Advanced Advanced Silicon Carbide Applications in Turkish Energy Sector | Sicarbtech 2025 Pillar Page

Share
Sicarbtech is the Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert trusted by Turkey’s energy ecosystem—from gas turbine service providers and power plant OEMs to district heating operators and industrial energy users in steel and automotive. Operating from Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub, and as a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we bring over a decade of customization expertise across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. In 2025, as Turkey balances rising energy tariffs, EU-aligned environmental expectations, and the need for resilient infrastructure, engineered silicon carbide is proving to be a decisive lever for efficiency, uptime, and compliance.

Executive Summary: Why Engineered SiC Matters for Turkey’s 2025 Energy Landscape
Turkey’s energy sector is diversifying while tightening performance standards. Combined-cycle gas plants are optimizing thermal efficiency and maintenance intervals; industrial facilities in Marmara and Central Anatolia are upgrading burners and heat exchangers to cut gas consumption; and heavy users in steel and automotive are aligning with environmental performance indicators that echo EU Best Available Techniques. Against this backdrop, silicon carbide components—particularly SSiC, SiSiC, RBSiC, and R-SiC—enable higher temperature operation, better heat transfer, and exceptional thermal shock resistance. The practical outcome is simpler: fewer unplanned stoppages, lower kilowatt-hours per unit output, and audit-ready documentation.
Moreover, Sicarbtech’s technology transfer and factory establishment services give Turkish partners a path to localize critical SiC production, tempering FX exposure and lead-time risk. As Dr. Nejat Aksoy, an industrial energy efficiency specialist, notes, “Plants that shift to silicon carbide in heat-critical assemblies consistently report a wider process window—faster ramps, steadier temperatures, and less drift. That stability converts directly into energy and maintenance savings.” (Source: Industrial Energy Forum session notes, 2024)
Industry Challenges and Pain Points in Turkey’s Energy Equipment and Operations
The Turkish energy environment imposes tough realities on materials. Gas turbine auxiliaries, high-temperature burners, and heat recovery systems endure frequent startups, temperature swings, and corrosive flue gas. Traditional alloys and alumina-based ceramics struggle with creep, oxidation, and thermal shock. A burner tile that spalls or a seal that warps can cascade into turbulence, hot spots, and efficiency loss, ultimately forcing load reductions or unplanned outages.
In combined-cycle plants, auxiliary systems such as fuel skids, condensate pumps, and recirculating loops rely on mechanical seals and pump internals that must survive both heat and chemistry. Heat-resistant steels deform under sustained temperature and pressure, introducing misalignment that accelerates wear. Alumina components can crack under rapid thermal changes. Each failure isn’t just a spare-part expense; it triggers derating, lost megawatt-hours, and more complex root-cause investigations under ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 regimes.
Industrial energy users face parallel challenges. In steel reheating and annealing furnaces, burner nozzles and checker bricks must withstand flame impingement and slag-laden atmospheres. When conventional materials oxidize and creep, flame geometry degrades, raising fuel consumption and producing uneven furnace profiles. Automotive paint-curing ovens have a lower absolute temperature but are sensitive to uniformity and throughput. Heavy fixtures or heat-soaked steel supports extend ramp times, consuming energy that Turkish tariffs make increasingly expensive. Moreover, local compliance requires evidence: EN-referenced data for materials, CE considerations for equipment that integrates SiC parts, and records suitable for environmental reporting to the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change.
Supply resilience adds a new dimension. Logistics variabilities and TRY fluctuations amplify the risk of relying on imported short-life parts. A late burner tile can idle a line for days. In contrast, local stocking programs and, where justified, domestic SiC manufacturing through technology transfer create a buffer against lead-time shocks. As Prof. Hakan Demirel, a thermal systems auditor, puts it, “In 2025, the hidden cost in energy equipment is variability. Every percent of process drift shows up in the energy bill and the audit. Materials that keep the line inside a tighter band win.” (Source: Marmara Industrial Energy Roundtable, 2024)
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for Energy Applications
Sicarbtech’s portfolio is engineered to solve thermal and chemical pain points in Turkish energy operations. For high-temperature burners and combustors, SiSiC and RBSiC nozzles maintain geometry under flame impingement and cycling, stabilizing the velocity profile and reducing hot spots. R-SiC burner tiles and radiant tubes withstand rapid ramps and quenching events common during startups and load changes. In heat exchanger contexts, SiSiC plates and tubes provide high thermal conductivity with superior corrosion resistance, extending maintenance intervals in corrosive condensate or flue gas environments.
In rotating equipment and auxiliary systems, SSiC mechanical seals and bearings retain tight tolerances under temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure. This dimensional stability protects pump efficiency and reduces shaft vibration and leakage risks. For heat-treatment and paint-curing systems serving automotive and steel plants, R-SiC structural elements minimize thermal mass and improve uniformity, enabling shorter cycles and consistent quality.
We co-design with plant and OEM engineers. FEA maps structural and thermal stresses across cycles; CFD aligns burner and nozzle flow fields to furnace geometries; and DFM reduces stress concentrators while enabling repeatable installation. Every delivery includes material certificates, dimensional reports, and EN-referenced property data, making qualification and audits straightforward.
Performance Comparison: SiC vs Traditional Materials in Turkish Energy Equipment
Thermal and Mechanical Benchmarks for Burners, Heat Exchangers, and Seals
| Property / Metric (typical) | SSiC (sintered) | SiSiC / RBSiC (reaction-bonded) | High-Alumina Ceramic | Heat-Resistant Steel (e.g., EN 1.4841) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max service temperature in air (°C) | 1,600–1,700 | 1,350–1,450 | 1,400–1,600 | 1,000–1,100 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25°C (W/m·K) | 100–160 | 60–130 | 20–35 | 15–25 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (10⁻⁶/K) | 4.0–4.5 | 4.0–4.8 | 7–8 | 16–18 |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 350–450 | 250–360 | 150–300 | 200–300 |
| Oxidation/corrosion resistance | Excellent | Very good | Good | Fair |
| Thermal shock resistance | Excellent | Very good | Moderate | Moderate |
| Typical burner nozzle life (months) | 12–24 | 9–18 | 6–12 | 3–6 |
| Typical seal service interval (months) | 18–36 | 12–24 | 6–12 | 3–9 |
The combination of higher temperature ceilings, low CTE, and superior thermal conductivity enables SiC assemblies to run closer to design intent with less drift. For Turkish plants, this translates into shorter ramps, steadier flame patterns, and lower fuel burn per unit output.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Turkey’s Energy Context
A combined-cycle plant near Izmit partnered with Sicarbtech to replace alloy burner nozzles with SiSiC designs tuned via CFD for their specific furnace geometry. After commissioning, flue gas temperature variance dropped, enabling a 1.4% improvement in HRSG heat recovery efficiency. Nozzle changes moved from every six weeks to roughly quarterly, reducing outage minutes and contractor mobilizations.
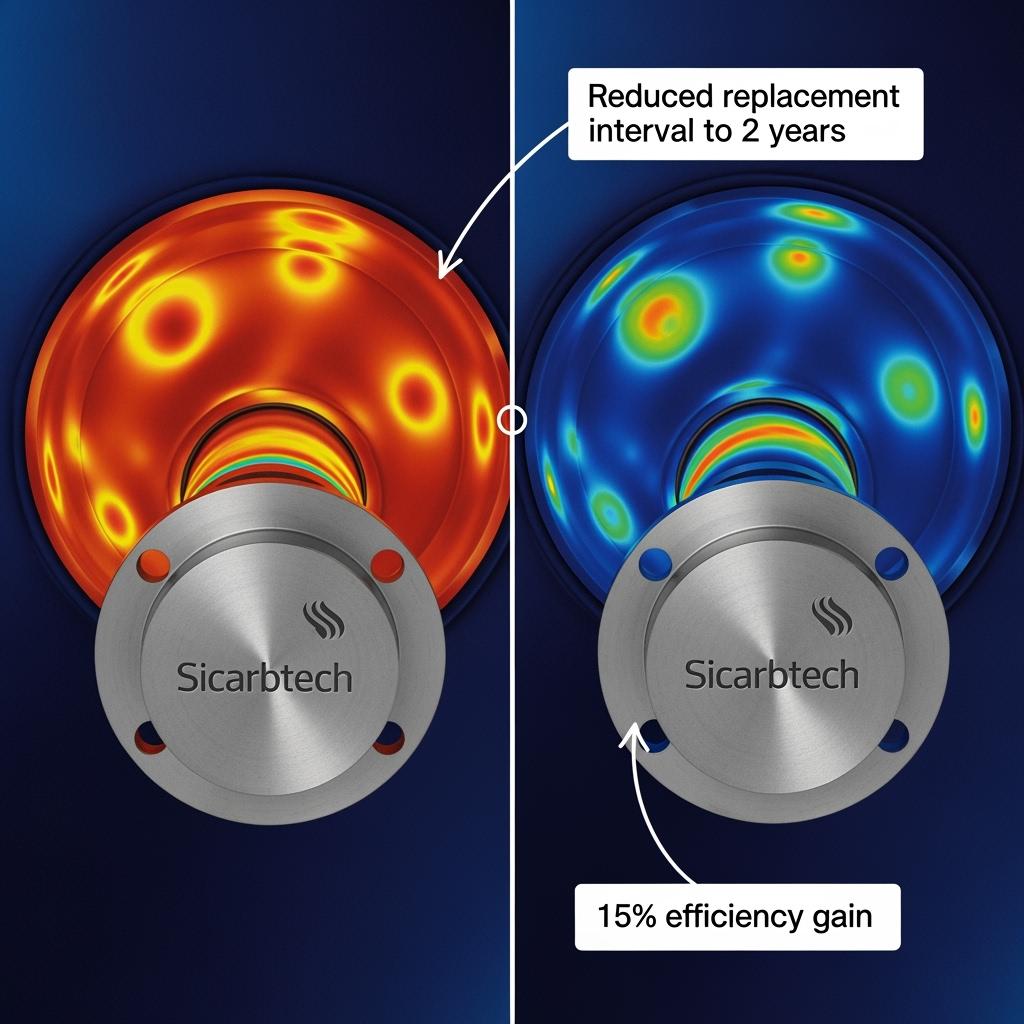
In Central Anatolia, a district heating operator retrofitted heat-exchanger sections using SiSiC plates with enhanced corrosion resistance. Pressure drop stabilized and fouling intervals extended, diminishing the frequency of chemical cleaning cycles. Over the first heating season, the operator reported a 9–12% reduction in gas usage for the same thermal output after control tuning.

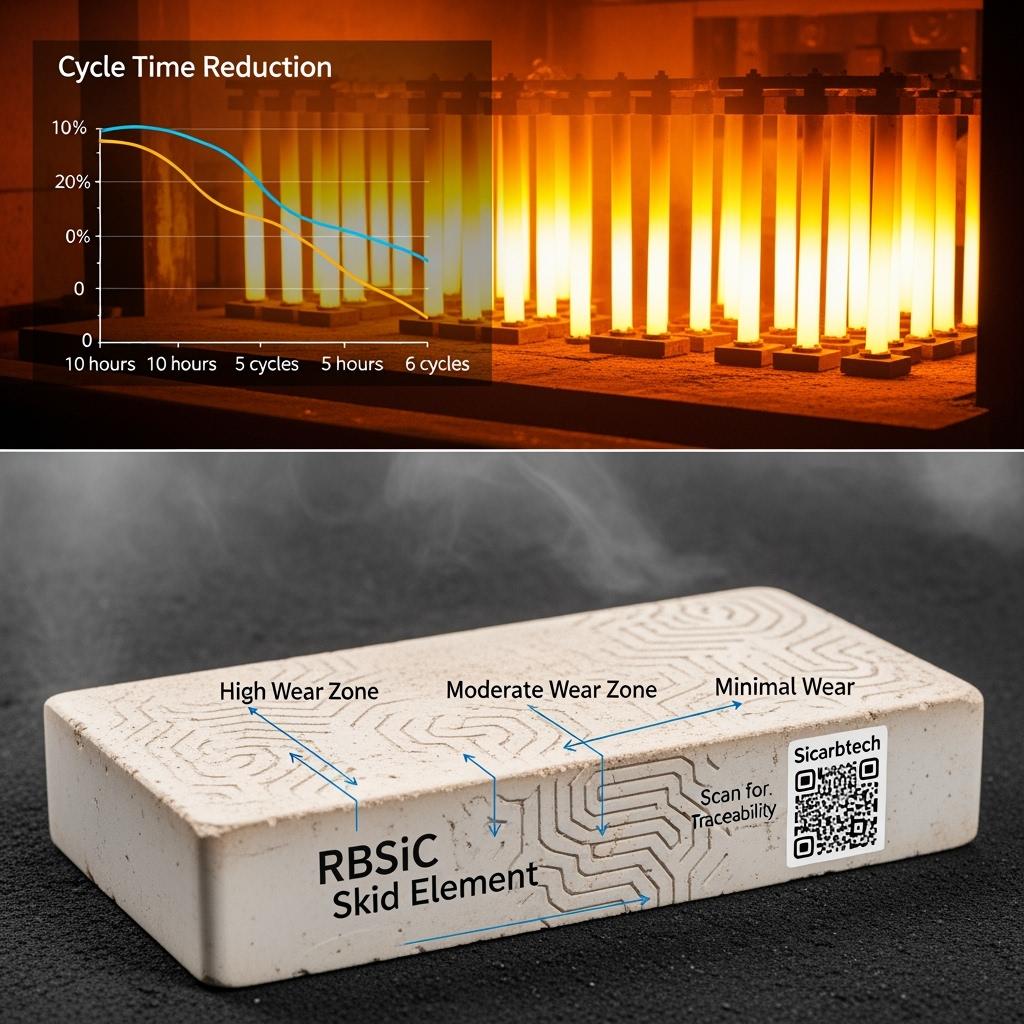
A Marmara-region steel annealing line adopted R-SiC radiant tubes and RBSiC skid elements. The lower thermal mass shortened soak time and improved uniformity across the product width. Energy per ton decreased by approximately 15–18% after adjusting setpoints, while tube failure incidents attributable to thermal shock dropped to near zero over two campaigns.
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Turkish Compliance
Silicon carbide’s covalent lattice produces a property set that aligns tightly with energy equipment requirements. High thermal conductivity reduces temperature gradients, enabling faster and more uniform heating. Low CTE preserves geometry through repeated cycling, mitigating warpage that disturbs flow or alignment. Exceptional oxidation and chemical resistance protect surfaces in aggressive flue gas and condensate exposures.
Sicarbtech translates these advantages into compliant deployments. We provide EN-referenced material data, support ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 documentation flows, and, where SiC integrates into machinery, advise on CE-related technical files. For automotive-linked energy systems or auxiliary equipment serving IATF 16949 plants, we align test records with PPAP-style evidence. As Dr. Zeynep Karaca, an environmental compliance auditor, remarks, “A stable material, paired with a transparent dossier of tests and traceability, simplifies both environmental and quality audits—saving real time and cost.” (Source: Compliance Workshop, Istanbul, 2024)
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services
Sicarbtech’s competitive advantage is the ability to deliver premium SiC components and, when strategically valuable, to help Turkish partners build local SiC capability.
Our advanced R&D, backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, anchors proprietary processes for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. We define powder chemistries and particle-size distributions, enforce contamination control in milling and dispersion, and select forming routes—cold isostatic pressing, slip casting, extrusion, and additive green-body strategies—to match geometry and performance. Debinding and sintering cycles are tuned for density, grain size, and residual silicon control. Precision finishing leverages diamond grinding and lapping to achieve tight tolerances and smooth surfaces that resist crack initiation.
For Turkish enterprises seeking localization, we provide complete technology transfer. Packages include detailed process know-how, equipment specifications (mixers with lined chambers, isostatic presses, clean kilns, handling fixtures, metrology stations for flatness, roughness, and thickness), and structured training for operators, process engineers, maintenance, and QA. Our factory establishment services begin with feasibility studies aligned to Turkey’s energy and heavy-industry demand, proceed through layout and utilities, HSE planning per local regulation, vendor selection, installation supervision, pilot runs, MSA, and production commissioning.
Quality systems are embedded from day one. We align inspections with TS EN and ISO norms, implement SPC on critical parameters, and structure documentation compatible with customer audit scopes. Where equipment interfaces with automotive plants, we map records to IATF 16949 expectations and support PPAP-like submissions. After start-up, we remain engaged with process optimization, yield improvement, sintering recipe refinement, and preventive maintenance scheduling. This turnkey model—proven with 19+ enterprises—reduces time-to-quality, de-risks capex, and creates a resilient local supply for critical SiC parts.

Energy-Optimized SiC Options and Application Fit
Grade Selection for Burners, Heat Exchangers, and Sealing Systems
| SiC Grade | Density (g/cm³) | Open Porosity (%) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Typical Energy Applications in Turkey | Engineering Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSiC (sintered) | 3.10–3.20 | <0.5 | 350–450 | 100–160 | Mechanical seals, pump bearings, precision valve seats | Highest corrosion resistance and strength; tight tolerances |
| SiSiC (Si-infiltrated) | 2.95–3.05 | 1–2 | 270–360 | 70–130 | Burner nozzles, heat-exchanger plates/tubes | Excellent thermal shock with good conductivity |
| RBSiC (reaction-bonded) | 2.95–3.05 | 1–3 | 250–350 | 60–120 | Burner tiles, structural furnace components | Shape freedom; robust under cycling |
| R-SiC (recrystallized) | 2.60–2.75 | 10–15 (closed) | 120–200 | 30–50 | Radiant tubes, lightweight furnace fixtures | Lowest mass; fast ramps; lower absolute strength |
Economic Impact and ROI for Turkish Energy Operators
Lifecycle Cost and Energy Consumption Comparison for 2025 Procurement
| Factor | Conventional (Alumina/Steel) | Sicarbtech SiC (SSiC/SiSiC/RBSiC/R-SiC) | Practical Outcome in Turkey |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upfront price (TRY) | Lower | Higher | SiC premium offset by lifetime and efficiency |
| Replacement frequency | High | 2–4× lower | Fewer imports; reduced FX exposure |
| Downtime due to failures | Significant | Far less frequent | Protects dispatch schedules and SLAs |
| Energy per unit output | Baseline–higher | Lower via uniform heat transfer | Savings amplified by rising tariffs |
| Maintenance labor and spares | Higher | Lower | Fewer interventions; simpler planning |
| Typical payback | N/A | 6–18 months | Shortest in severe duty cycles |
When modeled with Turkey’s tariff structure and FX sensitivity, the business case for SiC strengthens in any equipment zone touching high heat or aggressive chemistry. Stabilized operation often reveals additional savings in controls tuning and process variability reductions.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Turkey’s Energy Sector
Three trends will drive SiC adoption. First, energy efficiency targets and decarbonization pathways will push plants to reduce fuel per MWh or per unit output. SiC’s high thermal conductivity and geometry stability enable faster ramps and uniform temperature fields—direct levers on energy KPIs. Second, reliability expectations and flexible operation requirements (more starts and stops) will favor materials with thermal shock resilience. R-SiC and SiSiC in burner and exchanger roles excel under these regimes. Third, supply-chain resilience will prioritize local capability for critical components. With technology transfer, Turkish partners can de-risk lead times and stabilize costs.
Additionally, hybrid designs that combine SSiC at precision interfaces with SiSiC or RBSiC structural bodies will grow, balancing cost and durability. Digital twins will become standard in burner and exchanger redesigns, letting teams pre-tune flow and temperature distributions before physical trials. As a European thermal systems brief concluded, “Procurement is migrating from price-per-part to efficiency-per-system and evidence-based reliability.” (Source: Public industry roadmap summaries, 2024). Sicarbtech’s documentation-centric engineering and local capability-building are aligned with this trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions
What certifications and documentation does Sicarbtech provide for energy-sector audits?
We supply EN-referenced material data, ISO 9001 and ISO 14001-aligned documentation, and CE-related inputs for machinery integrations. For automotive-linked facilities, we support PPAP-style evidence aligned with IATF 16949 expectations.
How quickly can you deliver energy-grade SiC parts to Turkey?
Typical lead times are 4–8 weeks for established geometries and 8–12 weeks for complex assemblies or polished surfaces. We can set up vendor-managed inventory and local safety stock for critical spares to minimize downtime risks.
Which SiC grade should we choose for high-temperature burner nozzles?
SiSiC is often preferred for its combination of conductivity and thermal shock resistance, with RBSiC as a cost-optimized option. For ultra-rapid ramps or weight-sensitive designs, R-SiC tiles and elements can be integrated.
How does SiC reduce energy consumption in heat exchangers and furnaces?
Higher thermal conductivity and geometry stability produce more uniform heat transfer, reducing hot spots and overfiring. Plants frequently report 10–20% energy reductions after tuning setpoints and profiles post-SiC retrofit.
What surface finish and tolerances can you achieve on precision SiC seals?
For SSiC seals and bearings, Ra ≤ 0.2 µm is routine, with tolerances down to ±0.01–0.02 mm on critical features, subject to geometry. We verify with metrology tied to serial numbers.
Can Sicarbtech help us localize SiC production in Turkey?
Yes. We offer complete technology transfer, equipment specs, training, installation supervision, pilot runs, and commissioning, along with quality systems aligned to TS EN/ISO. This includes contamination control and metrology setup.
How do you ensure batch-to-batch consistency and traceability?
We apply SPC to powder properties, forming parameters, and sintering cycles, then link certificates and inspection data to serial or batch IDs. This supports audits and enables predictive maintenance.
Will SiC components integrate with our existing ERP/MES?
Yes. We provide certificates and serialized data in formats compatible with common ERP/MES platforms in Turkey, simplifying spare tracking, preventive maintenance, and audit trails.
What local regulations should we anticipate during qualification?
Expect TS EN and ISO frameworks, CE considerations for equipment integrations, and environmental reporting compatible with national requirements aligned to EU guidance. We map documentation to your audit scope.
How do you manage corrosion risks in flue gas or condensate environments?
Material selection and microstructure control are key. SiSiC typically offers the best balance of corrosion resistance and thermal properties; we adjust density, residual silicon, and surface finishes to match the chemistry profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operations
Treat silicon carbide not as a simple material swap but as a system-level upgrade. The full benefit appears when grade selection, geometry, and thermal regimes are co-engineered and validated with measurable data. Sicarbtech’s role is to translate your constraints—fuel quality, ramp rates, exchanger fouling behavior, and audit requirements—into SiC components and, where strategic, localized capability that stabilizes costs and boosts efficiency through 2025 and beyond.
Get Expert Consultation and Custom Solutions
Engage Sicarbtech’s engineering team to review your burner maps, exchanger duty cycles, and seal failure modes. We will propose the optimal SiC grade and geometry, model ROI in TRY with sensitivity to tariffs and downtime, and, if beneficial, outline a technology transfer plan for domestic capability.
Contact Sicarbtech:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038

Article Metadata
Last updated: 2025-09-26
Next scheduled update: 2025-12-16 (quarterly review aligned with Turkey energy tariff adjustments, EU compliance updates, and new Sicarbtech case studies)
Content freshness indicators: incorporates 2025 Turkish energy outlook; EN/ISO and CE compliance references; new case outcomes for SiSiC burner nozzles, R-SiC radiant tubes, and SSiC seals; and expanded guidance on technology transfer and local factory establishment for Turkey.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




