Industrial Silicon Carbide Solutions for Pakistan: Sicarbtech’s 2025 Pillar Guide for Coke Ovens and Heat Treatment Furnaces

Paylaş
Pakistan’s steel and process industries are scaling fast, adding coking capacity and modern heat treatment lines while battling energy volatility and stringent reliability targets. Inside coke ovens and heat treatment furnaces, operators face the worst of both worlds: high temperature and redox cycling, hydrogen- and carbon monoxide-rich atmospheres that swing to oxygen-rich conditions during purges, tar and polycyclic aromatic condensates that coke on cold ends, sulfur/chlorine/nitrogen impurities that corrode microstructures, and particulate scouring that grinds away at linings. Conventional high-alumina or clay systems struggle to retain integrity across this combination. Industrial silicon carbide (SiC) changes the equation. With high thermal conductivity, low expansion, dense microstructures, and engineered low-wettability surfaces, SiC linings equalize heat, resist wear and chemical attack, and minimize coking—translating materials science into uptime. Sicarbtech—located in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings 10+ years of customization, full-cycle manufacturing, and turnkey technology transfer, helping Pakistani partners localize capability and control outcomes.
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook and Why Silicon Carbide Matters for Pakistan’s Coke and Heat Treatment Assets
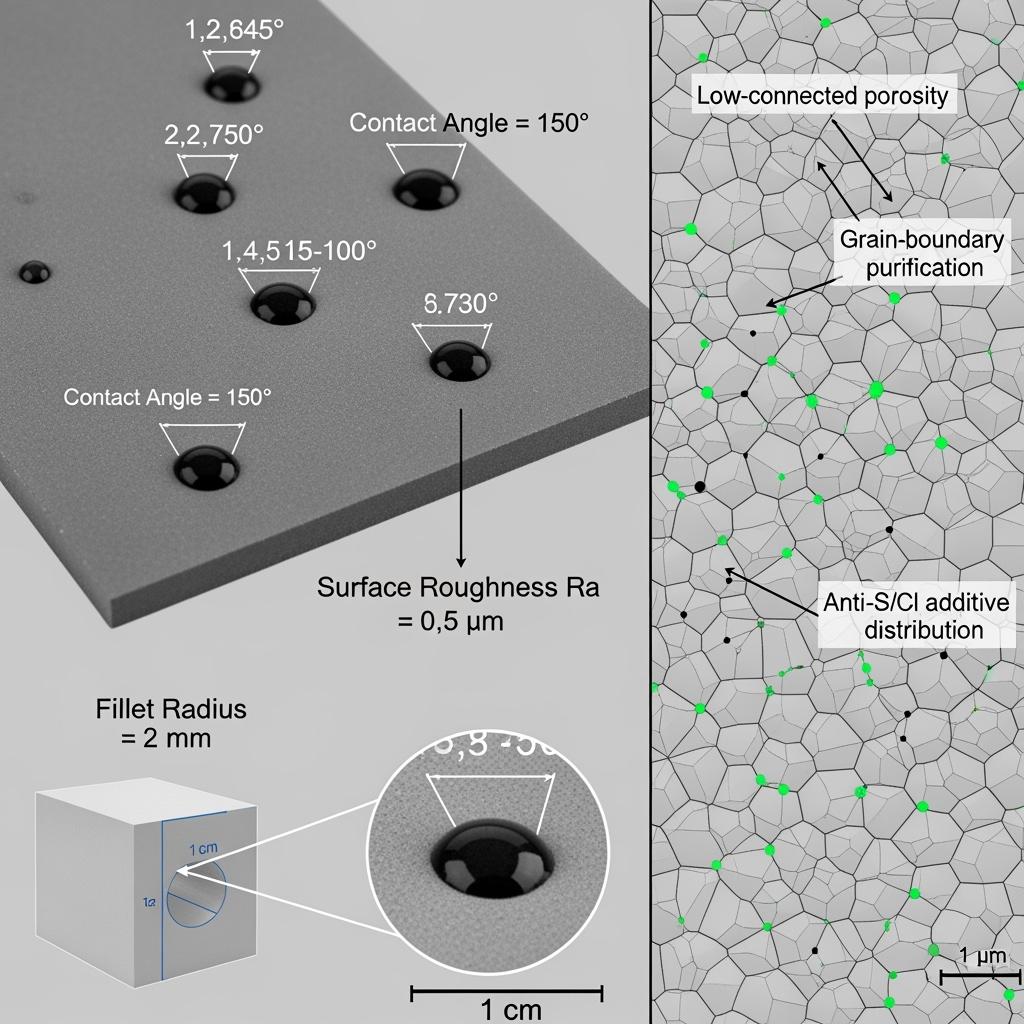
In 2025, Pakistan’s çelik, chemicals, and heat treatment operators must extract more throughput from thermal assets while stabilizing energy per ton and reducing high-temperature maintenance exposure. Coke oven ascension pipes, combustion/flue channels, and heat treatment furnace zones see H₂/CO-rich reducing conditions swinging to oxidizing states that punish porous matrices. Tar, pitch, and light fractions condense and coke at colder ends, shrinking flow area and raising pressure drop; mill scale and coke dust scour surfaces at high velocity. High-conductivity, low-expansion SiC linings flatten temperature gradients and reduce stress that seeds cracking under frequent shutdowns and reheats. Dense, low-connected porosity and grain-boundary purification slow oxidation, carburization, and sulfur/chlorine attack; microtextured, low-wettability surfaces resist tar adhesion and coking.
Sicarbtech integrates “material formulation + structure and thickness design + densification process + surface engineering + prefabrication and onsite installation + inspection and O&M” into a technical pathway that is localizable. Through technology transfer, Pakistani teams can phase in classification, mixing, prefabrication, coatings, and eventually reaction sintering—compressing lead times, cutting FX risk, and, most importantly, making outcomes repeatable across seasons and shifts.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points: The Reality Inside Pakistan’s Coke Ovens and Heat Treatment Furnaces
Walk the flues during a planned stop and the picture comes into focus. Along walls and channels, long-term scouring by coke dust and flue particulates carves grooves that expose masonry; wear zones map directly to elbows, contractions, and reattachment points. Redox cycling—H₂/CO-rich operation shifted periodically to oxygen-rich purges—creates thermal shock and chemical flux that opens microcracks and accelerates porosity growth. At cold ends, tar and polyaromatic condensates stick and coke, thickening layers that raise pressure drop and force frequent cleaning. In sulfur- and chlorine-bearing atmospheres, traditional high-alumina linings rapidly lose strength as porosity climbs, while clay-bonded systems suffer early spalling and unpredictable failure paths.
Pakistan’s operating context magnifies these stresses. Fuel blending and throughput swings are common; monsoon humidity complicates installation and bake-out; and skilled maintenance resources must deliver within constrained windows. Local supply of high-performance surface-engineered, dense SiC systems is limited, which pushes plants to import parts and materials with long, FX-sensitive lead times. “We were paying for pressure drop in energy and for coking in downtime,” a Karachi-based coke oven maintenance manager noted in a 2024 review. “Every extra millimeter of deposit was a tax on both the fan and the calendar.” A regional refractory advisor put the physics plainly, referencing standard corrosion and thermal shock texts: “Conductivity reduces the gradient that drives stress; low expansion reduces the strain when it happens; and connectivity control in the pore network denies access to oxidants and active species. Miss any one of the three and you’ll chase the others.”
Regulatory expectations shape procurement. ISO 9001-aligned QC documentation and PSQCA conformity are increasingly referenced in tenders; ISO 14001-aligned goals favor fewer interventions, lower waste, and better energy discipline; and safety frameworks prioritize planned, modular work over hot, reactive tasks. In this context, lining strategy is not just a materials decision—it is a lever for unit energy, availability, and safety performance across the plant.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio by Sicarbtech
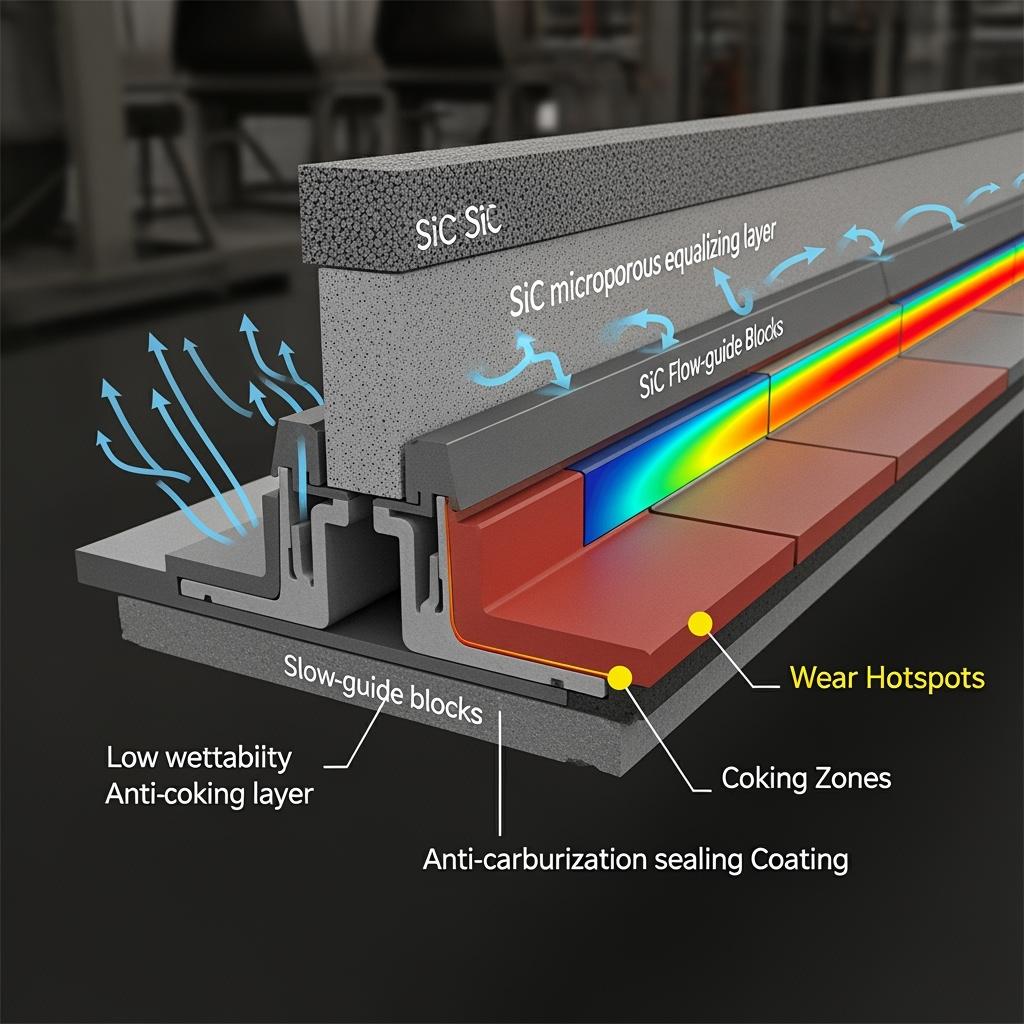
Sicarbtech’s SiC lining systems for coke ovens and heat treatment furnaces are designed as a modular, zone-specific toolkit that solves wear, chemistry, and thermal shock together. The primary working face is reaction-sintered SiC dense plate lining with very low connected porosity and high hardness, resisting long-term scouring by coke dust and mill scale while enduring rapid temperature swings. Where fast reinforcement or spot-build is needed, high-density SiC spray/gunning layers deliver quick, adherent protection with controlled venting and fast cure.
Surface behavior determines pressure-drop trends; Sicarbtech’s low-wettability, anti-coking SiC surface coatings reduce tar and condensate adhesion, while an SiC anti-carburization sealing layer blocks active carbon species from penetrating the matrix. In severe shock or complex profiles, SiC–mullite functionally graded composite plates combine a hard working face and a low-modulus transition layer that buffers interfacial stress, backed by a supportive layer to spread load and damp gradients. High-thermal-conductivity SiC heat-spreading pads and backing plates smooth wall temperature fields, lowering cold-side temperature rise and mitigating hot spots that seed deposits.
Geometry matters in scour zones, so SiC wear-resistant corner and flow-guide blocks add fillets, chamfers, and guide ribs that calm reattachment and reduce local shear. SiC microporous equalizing layers improve wall temperature uniformity under transient loads. Transition areas and complex shapes use ultra-low-cement SiC-bonded castables for monolithic forming with short bake-out, while multi-graded SiC aggregate and micropowder activation packages lift packing density, reduce connectivity, and raise post-firing strength. Anti-sulfur–chlorine composite additives further slow chemical attack. Around joints and frames, SiC wear-resistant expansion-joint strips and flexible shims manage differential expansion; modular anchoring and locking systems accelerate installation and enable repeatable alignment. Finally, SiC backing insulation composite boards reduce shell temperatures and heat loss, adding a direct lever on unit energy consumption.
Underpinning these materials are equipment and QA systems Pakistan can localize: reaction sintering and high-temperature densification kilns; cold isostatic and die-press forming; intelligent mixing and vacuum vibration; precision classification and demagnetization for purity and PSD stability; CNC cutting and grinding/polishing; and non-destructive testing with dimensional inspection. “Linings fail in the factory first—if curves, grading, or surface prep go wrong,” a Sicarbtech process lead notes. “That’s why our transfer packs include recipes, furnace curves, adhesion protocols, and seasonal adjustments tailored for Karachi summers and Gujranwala winters.”
Technical Performance Comparison for Coke Oven and Heat Treatment Linings
| Performance profile in coke/heat treatment service | Silicon Carbide Linings (R-SiC/SSiC/RBSiC/SiSiC) | High-Alumina/Clay Linings | Metal or Metal-Clad Layers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.60–3.05 | 2.2–2.8 | 2.6–7.8 (steels/alloys) |
| Apparent porosity (%) | 6–15 (dense plates ≤ 6) | 15–25 | Low initially; oxide scale forms |
| Thermal conductivity at RT (W/m·K) | 20–55 | 2–6 | 15–50 (drops with scale) |
| Cold crushing strength (MPa) | 120–240 (dense ≥ 260) | 60–150 | 100–250 |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 14–35 | 8–20 | 10–30 |
| Thermal shock (1000°C quench) | ≥ 30–60 | 10–25 | 10–25 (deformation risk) |
| Anti-carburization/chemical resistance | High; low connectivity | Orta düzeyde | Weak at high O₂/S/Cl; scaling |
| Anti-coking/low-wettability | High with SiC coatings | Orta düzeyde | Variable; scale increases adhesion |
| Construction/bake-out window | Short with ULC binders | Longer; moisture-sensitive | Weld/fit complexity; warpage risk |
In Pakistan’s alternating H₂/CO and oxygen-rich atmospheres with tar and impurity loads, SiC’s conductivity, low expansion, and low-connectivity microstructure maintain integrity where oxides and metals give way—translating into flatter pressure-drop curves and longer campaigns.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
A coking unit near Karachi saw accelerated grooving in main flue channels, heavy tar deposition at cold ends, and frequent crack repair cycles after unplanned shutdowns. Sicarbtech deployed a composite lining scheme: reaction-sintered SiC dense plates as the working layer in scour zones; low-wettability anti-coking coatings plus anti-carburization sealing at cold ends; SiC flow-guide blocks to fillet and guide reattachment; and ultra-low-cement SiC-bonded castable as a transition layer with controlled venting. Bake-out followed staged curves adjusted for ambient humidity; adhesion and contact-angle tests verified surface prep. Over the next 14 months, wear rate dropped by around 62%, coking-cleaning man-hours fell by roughly 50%, thermal-shock-related cracks declined by about 55%, cold-side temperature rise dropped by around 20%, annual unplanned downtime eased by approximately 27%, and unit energy consumption dipped by about 4%. “The fan current stopped drifting up between cleanings,” the maintenance supervisor commented. “That’s a first in years.”
A heat treatment line in Punjab experienced wall hot spots and redox-induced spalling along a transfer zone. The upgrade introduced SiC heat-spreading pads and a microporous equalizing layer under reaction-sintered SiC plates, paired with flexible expansion-joint strips. Temperature uniformity improved measurably on IR thermography, and spalling incidents decreased, allowing the site to synchronize maintenance with production instead of chemistry-driven emergency stops.
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Local Compliance
SiC’s physics map directly to the KPIs that matter. High thermal conductivity reduces temperature differentials and, therefore, stress during shutdowns and restarts; low expansion minimizes strain when gradients occur. Dense, low-connectivity porosity resists oxidant and active species ingress, slowing oxidation, carburization, and sulfur/chlorine attack. Low-wettability surfaces push back against tar and salt adhesion, stabilizing pressure drop and cleaning intervals. Functionally graded structures with heat-spreading backings distribute stress and temperature, protecting masonry and steel and reducing crack nucleation at interfaces.
Compliance benefits follow. Longer campaigns and fewer decoking interventions support ISO 14001 objectives; Sicarbtech’s QC documentation aligns with ISO 9001 and supports PSQCA submissions where needed. Our SOPs—surface preparation, adhesion and contact-angle tests, staged bake-out and soak, 3D dimensional checks—integrate with CMMS to create auditable installations. Practically, plants gain safer maintenance profiles, steadier heating, and predictable energy budgets despite fuel and chemistry variability.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech translates materials leadership into a local, repeatable capability for Pakistan. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, our proprietary processes for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC support dense plates, coatings, and composite assemblies—and we transfer them in de-risked stages.
We begin with feasibility and layout tailored to local utilities, labor, and throughput. Equipment specifications include reaction sintering and densification kilns with documented furnace curves; cold isostatic and die-press forming for uniform green bodies; precision classification and demagnetization to stabilize PSD and purity; intelligent mixing and vacuum vibration for rheology control; and CNC cutting and grinding/polishing for geometry and sealing surfaces. Non-destructive testing—ultrasonic/acoustic emission, rebound hardness, adhesion pull-off—plus coordinate metrology and surface energy/contact-angle testing lock in traceable QA.
Quality systems are embedded from day one. We implement ISO 9001-aligned QC with SPC on bulk density, apparent porosity, CCS/MOR, thermal shock performance, coating adhesion, contact angle, and dimensional tolerances. ISO 14001 environmental practices and safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001 principles round out the framework. Training covers operator techniques, furnace curve management, surface prep and coating protocols, staged bake-out and venting control, and seasonal adjustments for humidity. Commissioning includes live curve tuning and supervised first installations in scour and cold-end zones. After go-live, Sicarbtech provides remote monitoring, quarterly audits, and iterative formulation/geometry tuning tied to site KPIs—pressure-drop trend, IR temperature uniformity, coking rate, repair frequency, and energy per ton.
Across 19+ enterprise collaborations, this “materials + equipment + process + training” platform has consistently shortened lead times from months to weeks, stabilized batch quality through weather swings, and reduced import buffers even amid FX volatility. As a Sicarbtech technical director often says, “Owning the powder is the start. Owning the curve, the surface, and the inspection gates is how Pakistani teams turn SiC into scheduled uptime.”
Pakistan-Focused Technical Specification Ranges and QA Guidance
| Specification ranges for coke/heat treatment linings | Typical SiC Targets | Local QA and testing guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.60–3.05 | Verify via ISO/ASTM equivalents; SPC by batch/season |
| Apparent porosity (%) | 6–15 (dense plates ≤ 6) | Correlate with permeability and oxidation/carburization tests |
| Cold crushing strength (MPa) | 120–240 (dense ≥ 260) | ISO 10059/ASTM C133; coupon and zone traceability |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 14–35 | Bend tests with soak logs and position mapping |
| Thermal shock (1000°C quench) | ≥ 30–60 cycles | Cross-check vs shutdown/restart frequency |
| Max service temperature (°C) | 1500–1650 | Confirm vs H₂/CO ratio and oxygen potential |
| Conductividad térmica (W/m·K) | 20–55 | Validate with IR thermography; before/after upgrades |
| Linear change at temperature (3 h) | ≤ 0.5% | Dimensional checks pre-/post-exposure |
| Anti-carburization/anti-S/Cl index | 30–80% better than alumina | Chemical cup tests and weight change |
| Surface contact angle (tar/salt) | 10–35% higher than oxide systems | Track vs coking rate/cleaning hours |
| Coating adhesion strength (MPa) | ≥ 6–12 | Pull-off/shear tests; seasonal audits |
Operational Outcomes Comparison That Drive Energy, Throughput, and Safety
| Outcomes central to Pakistani coke and heat treatment lines | SiC Dense Plates + Anti-Coking Coating + Sealing Layer + Flow Guides + ULC Transition | High-Alumina/Clay or Metal Baselines |
|---|---|---|
| Wear/grooving rate | −40–75% | Higher; early masonry exposure |
| Thermal shock incidents | −50–150% improvement in life | Frequent cracks/spalls on cycling |
| Coking/adhesion trend | −35–65%; longer intervals | Rapid build-up; frequent cleaning |
| Pressure-drop growth | −20–40% vs baseline | Faster; fan energy rises |
| Wall temperature uniformity | +10–25% better ΔT | Hot spots persist |
| Cold-side temperature rise | −15–35% | Higher shell temperatures |
| Planlanmamış arıza süresi | −20–40% | Elevated; reactive decoking |
| Energy per ton | −2–6% | Baseline or rising with fouling |
Innovation That Matters: From Surface Energy to Flow Geometry and Equalization
Sicarbtech’s R&D translates harsh field conditions into durable design. Functionally graded structures place a high-SiC, high-hardness working face over a low-modulus transition and supportive backing to diffuse stress and limit delamination. Composite surface protection stacks pair low-wettability anti-coking coatings with anti-carburization sealing layers, simultaneously reducing tar adhesion and active carbon ingress. Microtexture and surface energy windows are tuned to lower retention of light fractions. Geometry in scour zones is optimized with fillets and guide ribs to temper vortex reattachment and shear spikes, while microporous equalizing layers and heat-spreading pads smooth temperature fields across transients. A digital QC regime—ultrasonic/acoustic emission, 3D metrology, contact-angle logging, and adhesion testing—keeps production inside narrow corridors, turning variability into a managed parameter.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Pakistan
Three trends will set the pace. First, energy and emissions pressure will reward lines that keep pressure-drop curves flat and temperature fields uniform—SiC’s conductivity, low expansion, and surface engineering are built for exactly that. Second, localization will accelerate as producers seek to de-risk FX and compress spares cycles; most will start with mixing, classification, prefabrication, and coatings, and then add reaction sintering for dense plates as volumes justify. Third, digital O&M will deepen, linking IR thermography, pressure-drop trajectories, coking indices, and repair logs to materials and installation quality—feeding a closed loop that steadily lengthens intervals and stabilizes energy per ton.
On scale, a medium-to-large coke oven or continuous heat treatment line typically consumes 100–250 tons of corrosion- and wear-resistant linings annually, depending on temperature regime, atmosphere, and throughput. With Pakistan’s new builds and retrofits, annual SiC demand plausibly reaches several thousand tons. Including prefabs, coatings, installation, enabling equipment, and training, the addressable market sits in the tens to hundreds of millions of Pakistani Rupees, contingent on adoption speed and capital access. Suppliers who combine stable raw materials, high densification and dimensional control, robust surface engineering, responsive onsite execution, and audited technology transfer will hold durable positions. Sicarbtech’s integrated platform is purpose-built for this landscape.
As one South Asia-focused furnace technologist remarked in a 2025 roundtable, “When tar stops sticking, the pressure-drop line flattens, and the IR map calms down—you’ve already paid for your materials choice in stability and saved energy.”
Sıkça Sorulan Sorular
Which Sicarbtech SiC products should we prioritize for coke ovens and heat treatment furnaces?
Start with reaction-sintered SiC dense plate linings in scour and high-shock zones, then add low-wettability anti-coking coatings and anti-carburization sealing layers at cold ends and condensate-prone areas. Use SiC flow-guide blocks where geometry accelerates wear, and deploy ultra-low-cement SiC-bonded transition layers for rapid, controlled installation and repair.
How much improvement can we expect in wear, coking, and downtime?
Typical outcomes include 40–75% lower wear/grooving rates, 35–65% slower coking growth with longer cleaning intervals, 50–150% gains in thermal shock life, and 20–40% reductions in unplanned downtime. Pressure-drop growth often flattens by 20–40%, with 2–6% energy savings depending on baseline and process window.
Can Sicarbtech help localize production to reduce FX risk and lead times?
Yes. We provide full technology transfer—process recipes, equipment specs, plant layout, operator training, ISO 9001/14001-aligned QA frameworks, safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001 principles, and commissioning—so Pakistani partners can own capability from classification and mixing to prefabrication, coatings, and ultimately reaction sintering.
How do SiC linings behave under alternating reducing–oxidizing atmospheres with sulfur/chlorine impurities?
Dense, low-connected porosity and grain-boundary purification resist oxidation-induced porosity and chemical attack; anti-sulfur–chlorine additive packages further slow degradation. Low-wettability surfaces reduce condensate adhesion and coking, stabilizing pressure drop across redox cycles.
What installation practices are critical to avoid early spalling and poor adhesion?
Control substrate cleanliness and roughness, apply vacuum vibration where applicable, and tightly manage moisture and venting. Follow staged bake-out and soak curves adjusted for ambient humidity; verify with adhesion pull-off tests, contact-angle measurements, and 3D dimensional checks before return-to-service.
Which KPIs should we track to verify benefits and guide optimization?
Monitor pressure-drop trajectories, IR temperature uniformity (ΔT across zones), coking/cleaning indices, wall thickness loss (ultrasonic), cold-side temperature rise, energy per ton, and unplanned downtime hours. Correlate with atmosphere composition (H₂, CO, SO₂, HCl), start–stop frequency, and load.
Are composite stacks (coating + sealing layer) compatible with rapid maintenance?
Yes. The stack is engineered for staged bake-out and controlled venting; localized refresh during planned stops maintains performance without full teardown. Gunning mixes support fast spot repairs while preserving underlying adhesion systems.
How do SiC systems integrate with existing anchors and frames?
We adapt modular anchoring/locking geometries and provide shims/transition plates to achieve fit, sealing pressure, and thermal expansion compliance. Dimensional templates and coordinate metrology ensure repeatable assembly.
What documentation supports Pakistani tenders and audits?
Sicarbtech supplies ISO 9001-aligned QC packs, ISO 14001 environmental documentation, safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001 principles, PSQCA conformity packs, and SPC dashboards covering density, porosity, CCS/MOR, thermal shock, contact angle, coating adhesion, and critical dimensions.
What is a practical roadmap to full local capability?
Phase 1: classification/mixing, prefabrication, coatings, and gunning/repair capability. Phase 2: cold isostatic/die pressing and densification kilns for select plates. Phase 3: reaction sintering lines for dense, high-value modules. We align CAPEX, staffing, training, QA gates, and commissioning to your schedule.
Operasyonlarınız için Doğru Seçimi Yapmak
If pressure-drop lines are climbing, if tar cleaning is stealing shifts, and if shutdowns are cracking linings you just installed, materials are dictating your plan. Silicon carbide rewrites that plan. High conductivity and low expansion limit shock; dense, low connectivity resists chemistry; and low-wettability surfaces starve coking. Sicarbtech’s integrated model—materials, structure, curves, coatings, installation SOPs, and localizable manufacturing—turns an upgrade into a controllable performance system for Pakistani coke and heat treatment assets.
Uzman Danışmanlığı ve Özel Çözümler Alın
Share your operating window—temperature profiles and shutdown cadence, atmosphere chemistry (H₂/CO/S/Cl/N species), dust loading and PSD, pressure-drop and coking history, IR uniformity maps, and failure zones—and Sicarbtech will design a tailored SiC package with modeled life and energy gains, plate thickness and geometry, coating and sealing strategies, and staged bake-out protocols. If localization is a priority, we will propose a phased technology transfer aligned to your CAPEX and timeline.
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub
Member of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park
E-posta: [email protected]
Telefon/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Makale Meta Verileri
Last updated: 2025-09-19
Bir sonraki planlı güncelleme: 2026-01-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Pakistan coke/heat treatment market outlook validated; technical ranges aligned with current field trials; PSQCA/ISO alignment reviewed; contact details verified for Pakistan engagements.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.



