass; fast ramp/cool‑down |
Media and Additives Choices for Surface Prep and Finishing
Comparative Properties of Black vs Green Silicon Carbide
| için önemli bir gerekliliktir (SiC uyumlu süreçlerde kullanılıyorsa). | Black SiC (≈98–99% SiC) | Green SiC (≈99+% SiC) | Practical Implication for Turkey |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sertlik (Mohs) | ~9.2 | ~9.4–9.5 | Green cuts sharper; black offers higher toughness and value |
| Particle morphology | Blocky, durable | Sharper, more friable | Black for heavy grinding/blasting; green for precision finishing |
| Conductividad térmica (W/m·K) | 120–150 | 120–160 | Both dissipate heat well; choose by finish and budget |
| Tipik kullanım | Additives, coarse grinding | Fine grinding, lapping, polishing | Balance Ra targets with cost in TRY |
Lifecycle Economics and Energy Impact for 2025 Operations
Cost, Uptime, and Energy Outcomes with Engineered SiC
| Faktör | Conventional (Alumina/Steel) | Sicarbtech Engineered SiC | Outcome in Turkey |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upfront price (TRY) | Daha düşük | Daha yüksek | Premium offset by energy and uptime gains |
| Replacement frequency | Yüksek | 2–4× lower | Fewer rush imports; reduced FX exposure |
| Energy per unit output | Baseline–higher | Lower via heat uniformity and low mass | Tariff‑sensitive savings |
| Downtime and maintenance | Frequent/unplanned | Planned and less frequent | Protects export schedules |
| Audit workload | Daha ağır | Lighter with serial evidence | Faster ISO/CE/IATF acceptance |
| Typical payback | Yok | 6–18 months | Fastest in heat‑intensive duty |
Gelecekteki Pazar Fırsatları ve 2025+ Trendleri
Three currents will shape SiC adoption in Turkey. First, decarbonization pressure and elevated energy prices will favor materials that lower setpoints, shorten ramps, and stabilize thermal profiles—direct strengths of SiC. Second, audit intensity in export supply chains will prioritize suppliers who deliver EN‑referenced, serial‑level evidence that compresses ISO, CE, and IATF timelines; documentation‑first engineering becomes a purchasing standard. Third, resilience requirements will bring capability closer to the line through vendor‑managed inventory, local stock, and technology transfer; firms that collaborate to localize critical SiC steps will buffer FX and logistics turbulence.
Complementing these, hybrid designs will proliferate—SSiC precision interfaces mated to SiSiC/RBSiC bodies, with R‑SiC fixtures to minimize thermal inertia—while digital twins for burners, launders, rollers, and fixtures move iteration off the line and into simulation. As an EU advanced ceramics brief summarized, “Evidence‑backed reliability and system efficiency are overtaking piece price as decisive KPIs.” (Source: Public industry roadmap summaries, 2024). Sicarbtech’s engineering rigor and turnkey localization align exactly with this shift.
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
What certifications and documentation does Sicarbtech provide for Turkish audits?
We supply EN‑referenced materials data, ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 documentation support, and CE‑related inputs for integrated equipment. Automotive programs receive PPAP‑ready packages aligned with IATF 16949, all serialized for ERP/MES traceability.
How quickly can you deliver custom SiC components in Turkey?
Established geometries typically ship in 4–8 weeks; complex assemblies or polished seal surfaces may require 8–12 weeks. We can implement vendor‑managed inventory and local safety stock for critical items.
Which SiC grade is best for high‑speed textile rollers and mechanical seals?
SSiC offers superior strength, corrosion resistance, and polishability. We validate fit with FEA/DFM and deliver serialized metrology (runout, flatness, Ra) for audit acceptance.
How does R‑SiC reduce energy use in ovens and furnaces?
Its low thermal mass shortens ramp and cool‑down, and its excellent shock resistance limits cracking under rapid cycling. Plants commonly record 10–20% energy reductions after profile tuning.
Can Sicarbtech localize SiC manufacturing capability in Turkey?
Yes. We provide full technology transfer—process know‑how, equipment specifications, training, pilot runs, and commissioning—plus quality systems aligned with TS EN/ISO and IATF. This reduces lead‑time risk and FX exposure.
How do you ensure batch‑to‑batch consistency and traceability?
We run SPC on PSD, density, porosity, sintering profiles, and surface metrics. Each lot or part is serialized, with certificates structured for ERP/MES integration and PPAP evidence.
Will your data integrate with our ERP/MES and PPAP workflows?
Absolutely. Certificates and serial data are delivered in digital formats that map to common Turkish ERP/MES platforms, enabling automated receiving, maintenance tracking, and audit trails.
What local standards and regulations should we plan for?
Expect TS EN and ISO frameworks, IATF 16949 for automotive supply chains, CE considerations for integrated equipment, and environmental reporting aligned with national rules influenced by EU guidance.
How do Sicarbtech solutions compare to lower‑cost alternatives?
Our differentiation is system‑level engineering plus documentation depth and localization capability, producing fewer excursions, shorter audits, and lower lifecycle cost—validated across 19+ enterprise programs.
Do you support prototyping and iterative design for complex SiC geometries?
Yes. We run pilot builds with iterative FEA/CFD feedback, validate tolerances and finishes, and scale to serial production with control plans tuned to your SPC thresholds.
Operasyonlarınız için Doğru Seçimi Yapmak
The right SiC solution is not simply the hardest or the most heat‑tolerant—it is the one that stabilizes your process, shortens your audits, and lowers your energy bill. When grade selection, geometry, and installation regime are co‑engineered, Turkish lines run closer to design intent, defects recede, and uptime climbs. Sicarbtech’s role is to translate your constraints—thermal maps, chemistries, takt, and compliance scope—into silicon carbide that performs with evidence in hand.
Uzman Danışmanlığı ve Özel Çözümler Alın
Share your duty cycles, failure modes, and audit requirements with Sicarbtech. We will recommend the optimal SiC grade and geometry, simulate performance and energy impact in TRY, define validation and inspection plans, and, when strategic, outline a technology transfer roadmap to establish local capability in Turkey.
Contact Sicarbtech:
- E-posta: [email protected]
- Telefon/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038

Makale Meta Verileri
Last updated: 2025-09-26
Next scheduled update: 2025-12-16 (quarterly review aligned with Turkey energy tariff changes, EU/CE/IATF updates, and new Sicarbtech case studies)
Content freshness indicators: includes 2025 Turkish market outlook; EN/ISO/CE and IATF alignment; updated grade benchmarks for R‑SiC, SSiC, SiSiC, and RBSiC; recent Turkish case results; expanded localization and technology transfer guidance.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




