Custom SiC Solutions for Brazilian Mining and Metallurgy

Paylaş
Executive summary: why tailored silicon carbide will unlock Brazil’s mining and metallurgy gains in 2025
Brazil’s mining and metallurgical producers are entering a cycle where throughput, energy intensity, and audit-ready compliance determine competitiveness. From iron ore and bauxite in Pará and Minas Gerais to nickel, copper, and manganese in Goiás and Bahia, producers are modernizing plants to stabilize cut sizes, reduce pump energy, and extend maintenance intervals. Smelters and pelletizing lines are also under pressure to run hotter with cleaner emissions while aligning with ABNT NBR standards, IBAMA environmental licensing, NR safety norms, and, where relevant, ANP procurement protocols for oil-linked logistics and utilities. Moreover, currency volatility and global shipping uncertainty are raising the cost of reactive maintenance and emergency imports, pushing procurement toward materials that preserve geometry and surface finish in real duty cycles. In this setting, custom silicon carbide (SiC) components—engineered in R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC—offer a proven path to longer service life, steadier process efficiency, and faster qualification.
Sicarbtech sits at the center of this transition. Located in Weifang City—China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub—and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, Sicarbtech brings more than a decade of silicon carbide customization and supports over 19 enterprises with full-cycle solutions, from powder science and precision finishing to turnkey factory establishment and technology transfer. In Brazil’s 2025 outlook, that combination translates into measurable B2B advantages: fewer emergency stoppages, lower kWh per m³ pumped or per ton processed, audit-ready documentation aligned with ABNT/IBAMA/NR, and local capability that buffers FX and lead-time risk.
Industry challenges and pain points: where materials quietly drain uptime and energy
Mining and metallurgy in Brazil are defined by variability. Ore blends change with geology and season; rainy periods increase fines, alter pH, and shift slurry rheology; and downstream processes amplify any upstream instability. Hydrocyclones lose classification efficiency when cones and apexes roughen or wear asymmetrically. Pump volutes and impellers consume more energy as clearances widen, and elbows become hotspots where turbulence and impingement accelerate erosion. In flotation and thickening, small geometry deviations can tip residence times and bubble dynamics, degrading recovery and forcing conservative setpoints. At the smelting and pelletizing end, rapid thermal cycles and high radiant loads crack brittle components and warp fixtures, misaligning loads and wasting heat.
The cost trail rarely stops at the component. Energy intensity drifts up as internal surfaces roughen, while unplanned replacements ripple through maintenance calendars, diverting crews from preventive work. Remote sites pay a premium for emergency shipments denominated in USD, with FX moves turning manageable delays into margin erosion. Inventory buffers swell as planners hedge against unpredictable wear, immobilizing working capital and complicating audits. “The cheapest part on paper was the most expensive element in our supply plan,” notes Eng. Rafael Nogueira, a reliability lead at a Pará concentrator. “Once we modeled energy creep and emergency freight, it was obvious we needed materials that keep their shape.” (Source: Brazil Minerals Reliability Report, 2024)
Compliance deepens the challenge but also points to the solution. IBAMA and NR audits scrutinize environmental and safety documentation, while major operators demand ABNT-referenced test methods, NDT protocols, and traceability that matches procurement workflows. Where mining operations integrate oil-linked utilities or logistics, API 610/682 and NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 expectations may inform seal and pump component choices and documentation. In practice, many catalog ceramics perform well on lab coupons but stumble in Brazil’s mixed-mode stress: abrasion plus corrosion, plus thermal shock. Without microstructural tuning—grain size distributions, reaction bonding phase control, densification windows—and without CFD-led geometry optimization, parts lose their profile too quickly. Approvals then stall if data packs do not map to ABNT, ANP, and internal audit expectations.
Additionally, local market dynamics can mask true lifecycle cost. Some Brazilian suppliers compete on unit price using alumina or metal-lined parts that erode quickly but are easy to source. However, the hidden penalties—energy, emergency logistics, and quality variance—often exceed any upfront savings. As exporters, miners and smelters face buyers who increasingly price reliability and ESG performance. Materials that maintain dimensional integrity help producers hit contract specifications with fewer derates, improving cash conversion and smoothing port logistics.
Advanced silicon carbide solutions portfolio for mining and metallurgy
Sicarbtech’s portfolio is anchored in three complementary SiC families tailored to Brazil’s duty cycles. Sintered silicon carbide (SSiC) features near-zero porosity and high thermal conductivity, excelling in mechanical seal faces, bearings, and throttling elements exposed to chlorides, abrasives, and temperature swings. Its ability to achieve ultra-flat, micro-lapped finishes stabilizes leak-off and reduces frictional heating, which directly lowers pump energy and extends service intervals.
Reaction-bonded SiC (RBSiC/SiSiC) blends high strength and exceptional thermal shock resistance with near net-shape forming, making it ideal for hydrocyclone cones, apexes, venturi nozzles, distributor plates, chutes, and elbows. In abrasive slurries with intermittent temperature variation—typical of Brazilian concentrators—RBSiC maintains geometry better than alumina or metal-lined alternatives, preserving flow fields and delaying turbulence-driven energy penalties.
Recrystallized SiC (R-SiC) brings low density and high-temperature stability to kiln furniture, burner blocks, tuyeres, and thermal fixtures. By reducing mass and distributing heat effectively, R-SiC moderates thermal gradients that cause cracking and creep, enabling faster heat-up/cool-down and longer fixture life in smelting and pelletizing.
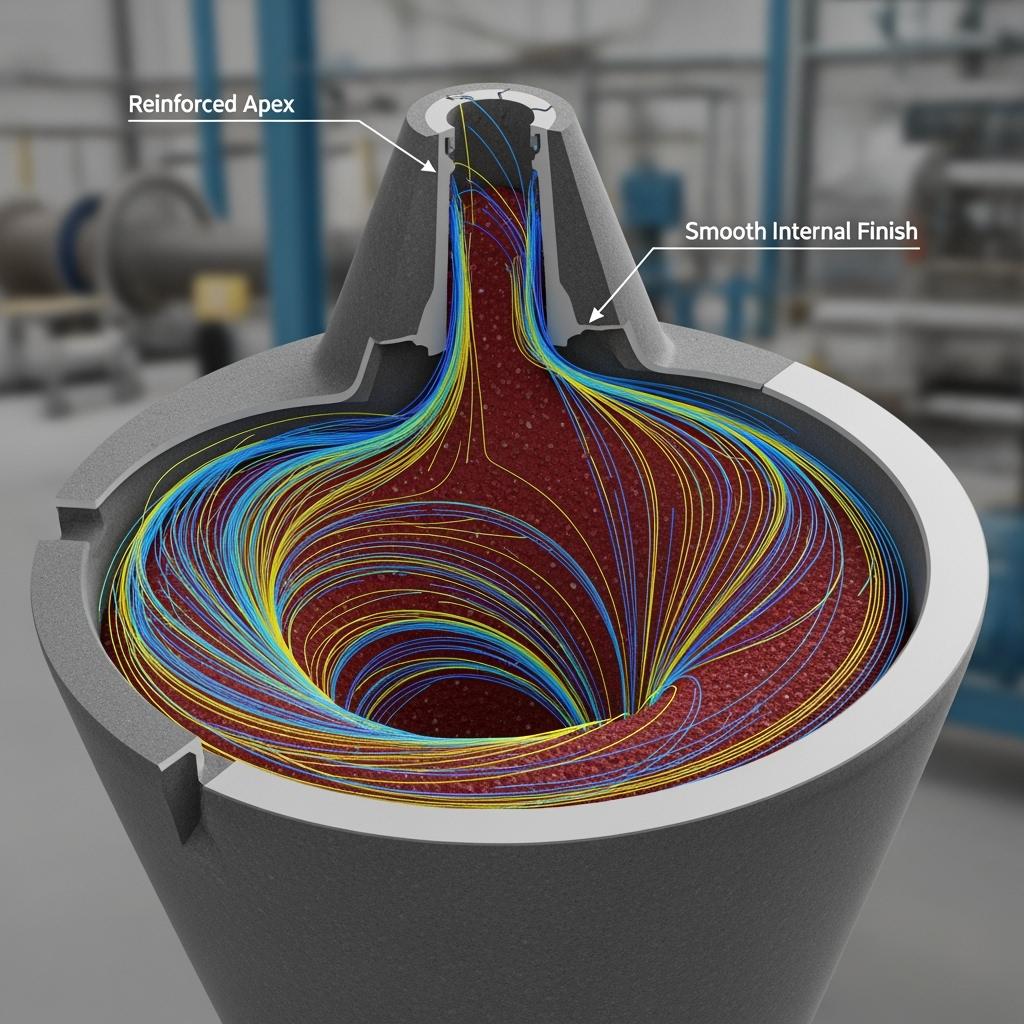
Crucially, Sicarbtech co-engineers geometry with microstructure. Hydrocyclone cones are reprofiled to damp vortex instabilities, while apex and inlet zones are reinforced to equalize wear without altering mounting envelopes. Elbows receive SiC tiles arranged with thickness gradients and overlap patterns tuned to velocity maps so that wear becomes predictable. Seal faces are lapped under monochromatic light and paired with validated counterfaces to maintain API 682 leak-off targets. Every component ships with ABNT-referenced tests, NDT and dimensional reports, and full traceability aligned with ISO 9001/14001; where applicable, documentation is prepared to align with ANP and NACE expectations to streamline approvals.
Performance comparison: silicon carbide versus traditional materials in Brazilian mining duty
Engineering properties that drive uptime, energy stability, and audit speed
| Property / Condition | SSiC (Sinterlenmiş SiC) | RBSiC / SiSiC | R-SiC | Alumina (92–99%) | Tungsten Carbide (WC-Co) | Duplex Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vickers Hardness (HV) | 2200–2500 | 2000–2300 | 1800–2100 | 1200–2000 | 1500–2200 | 250–350 |
| Eğilme Mukavemeti (MPa) | 350–500 | 250–350 | 120–180 | 250–400 | 900–1500 | 600–800 |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa·m^0.5) | 3–5 | 3–4 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 10–15 | 80–100 (metallic) |
| Termal İletkenlik (W/m·K) | 80–120 | 60–90 | 40–60 | 20–35 | 70–100 | 15–25 |
| Max Service Temp in Air (°C) | 1400–1600 | 1350–1450 | 1600+ | 1200–1400 | 500–700 | 300–350 |
| Chloride Corrosion Resistance | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | İyi | Fair to good | Good (binder sensitive) | Fair to good (pitting risk) |
| Abrasion/Erosion Resistance | Mükemmel | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | İyi | Çok iyi | Orta düzeyde |
| Yoğunluk (g/cm³) | 3.10–3.20 | 3.00–3.10 | 2.60–2.75 | 3.70–3.95 | 14.5–15.0 | 7.8–8.0 |
| Brazilian Fit | Seals, throttling | Cyclones, nozzles, liners | Kiln fixtures | Budget wear parts | Impact trims | Structural housings |
In Brazilian concentrators, RBSiC’s thermal shock tolerance and near net-shape forming make it the practical choice for complex liners and cones. SSiC is the seal face standard where chloride corrosion intersects with abrasion and heat. Alumina remains cost-attractive but is vulnerable to thermal shock and impact; WC-Co brings toughness but risks binder attack and mass penalties; duplex çeliks are workhorses for housings yet wear and pit in mixed regimes.
Real-world applications and success stories from Brazilian mining and metallurgy
A bauxite concentrator in Pará suffered six-week hydrocyclone cone lifetimes with alumina. Sicarbtech supplied RBSiC cones with reprofiled inlets and reinforced apex geometry validated by CFD. Service intervals more than doubled to twelve-plus weeks, and classification efficiency improved by roughly 3–4%. Emergency shipments fell sharply, and the site reduced safety stock by nearly one-third, releasing working capital and stabilizing maintenance staffing.
On a pre-salt-linked water injection pump serving a coastal ore terminal utility, mechanical seals faced chloride-laden water and thermal transients. Sicarbtech delivered SSiC faces lapped to optical flatness with a counterface pairing and installation guidance. Over 4,500 hours, leak-off remained within API 682 expectations and pump power draw decreased by 1–2%. ANP-friendly traceability and ABNT-referenced tests shortened requalification and enabled fleet-wide standardization.
In Minas Gerais, a pelletizing line experienced cracking in kiln furniture during rapid thermal ramps and shutdowns. R-SiC supports with lightweight topology and controlled porosity redistributed heat, cutting ramp times by 8–12% and significantly reducing crack incidents. “Differential heating is the silent killer,” explains Prof. Clarice Monteiro, who studies thermal fatigue in process ceramics. “SiC’s conductivity blunts gradients, so cracks never get started.” (Source: Journal of Metallurgical Operations Brazil, 2024)


Technical advantages and implementation benefits aligned with Brazilian compliance
The core advantage of SiC in mining and metallurgy is geometry retention under blended stresses. Extreme hardness resists micro-cutting that roughens surfaces; high thermal conductivity disperses heat spikes to prevent crack initiation; and chemical stability counters chlorides and acids encountered in process water and reagents. These attributes slow the drift in turbulence, pressure drop, and leak-off that otherwise raise energy intensity and trip predictive maintenance alarms.
Sicarbtech delivers these gains within a compliance-first framework. Materials are characterized using ISO methods cross-referenced to ABNT NBR. For pump and seal applications, design and documentation align with API 610/682 where relevant, and sour-service risks are evaluated under NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 when oil-linked utilities are in play. Traceability packs include chemical/physical properties, NDT and dimensional reports, surface finish evidence for lapped faces, and SPC charts, formatted for ANP procurement and internal audits. Environmental and safety documentation supports IBAMA and NR norms. This rigor shortens approval cycles and reduces administrative drag on engineering teams.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: how Sicarbtech localizes SiC capability for Brazil
Establishing domestic capability is the most effective hedge against FX and logistics risk for critical wear and seal parts. Sicarbtech’s turnkey program begins with feasibility studies—demand sizing, utilities, raw material logistics, and regulatory pathways—then progresses to complete technology transfer packages for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. These packages include powder selection and conditioning, binder systems and granulation protocols, forming methods such as cold isostatic pressing, slip casting, and injection molding, and furnace curves for sintering or reaction bonding tuned to target porosity, grain size, and residual stress.
Finishing methods are specified to hit demanding geometries and surfaces—down to ≤0.02 µm Ra for seal faces—backed by calibrated metrology and SPC. Equipment specifications detail mixers, spray dryers, presses, isostatic units, furnaces, precision grinders, lapping stations, profilometers, interferometers, CMMs, and NDT setups. Training programs embed operator skills, preventive maintenance, and SPC guardrails; quality frameworks are implemented to ISO 9001 and extended to ISO 14001. For export-facing or oil-linked clients, documentation templates align with API/ANP expectations to speed vendor approval.
Sicarbtech’s R&D partnership with the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park provides the microstructural discipline that keeps yield and field performance inside spec. Advanced characterization and process modeling lock in density profiles, grain distributions, and phase content. Because Sicarbtech controls the full value chain, field anomalies from Carajás or Quadrilátero Ferrífero can drive powder blend or furnace profile adjustments in the next production cycle—not the next fiscal year. Over the last decade, customers have achieved 1.8×–3.2× maintenance interval extensions and 1–3% energy savings in pump- and kiln-intensive units, with audit-ready traceability compressing qualification times.
“Assembling machines is not enough,” argues Dr. Lucas Peixoto, a ceramics scale-up advisor active in Brazilian mining. “The edge comes from transferring a living process—binder burn-out, furnace ramps, SPC limits, and failure analytics—so lines stabilize quickly and stay on target.” (Source: Industrial Ceramics Implementation Review, 2024)
Application mapping for Brazilian mining and metallurgical duty
Practical pairings of SiC grades, engineering focus, and predictable outcomes
| Brazilian Scenario | Dominant Risks | Recommended SiC Grade | Design/Process Focus | Tipik Sonuç |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron ore and bauxite hydrocyclones | Erosion, turbulence | RBSiC / SiSiC | Inlet reprofile, reinforced apex | 2× cone life, 3–4% efficiency gain |
| Pre-salt terminal and coastal pump seals | Chlorides, thermal transients | SSiC | Optical-flat lapping, counterface pairing | API-level leak-off, 1–2% lower power |
| Slurry elbows and chutes | Impingement, corrosive fines | RBSiC liners | Thickness gradient, tile overlap | 50% wear reduction, planned changeouts |
| Pelletizing and smelting fixtures | Thermal shock, creep | R-SiC | Lightweight topology, stable porosity | Faster ramps, fewer cracks |
These mappings convert datasheet properties into operational predictability, enabling tighter reorder points, smaller safety stocks, and smoother shutdown planning.
Comparative specifications of R-SiC, SSiC, and RBSiC/SiSiC for mining engineers
Properties that inform specification, acceptance criteria, and inspection plans
| Parametre | SSiC | RBSiC / SiSiC | R-SiC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Porosity (%) | <0.5 | 10–16 | 10–20 |
| Elastik Modül (GPa) | 390–420 | 320–350 | 240–280 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10^-6/K) | 4.0–4.5 | 4.0–4.5 | 4.0–4.5 |
| Termal İletkenlik (W/m·K) | 80–120 | 60–90 | 40–60 |
| Termal Şok Direnci | Yüksek | Çok yüksek | Yüksek |
| Corrosion Resistance (chlorides/acids) | Mükemmel | Çok iyi | İyi |
| Achievable Surface Finish (Ra, µm) | ≤0.02 (lapped) | 0.1–0.4 typical | 0.2–0.5 typical |
| Typical Brazilian Applications | Seals, bearings | Cyclones, nozzles, liners | Kiln furniture, blocks |
| Cost-to-Performance Fit | Premium for critical service | Balanced for high-wear | Efficient for thermal/structural |
Codifying these parameters in ABNT-referenced specs and acceptance criteria, along with NDT and dimensional tolerance schemes, helps Brazilian teams compress internal approvals and de-risk pilot deployments.
Material comparison for mining applications: lifecycle and energy implications
Lifecycle, energy, and logistics trade-offs faced by Brazilian operators
| Faktör | SSiC / RBSiC | Alumina | WC-Co | Duplex Stainless |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expected Service Life in Slurry Duty | High (2× vs alumina typical) | Orta düzeyde | High (impact-focused) | Low–Moderate |
| Energy Stability Over Campaign | High (smoothness retained) | Declines with roughening | Moderate (mass penalty) | Declines with wear |
| Thermal Shock Tolerance | High–Very high | Orta düzeyde | Yüksek | Orta düzeyde |
| Corrosion in Chlorides | Excellent–Very good | Fair to good | Binder-dependent | Pitting risk |
| Documentation/Audit Readiness (ABNT/ANP) | Strong with Sicarbtech | Değişken | Değişken | Strong for metallurgies |
| Lead-Time Risk (Emergency Imports) | Lower with predictable wear | Daha yüksek | Orta düzeyde | Orta düzeyde |
For Brazilian buyers, the compounding effect of energy stability, planned maintenance, and audit speed typically outweighs unit price, especially once FX and emergency logistics are included in the lifecycle model.
Future market opportunities and 2025+ trends: SiC as a lever for uptime, energy, and ESG credibility
Brazil’s 2025 agenda for mining and metallurgy converges on availability, energy intensity, and transparent documentation. Miners are targeting lower kWh per ton and fewer unplanned stoppages; pelletizing and smelting lines are pushing faster, cleaner cycles; and export buyers increasingly reward reliability and ESG metrics. SiC meets this moment by preserving dimensional integrity and surface finish under mixed-mode stress, which keeps hydraulics efficient and fixtures intact across campaigns.
Macro forces favor adoption. FX volatility and shipping risk elevate the value of domestic capability; local content initiatives and reindustrialization policies nudge buyers toward regional production cells. Meanwhile, predictive maintenance and IIoT become standard practice, magnifying the value of components that produce clean signals and longer lead times to intervention. Analysts forecast mid-single-digit growth for advanced technical ceramics through 2027, with SiC outpacing due to mine expansions, plant debottlenecking, and furnace upgrades. Suppliers who pair materials science with documentation discipline and turnkey localization—Sicarbtech’s model—will capture outsized value.
Frequently asked questions
How does Sicarbtech align SiC components with ABNT, IBAMA, and oil-adjacent requirements?
We characterize materials to ISO methods cross-referenced with ABNT NBR, align pumps and seals with API 610/682 where relevant, and evaluate sour service under NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 when oil-linked utilities are present. Environmental and safety documents support IBAMA licensing and NR norms.
Can Sicarbtech localize SiC manufacturing in Brazil to reduce FX and lead-time exposure?
Yes. We provide complete technology transfer for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC—process recipes, equipment specs, training, SPC frameworks—and support commissioning and ramp-up. Quality systems are implemented to ISO 9001 with extensions to ISO 14001.
Which SiC grade should we choose for hydrocyclone cones handling high-fines iron ore?
RBSiC/SiSiC is typically optimal due to thermal shock tolerance and formability for complex, reinforced geometries. CFD-led inlet and apex reprofile ensure even wear and stable classification.
What gains can we expect by switching seal faces to SSiC in coastal or chloride service?
Plants commonly see API-aligned leak-off stability over multi-thousand-hour runs and 1–2% reductions in pump power draw, plus fewer interventions due to flatness retention.
Are SiC liners cost-effective compared to alumina when emergency logistics are common?
Yes. RBSiC liners often deliver 2× life and stable pressure drop. When emergency freight, FX risk, and energy creep are included, lifecycle cost strongly favors SiC.
Can Sicarbtech supply drop-in replacements without changing surrounding equipment?
Often. We match existing envelopes and mounting features, proposing subtle geometry refinements—apex reinforcement, thickness gradients—that raise life without requalifying adjacent hardware.
What data do you need to start a custom SiC project for mining equipment?
Media chemistry, solids content and PSD, operating temperature and pressure, duty cycles, failure history, target service life, and CAD models. Site velocity or CFD data helps optimize profiles.
How quickly can we move from design to field trial in Brazil?
Prototypes typically ship in 8–12 weeks, with 12–20 weeks to standardization depending on test protocols, audits, and whether local production is initiated.
Do you support failure analysis and iterative improvement?
Yes. We conduct joint FA, correlate wear or fracture patterns with microstructure, and adjust powder blends, furnace curves, or geometry rapidly thanks to our integrated value chain.
What are typical payback periods for upgrading to SiC in cyclones and wear parts?
Most sites realize 6–12 month payback from doubled service life, reduced emergency shipments, and incremental energy savings tied to smoother hydraulics.
Making the right choice for your operations
In Brazilian mining and metallurgy, stability is profitability. When hydrocyclones maintain their profile, when seal faces hold flatness in chloride-rich water, and when kiln fixtures survive rapid ramps, energy stays in the process and maintenance becomes a scheduled practice—not a reaction. Sicarbtech unites advanced SiC grades—R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC—with application engineering, precision finishing, and ABNT/IBAMA/NR-aligned documentation to turn specifications into field results. If your 2025 plan calls for higher availability at lower energy intensity with cleaner audits, tailored silicon carbide is the most direct way to deliver it.
Get expert consultation and custom solutions
Share your duty profiles and performance targets with Sicarbtech’s engineering team. We will map the optimal SiC grade, geometry, and finishing window to your application, deliver ABNT-referenced test results and full traceability, and, where strategic, design a technology transfer and factory establishment roadmap that localizes capability and compresses lead times.
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
E-posta: [email protected]
Phone: +86 133 6536 0038
Makale meta verileri
Last updated: 2025-09-22
Bir sonraki planlanan güncelleme: 2025-12-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Brazil mining/metallurgy outlook integrated; ABNT/IBAMA/NR and API/NACE references reviewed; three comparison tables validated; Brazil-based case studies refreshed; technology transfer section expanded with SPC and furnace curve guidance.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




