Unyielding Guardians: Leveraging Custom Silicon Carbide for Peak Performance in Chemical Processing

Share
The chemical processing industry stands as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, producing a vast array of products essential to our daily lives. However, the very nature of chemical synthesis and transformation involves navigating some of the most aggressive operational environments imaginable. Extreme temperatures, high pressures, corrosive media, and abrasive slurries constantly challenge the integrity and longevity of processing equipment. In this demanding landscape, material selection is not just a detail; it’s a critical factor determining operational efficiency, safety, and profitability. Among the advanced materials stepping up to these challenges, custom silicon carbide (SiC) products have emerged as a true champion, offering an unparalleled combination of resistance properties that make it an indispensable asset for high-performance industrial applications in the chemical sector. This blog delves into the multifaceted role of silicon carbide in chemical processing, exploring its applications, the benefits of customization, and how to partner with expert suppliers like Sicarb Tech to unlock its full potential.
Introduction: The Unyielding Strength of Silicon Carbide in Demanding Chemical Processing Environments
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a synthetic crystalline compound of silicon and carbon, renowned for its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, excellent thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion, and, crucially for the chemical industry, its outstanding chemical inertness. Unlike many traditional metals and alloys that succumb to rapid degradation in corrosive environments, SiC maintains its structural and chemical integrity across a wide pH range and in the presence of aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, even at elevated temperatures.
The chemical processing industry is relentless in its demands. Equipment must reliably handle substances that can dissolve, corrode, or erode conventional materials in short order. This necessitates the use of materials that not only withstand these harsh conditions but also contribute to process purity by not leaching contaminants. Standard, off-the-shelf components often fall short of meeting the unique and highly specific requirements of diverse chemical processes. This is where custom silicon carbide components become essential. Tailoring the design, grade, and geometry of SiC parts to the precise operational parameters of a given application ensures optimal performance, extended service life, and enhanced safety. The growing complexity of chemical manufacturing and the continuous push for process optimization further underscore the critical need for advanced material solutions like technical ceramics, with SiC leading the charge.
Main Applications of Silicon Carbide in the Chemical Processing Industry
The remarkable properties of silicon carbide lend themselves to a wide array of critical applications within chemical processing plants. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions translates directly into enhanced reliability and reduced downtime for essential equipment. Industrial buyers and technical procurement professionals are increasingly specifying SiC for new installations and retrofits to improve overall plant performance.
Key applications include:
- Pumps: SiC is extensively used for components like impellers, casings, shafts, sleeves, bushings, and wear rings in centrifugal and positive displacement pumps handling corrosive and abrasive fluids. SiC pump components chemical applications benefit from minimal wear and extended mean time between failures (MTBF).
- Valves: Valve seats, balls, plugs, stems, and liners made from SiC offer superior resistance to erosion and corrosion, ensuring tight sealing and longevity in aggressive media flow control.
- Mechanical Seals: SiC faces are a standard in mechanical seals for pumps and mixers, providing excellent tribological properties (low friction, high wear resistance) against various counter-face materials, even in dry-running conditions or when handling particle-laden fluids. SiC seals chemical applications are critical for preventing fugitive emissions and ensuring process containment.
- Heat Exchangers: SiC heat exchangers chemical tubes and plates are ideal for processes involving highly corrosive fluids at high temperatures, such as in the production of strong acids or halogenated chemicals. Their high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer, while their corrosion resistance prevents contamination and material degradation.
- Reactors and Vessels: Linings and critical internal components for chemical reactors, such as thermowells, dip tubes, and spargers, can be fabricated from SiC to withstand harsh chemical environments and high temperatures, ensuring process integrity and longevity. SiC reactors benefit from the material’s inertness.
- Pipes and Linings: For the safe and reliable transport of highly corrosive or abrasive slurries, SiC pipes and pipe linings offer a long-lasting solution, significantly outperforming traditional lined steel or exotic alloys in many cases.
- Nozzles and Injectors: Atomization nozzles, spray nozzles, and injectors used for introducing reactants or scrubbing gases benefit from SiC’s wear resistance and ability to maintain precise orifice dimensions over extended periods.
- Distillation and Scrubber Components: Packing materials, trays, and other internal components in distillation columns and gas scrubbers can leverage SiC’s chemical resistance and high-temperature stability.
Below is a table summarizing some common SiC components and their functions in chemical processing:
| SiC Component | Equipment | Primary Function(s) | Key SiC Benefits Utilized |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seal Faces, Rings | Mechanical Seals, Pumps, Mixers | Provide a dynamic sealing interface, prevent leakage | Wear resistance, chemical inertness, low friction |
| Impellers, Casings | Pumps | Move and contain fluids | Abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, high strength |
| Valve Balls, Seats, Trims | Valves | Control fluid flow, ensure tight shut-off | Erosion resistance, corrosion resistance, hardness |
| Heat Exchanger Tubes/Plates | Heat Exchangers | Facilitate heat transfer between fluids | High thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, strength |
| Nozzles, Orifices | Sprayers, Burners, Reactors | Control fluid dispersion, injection, or flow rate | Wear resistance, chemical stability, dimensional stability |
| Liners, Tiles | Pipes, Chutes, Cyclones, Vessels | Protect underlying structures from wear and chemical attack | Abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance |
| Thermowells, Dip Tubes | Reactors, Tanks | Protect temperature sensors, allow sampling/injection in aggressive environments | Chemical inertness, thermal stability |
The versatility of SiC allows OEMs and plant engineers to design more robust and efficient chemical processing systems, ultimately leading to lower operational costs and improved product quality.
Why Custom Silicon Carbide is the Superior Choice for Your Chemical Processing Needs
While the inherent properties of silicon carbide are impressive, the ability to customize SiC components unlocks a new level of performance and efficiency in chemical processing. Generic, off-the-shelf parts may offer some benefits, but they rarely address the specific nuances of a particular chemical environment or mechanical stress profile. Custom SiC components chemical industry applications are driven by the need for precision-engineered solutions that maximize operational uptime and safety.
The key advantages of opting for custom silicon carbide include:
- Unmatched Chemical Inertness Tailored to Specific Media: While SiC is broadly resistant, customization allows for the selection of specific SiC grades (like high-purity SSiC) that offer optimal resistance to a precise cocktail of chemicals, pH levels, and concentrations present in a particular process. This ensures maximum material longevity and minimizes any potential for process contamination.
- Optimized Thermal Performance for Unique Process Conditions: Chemical reactions can involve extreme temperatures and rapid thermal cycling. Custom SiC parts can be designed with geometries and material grades (e.g., RBSC for excellent thermal shock) that specifically manage these thermal stresses, preventing cracks and failures often seen in less adaptable materials.
- Engineered Wear and Abrasion Resistance for Specific Flow Regimes: Processes involving abrasive slurries, high-velocity particle impingement, or cavitating flows demand components designed to withstand these specific wear mechanisms. Customization allows for optimized shapes, surface finishes, and reinforcement where needed, significantly extending the part’s service life beyond what standard components could achieve.
- Precision Geometric Design for Seamless Integration and Enhanced Efficiency: Custom SiC parts are manufactured to precise dimensional specifications, ensuring perfect fitment into existing assemblies or new equipment designs. This can improve hydrodynamic efficiency in pumps and valves, optimize flow paths, and eliminate dead zones where corrosion or deposition might occur.
- Enhanced Structural Integrity for Demanding Mechanical Loads: Components in chemical plants often face high pressures, vibrational forces, and mechanical stresses. Custom design allows engineers to specify thicker sections, reinforcing features, or specific microstructures that enhance the overall strength and reliability of the SiC part under its unique loading conditions.
- Significant Long-Term Cost Reduction: While the initial investment in custom silicon carbide products might be higher than for some conventional materials, the extended service life, drastically reduced maintenance requirements, minimized downtime, and prevention of catastrophic failures lead to a significantly lower total cost of ownership. This makes custom SiC an economically sound choice for wholesale buyers and procurement managers focused on long-term value.
In essence, customization transforms silicon carbide from a high-performance material into a targeted engineering solution, directly addressing the operational pain points of specific chemical processes. This level of tailored performance is something that generic solutions or less versatile materials simply cannot offer.
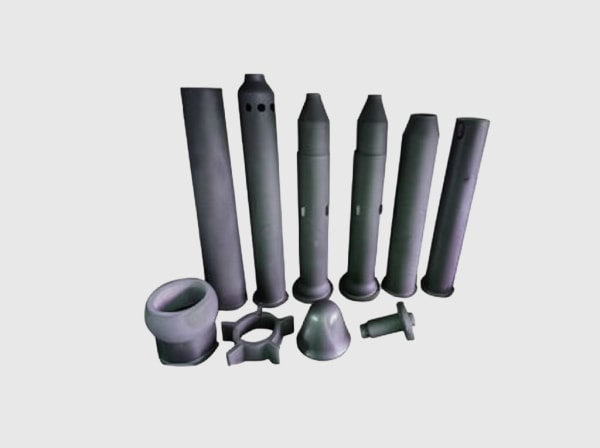

Recommended SiC Grades Tailored for Chemical Processing Environments
Not all silicon carbide is created equal. Different manufacturing processes result in various SiC grades with distinct microstructures and property profiles. Selecting the appropriate grade is paramount for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in specific chemical processing applications. Partnering with a knowledgeable supplier, such as Sicarb Tech, who possesses deep expertise in technical ceramics and their applications, is crucial for making this critical decision. Sicarb Tech, with its strong backing from the Chinese Academy of Sciences National Technology Transfer Center and its pivotal role in the Weifang SiC manufacturing hub, offers unparalleled guidance in material selection.
Here are some commonly recommended SiC grades for chemical processing:
- Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RBSC or SiSiC – Silicon-Infiltrated Silicon Carbide):
- Properties: RBSC is produced by infiltrating a porous carbon-SiC preform with molten silicon. The resulting material contains free silicon (typically 8-15%) within the SiC matrix. It offers good mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, high thermal conductivity, and very good thermal shock resistance. Its chemical resistance is generally good, particularly against acids. However, it can be attacked by strong alkalis and certain halogens at high temperatures due to the presence of free silicon.
- Pros: Relatively lower cost compared to SSiC, easier to produce complex shapes, good overall performance for many applications.
- Cons: Presence of free silicon can be a limitation in extremely corrosive alkaline or halogenated environments.
- Typical Chemical Applications: Pump components (shafts, sleeves, impellers), valve parts, mechanical seal faces, nozzles, and wear liners where extreme chemical purity is not the primary driver and cost is a significant factor. Often used for handling abrasive slurries and moderately corrosive chemicals.
- Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSiC):
- Properties: SSiC is produced by sintering fine SiC powder at high temperatures (typically >2000°C), often with non-oxide sintering aids. This results in a single-phase material with very high purity (typically >98-99% SiC), fine grain size, exceptional hardness, high strength, and superior corrosion resistance across a very broad range of chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and oxidizing agents, even at elevated temperatures. It also exhibits excellent wear resistance.
- Pros: Highest level of chemical inertness and corrosion resistance among SiC grades, excellent wear resistance, maintains strength at high temperatures. The top choice for the most aggressive chemical environments.
- Cons: Generally higher cost than RBSC, can be more challenging to manufacture into highly complex shapes.
- Typical Chemical Applications: Critical components in contact with highly corrosive media such as concentrated nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and strong alkalis. Ideal for mechanical seal faces, pump bearings, valve components, heat exchanger tubes, and reactor components in demanding pharmaceutical, fine chemical, and petrochemical applications.
- Nitride-Bonded Silicon Carbide (NBSC):
- Properties: NBSC is produced by bonding SiC grains with silicon nitride (Si3N4). This material offers good thermal shock resistance, moderate strength, and good resistance to wetting by molten metals. Its chemical resistance is generally good but may not be as comprehensive as SSiC in certain aggressive environments.
- Pros: Excellent thermal shock resistance, good refractory properties.
- Cons: Lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to RBSC and SSiC. Chemical resistance is good but not as universal as SSiC.
- Typical Chemical Applications: Primarily used in high-temperature applications such as kiln furniture, burner nozzles, and components for incinerators. In chemical processing, it might be found in areas requiring extreme thermal cycling rather than primary contact with highly corrosive process fluids.
The selection process involves a careful analysis of the chemical environment (specific chemicals, concentrations, pH), operating temperature and pressure, presence of abrasive particles, mechanical stresses, and desired service life. Sicarb Tech leverages its extensive material science knowledge, stemming from its association with the Chinese Academy of Sciences and its experience supporting over 10 local enterprises in Weifang’s SiC cluster, to guide clients in selecting the optimal grade that provides the best balance of performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness for their unique custom SiC chemical processing needs.
| SiC Grade | Key Characteristics | Chemical Resistance (General) | Common Chemical Processing Applications | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBSC / SiSiC | Good strength, wear resistance, thermal conductivity, thermal shock resistance. Contains free Si. | Good against acids, moderate against alkalis. | Pump parts, valve components, mechanical seals, wear liners for moderately corrosive/abrasive conditions. | Medium |
| SSiC (Pressureless Sintered) | Highest purity, superior corrosion & wear resistance, high strength at temp. | Excellent against strong acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents. | Critical components in highly corrosive environments: seals, bearings, heat exchangers, reactor internals. | High |
| NBSC | Excellent thermal shock resistance, good refractory properties. | Good, but generally less than SSiC in extreme conditions. | High-temp applications, burner nozzles, kiln furniture; less common for direct corrosive fluid contact. | Medium-High |
This table serves as a general guideline. For any specific application, a detailed consultation with material experts, such as the team at Sicarb Tech, is highly recommended to ensure the selection of the most suitable SiC grade for your custom ceramic fabrication project.
Design and Manufacturing Considerations for Custom SiC Components in Chemical Applications
Creating effective custom SiC components for the chemical industry involves more than just selecting the right grade; it requires careful consideration of design for manufacturability and the specific demands of the application. Silicon carbide, while incredibly robust in service, is a hard and brittle ceramic, which presents unique challenges and opportunities during the design and manufacturing phases. Collaborating with an experienced supplier like Sicarb Tech, who offers comprehensive customizing support including material, process, design, and measurement technologies, is vital for success. Their integrated approach, from raw materials to finished products, honed within the Weifang SiC manufacturing ecosystem, ensures that designs are optimized for both performance and producibility.
Key design and manufacturing considerations include:
- Geometry and Complexity:
- Simplicity is Preferred: While advanced manufacturing techniques allow for complex SiC shapes, simpler geometries generally lead to lower manufacturing costs and reduced risk of stress concentrations. Generous radii should be used on internal corners to minimize stress.
- Wall Thickness: Minimum and maximum wall thicknesses are process-dependent. Thin sections can be fragile, while overly thick sections may present challenges in uniform sintering or reaction bonding and can increase material costs. Uniform wall thickness is generally advisable to prevent stress during firing.
- Avoiding Sharp Edges and Corners: These can be points of weakness and are prone to chipping. Chamfered or radiused edges are recommended.
- Near-Net-Shape Manufacturing: Due to SiC’s hardness, extensive machining is costly and time-consuming. Designs should aim for near-net-shape forming (e.g., through pressing, slip casting, or injection molding prior to firing) to minimize post-sintering grinding.
- Tolerances, Surface Finish, and Dimensional Accuracy:
- Achievable Tolerances: While tight tolerances are achievable with SiC through precision grinding and lapping, they significantly impact cost. Designers should specify only the level of precision truly required for the component’s function. Typical as-sintered tolerances might be around ±1−2%, while ground tolerances can be as tight as a few micrometers (μm).
- Surface Finish: The required surface finish depends heavily on the application. For example, mechanical seal faces require highly polished, extremely flat surfaces (Ra<0.2μm) to ensure effective sealing. Pump impellers or liners may tolerate a rougher, as-sintered finish. Specific surface roughness values should be clearly defined.
- Dimensional Stability: SiC exhibits excellent dimensional stability over a wide range of temperatures, which is a key advantage in precision applications.
- Integration with Mating Parts:
- Differential Thermal Expansion: When SiC components are assembled with metallic parts, differences in thermal expansion coefficients must be carefully considered in the design to avoid stress buildup and potential failure at operating temperatures.
- Joining and Assembly: Methods for joining SiC to itself or other materials (e.g., brazing, shrink-fitting, adhesive bonding) should be considered during the design phase if complex assemblies are required.
- Post-Processing Needs:
- Grinding and Lapping: Diamond grinding is typically required to achieve tight dimensional tolerances and fine surface finishes on SiC parts after sintering. Lapping and polishing are used for applications requiring extreme flatness and smoothness, such as seal faces.
- Cleaning and Purity: For applications in high-purity chemical or pharmaceutical processes, specific cleaning and handling protocols may be necessary to ensure no contaminants are introduced from the manufacturing process.
- Coatings (Rarely needed for chemical resistance): While SiC’s inherent properties are usually sufficient, in some highly specialized cases, thin coatings might be considered for enhancing specific surface characteristics, though this is uncommon for chemical resistance which is already a core strength.
Sicarb Tech works closely with OEMs and end-users from the initial design concept through to final production and quality assurance. Their expertise in custom ceramic fabrication, combined with advanced design tools and a deep understanding of SiC processing technologies, allows them to provide valuable input on design optimization, ensuring that the final components deliver maximum performance and reliability in demanding chemical environments. Their location in Weifang City, the hub of China’s silicon carbide customizable parts manufacturing (accounting for over 80% of the nation’s total SiC output), provides them with unparalleled access to a skilled workforce and a robust supply chain, further enhancing their manufacturing capabilities.
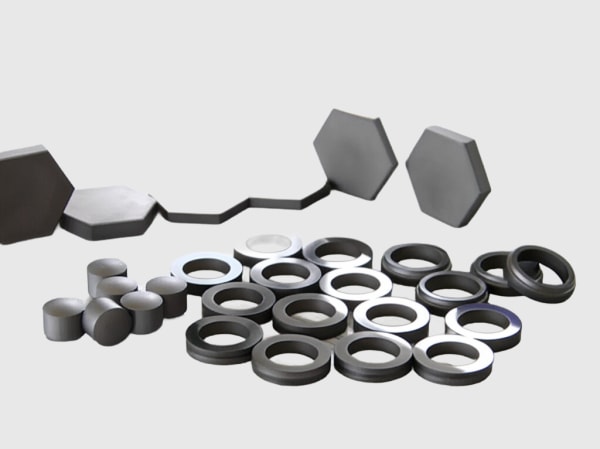
Overcoming Challenges: Navigating the Use of SiC in Chemical Processing
Despite its many advantages, silicon carbide is not without its challenges. Understanding these potential hurdles and how to mitigate them is key to successfully implementing SiC components in chemical processing equipment. An experienced partner like Sicarb Tech can provide invaluable assistance in navigating these complexities, drawing upon their extensive technological expertise and practical experience.
Common challenges and mitigation strategies include:
- Brittleness and Low Fracture Toughness:
- Challenge: Like most advanced ceramics, SiC is inherently brittle, meaning it has a low tolerance for impact loads or high tensile stresses, and can fracture without significant prior plastic deformation. This can be a concern during handling, installation, and in applications with severe mechanical shock or vibration.
- Mitigation:
- Design Optimization: Careful design to minimize stress concentrations (e.g., using fillets and radii, avoiding sharp corners), and designing for compressive rather than tensile loads where possible.
- System Design: Protecting SiC components from direct impact, and implementing vibration dampening in the broader system.
- Grade Selection: Some SiC grades (e.g., certain RBSC formulations or toughened composites, though less common for pure chemical resistance needs) may offer slightly improved toughness.
- Proper Handling and Installation Procedures: Training personnel on correct handling techniques is crucial.
- Machining Complexity and Cost:
- Challenge: The extreme hardness of SiC makes it very difficult and time-consuming to machine after sintering. This requires specialized diamond tooling and techniques, adding to the overall cost of the component, especially for complex geometries or tight tolerances.
- Mitigation:
- Near-Net-Shape Manufacturing: As discussed previously, designing for near-net-shape forming significantly reduces the need for extensive post-sintering machining. This is a core competency that expert suppliers focus on.
- Advanced Machining Techniques: Utilizing advanced grinding, lapping, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining for certain conductive SiC grades), or laser machining where appropriate and cost-effective.
- Supplier Expertise: Partnering with a supplier like Sicarb Tech, who has mastered these specialized machining processes and has access to the necessary equipment and expertise, is essential for cost-effective and precise fabrication. Their experience supporting numerous local enterprises has built a deep well of processing knowledge.
- Thermal Shock Sensitivity (Under Extreme Conditions or for Certain Grades):
- Challenge: While SiC generally has good thermal shock resistance (especially RBSC and some NBSC grades), extremely rapid temperature changes or very large thermal gradients can still lead to cracking, particularly in SSiC if not properly managed due to its higher thermal expansion relative to some other ceramics and its rigidity.
- Mitigation:
- Appropriate Grade Selection: Choosing a grade known for superior thermal shock resistance (like RBSC) if severe thermal cycling is anticipated.
- Design for Thermal Management: Designing components to minimize thermal gradients and allow for controlled heating and cooling within the system.
- Process Control: Implementing operational procedures that avoid unnecessarily rapid temperature fluctuations.
- Sealing and Joining:
- Challenge: Creating reliable, leak-tight seals between SiC components or between SiC and other materials (like metals) can be challenging due to SiC’s hardness, rigidity, and potentially different thermal expansion characteristics compared to mating parts.
- Mitigation:
- Precision Mating Surfaces: Ensuring highly flat and smooth surfaces for gasketed or direct seals.
- Appropriate Gasketing Materials: Selecting gaskets that are chemically compatible and can accommodate minor surface imperfections or differential expansion.
- Advanced Joining Techniques: Utilizing methods such as brazing (with active braze alloys), shrink fitting, or specialized adhesive bonding for permanent SiC-to-metal or SiC-to-SiC joints, considering the chemical environment.
- Initial Cost:
- Challenge: The raw materials and specialized processing required for high-quality SiC components can result in a higher upfront cost compared to some traditional metals or plastics.
- Mitigation:
- Lifecycle Cost Analysis: Focusing on the total cost of ownership. The superior longevity, reduced maintenance, and minimized downtime offered by SiC often lead to significant long-term savings that far outweigh the initial investment.
- Value Engineering: Working with the supplier to optimize designs for cost-effectiveness without compromising performance, for example, by using SiC only where its properties are critically needed (e.g., as liners or key inserts rather than solid components if feasible). Sicarb Tech is committed to offering higher-quality, cost-competitive customized SiC components from China.
By proactively addressing these challenges through informed design, material selection, and collaboration with seasoned industrial ceramics manufacturers, the full benefits of silicon carbide can be realized in demanding chemical processing applications.
Choosing Your Strategic Partner: Selecting the Right Supplier for Custom SiC Chemical Processing Components
The successful implementation of custom silicon carbide products in your chemical processing operations hinges significantly on the capabilities and expertise of your chosen supplier. This is not merely a transactional purchase; it’s a partnership that can impact your operational efficiency, product quality, and bottom line for years to come. For technical procurement professionals and engineers seeking reliable, high-performance advanced ceramics solutions, a rigorous supplier evaluation process is essential.
Here are key criteria to consider when selecting a supplier for custom SiC components for chemical applications:
- Deep Material and Application Expertise:
- The supplier should possess a profound understanding of the different SiC grades (RBSC, SSiC, NBSC, etc.) and their specific performance characteristics in various chemical environments, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress conditions.
- Look for evidence of their ability to guide you in selecting the optimal material based on your detailed process parameters. Sicarb Tech, backed by the scientific and technological prowess of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and its role within the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, embodies this deep expertise. Having introduced and implemented SiC production technology since 2015, they have witnessed and contributed to the industry’s development in Weifang, the hub of China’s SiC customizable parts manufacturing.
- Proven Customization and Manufacturing Capabilities:
- Assess their ability to manufacture complex geometries to tight tolerances. This includes their range of forming techniques (pressing, slip casting, extrusion, injection molding), sintering capabilities, and precision machining (grinding, lapping, polishing).
- Inquire about their design support, including CAD/CAM capabilities and experience in design for manufacturability (DfM) for ceramics. Sicarb Tech boasts a domestic top-tier professional team specializing in customized SiC production, with an integrated process from materials to products, encompassing design, measurement, and evaluation technologies.
- Robust Quality Management Systems and Certifications:
- Reliability in chemical processing is paramount. The supplier must have stringent quality control procedures at every stage, from raw material inspection to final product verification.
- Ask about relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and their quality assurance protocols. Sicarb Tech emphasizes more reliable quality and supply assurance within China.
- Manufacturing Capacity, Lead Times, and Supply Chain Reliability:
- Evaluate their capacity to handle your required volumes, from prototypes to large-scale production.
- Discuss typical lead times for custom orders and their strategies for ensuring on-time delivery. The concentration of over 40 SiC enterprises in Weifang, accounting for over 80% of China’s SiC output, provides a robust local supply chain that Sicarb Tech) is deeply integrated with.
- Track Record, Case Studies, and Industry References:
- A reputable supplier should be able to provide evidence of their success in supplying SiC components for similar chemical processing applications. Request case studies or references from other clients in your industry. The fact that 10+ local enterprises have benefited from Sicarb Tech’s technologies speaks to their established track record.
- Technical Support and Collaboration:
- The ideal supplier acts as a collaborative partner, offering ongoing technical support, troubleshooting assistance, and willingness to co-develop solutions for unique challenges.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Overall Value:
- While price is a factor, it should be weighed against the quality, reliability, and service offered. Aim for the best overall value, considering the lifecycle cost benefits of high-quality SiC components. Sicarb Tech is committed to offering higher-quality, cost-competitive customized SiC components in China.
Why Sicarb Tech Stands Out:
Sicarb Tech is uniquely positioned to be your strategic partner for custom SiC needs. Situated in Weifang City, the epicenter of China’s silicon carbide industry, they are not just a manufacturer but a technology enabler. Their association with the Chinese Academy of Sciences National Technology Transfer Center provides them access to cutting-edge research and a vast talent pool. They have been instrumental in advancing SiC production technology locally since 2015, fostering large-scale production and process improvements.
Their strengths include: * Unparalleled Expertise: Leveraging the scientific might of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. * Comprehensive Customization: Offering an integrated process from materials to finished products, covering design, process, material, measurement, and evaluation technologies. * Quality and Reliability: A commitment to providing high-quality, cost-competitive components, backed by a top-tier professional team. * Strategic Location: Based in Weifang, the heart of China’s SiC industry, ensuring a robust supply chain and access to specialized skills. * Technology Transfer Capabilities: Beyond supplying components, Sicarb Tech can assist clients in establishing their own specialized SiC production plants through turnkey project services, including factory design, equipment procurement, installation, commissioning, and trial production. This unique offering demonstrates their deep technological mastery and commitment to industry development.
Choosing a supplier like Sicarb Tech means partnering with an organization that understands the nuances of silicon carbide for chemical processing and is dedicated to providing solutions that enhance your operational performance and competitive edge.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about SiC in Chemical Processing
Navigating the selection and implementation of advanced materials like silicon carbide often brings up specific questions from engineers, technical buyers, and plant managers. Here are some common queries with practical answers:
- Q1: How does Silicon Carbide (SiC) compare to other corrosion-resistant materials like Hastelloy, Titanium, or high-performance polymers (e.g., PTFE, PEEK) in chemical applications?
- A1: SiC offers a unique combination of properties that often surpass other materials in specific contexts:
- Vs. Metals (Hastelloy, Titanium): SiC generally exhibits superior resistance to a wider range of corrosive chemicals, especially strong acids and mixed-acid environments, and at higher temperatures. Metals can suffer from galvanic corrosion or specific ion attacks (e.g., chloride stress corrosion cracking) where SiC remains inert. SiC also has significantly higher abrasion and wear resistance than even hardened alloys. However, metals offer better ductility and fracture toughness.
- Vs. Polymers (PTFE, PEEK): While polymers offer excellent chemical resistance to many substances and are easier to fabricate, they have significant limitations in terms of temperature resistance, mechanical strength, creep resistance, and abrasion resistance compared to SiC. SiC can operate at much higher temperatures and pressures and withstand abrasive slurries far more effectively.
- A simplified comparison is provided below:
- A1: SiC offers a unique combination of properties that often surpass other materials in specific contexts:
- Q2: What is the typical lead time for custom SiC components for chemical processing?
- A2: Lead times can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Complexity of the Part: More intricate designs require more complex tooling and longer manufacturing times.
- Size of the Component: Larger parts may have longer processing cycles.
- SiC Grade: Some grades might have longer sintering or infiltration cycles.
- Quantity Ordered: Prototypes or small batches might have shorter lead times than large production runs, though tooling setup can affect small orders.
- Tolerance and Finish Requirements: Tighter tolerances and highly polished finishes require more extensive post-processing.
- Supplier Capacity and Backlog: Current workload at the manufacturing facility.
- Generally, lead times can range from a few weeks for simpler, smaller parts to several months for highly complex, large, or high-volume orders. It’s crucial to discuss specific lead time requirements with your supplier early in the project. Sicarb Tech strives for efficient turnarounds by leveraging its integrated processes and strong local supply chain in Weifang.
- A2: Lead times can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Q3: Can SiC components be repaired if damaged in a chemical plant?
- A3: Generally, repairing damaged SiC components is very difficult and often not economically feasible. Due to its extreme hardness and brittleness, attempting to weld or patch SiC often results in further damage or a repair that lacks the integrity of the original part. Minor surface chips or wear might sometimes be re-ground or lapped if sufficient material exists and the damage doesn’t compromise structural integrity, but this is rare. In most cases, replacement of the damaged component is the standard approach. This underscores the importance of proper design, material selection, and careful handling/installation to maximize service life and prevent premature failure.
- Q4: What information do I need to provide to a supplier like Sicarb Tech to get an accurate quote for custom SiC parts for my chemical process?
- A4: To receive a timely and accurate quotation, provide as much detailed information as possible, including:
- Detailed Engineering Drawings: With all dimensions, tolerances, surface finish specifications, and critical features clearly indicated (CAD files like STEP or IGES are often preferred).
- Operating Conditions:
- Specific chemicals involved (names, concentrations, pH).
- Operating temperature range (minimum, maximum, normal, cycling).
- Operating pressure range.
- Flow rates and velocities.
- Presence and nature of any abrasive particles (size, hardness, concentration).
- SiC Grade Preference (if known): Or allow the supplier to recommend based on application details.
- Quantity Required: For prototypes, initial batches, and annual usage estimates.
- Application Description: How and where the part will be used.
- Any Special Testing or Certification Requirements.
- A4: To receive a timely and accurate quotation, provide as much detailed information as possible, including:
- Q5: Beyond supplying custom components, can Sicarb Tech assist with establishing SiC production capabilities for specialized chemical application parts in our own country?
- A5: Yes, absolutely. This is a unique strength of Sicarb Tech. Leveraging their deep technological expertise and their platform within the Chinese Academy of Sciences National Technology Transfer Center, they offer comprehensive technology transfer services. This includes providing a full-range of “turnkey project” services for clients wishing to build their own professional silicon carbide products manufacturing plant. These services encompass factory design, procurement of specialized equipment, installation and commissioning, and trial production support. This enables clients to establish their own professional SiC manufacturing capabilities with a more effective investment, reliable technology transformation, and a guaranteed input-output ratio, which is particularly beneficial for OEMs or large-scale users needing a dedicated, localized supply of critical SiC parts for chemical processing or other demanding industries.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Custom Silicon Carbide in Demanding Industrial Environments
In the relentless world of chemical processing, where equipment is constantly under siege from corrosive substances, extreme temperatures, and abrasive forces, the choice of materials is paramount. Custom silicon carbide has unequivocally proven its mettle, emerging as a critical enabler of reliability, efficiency, and safety. Its exceptional resistance to chemical attack, thermal shock, and wear, coupled with high strength and hardness, translates into significantly extended component life, reduced plant downtime, and lower lifecycle costs.
The journey to leveraging the full potential of SiC lies in customization and collaboration. By tailoring the SiC grade, design, and manufacturing process to the specific demands of each application, engineers can unlock performance levels that generic materials simply cannot match. Partnering with a knowledgeable and capable supplier, such as Sicarb Tech, is instrumental in this process. With their deep expertise rooted in the scientific strength of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, their strategic location in Weifang – the heart of China’s SiC industry – and their comprehensive capabilities in custom fabrication and even technology transfer, Sicarb Tech offers more than just components; they deliver robust, engineered solutions.
For distributors, OEMs, technical procurement professionals, and engineers striving to optimize their chemical processing operations, investing in custom silicon carbide products is an investment in long-term performance, reliability, and a stronger competitive position in the advanced ceramics industry. The unyielding guardianship of SiC ensures that your processes can run smoother, longer, and more efficiently, even in the face of the industry’s most formidable challenges.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




