Silicon Carbide MOSFET Gate Driver Circuits with dv/dt Control, Short-Circuit Protection, and DESAT Sensing

Share
Product Overview and 2025 Market Relevance
Silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET gate driver circuits are the control backbone of high-efficiency, high-density power stages. They dictate switching behavior, manage dv/dt and di/dt, and provide critical protection features such as short-circuit shut-down and DESAT sensing. For Pakistan’s textile, cement, and steel sectors—where electrical rooms face 45–50°C ambients and airborne dust—robust gate drivers are essential to achieve ≥98.5% inverter efficiency, up to 2× power density, and long operational life in 11–33 kV distribution-level photovoltaic interconnections and industrial drives.
In 2025, market leaders are aligning gate driver design with SiC device physics: fast Miller plateau transitions, narrow safe operating areas during short-circuit events, and susceptibility to EMI from high dv/dt edges. Application-optimized drivers combine high CMTI (>100 V/ns), precise turn-on/off gate resistors, two-level turn-off (TLO), negative gate bias for immunity, and low-latency DESAT detection. Coupled with isolated power, reinforced digital isolation, and PCB layout rules (Kelvin source, low-inductance loops), these drivers reduce losses, mitigate EMI, and protect modules—even under dust, heat, and grid disturbances common in Pakistan’s industrial environments.
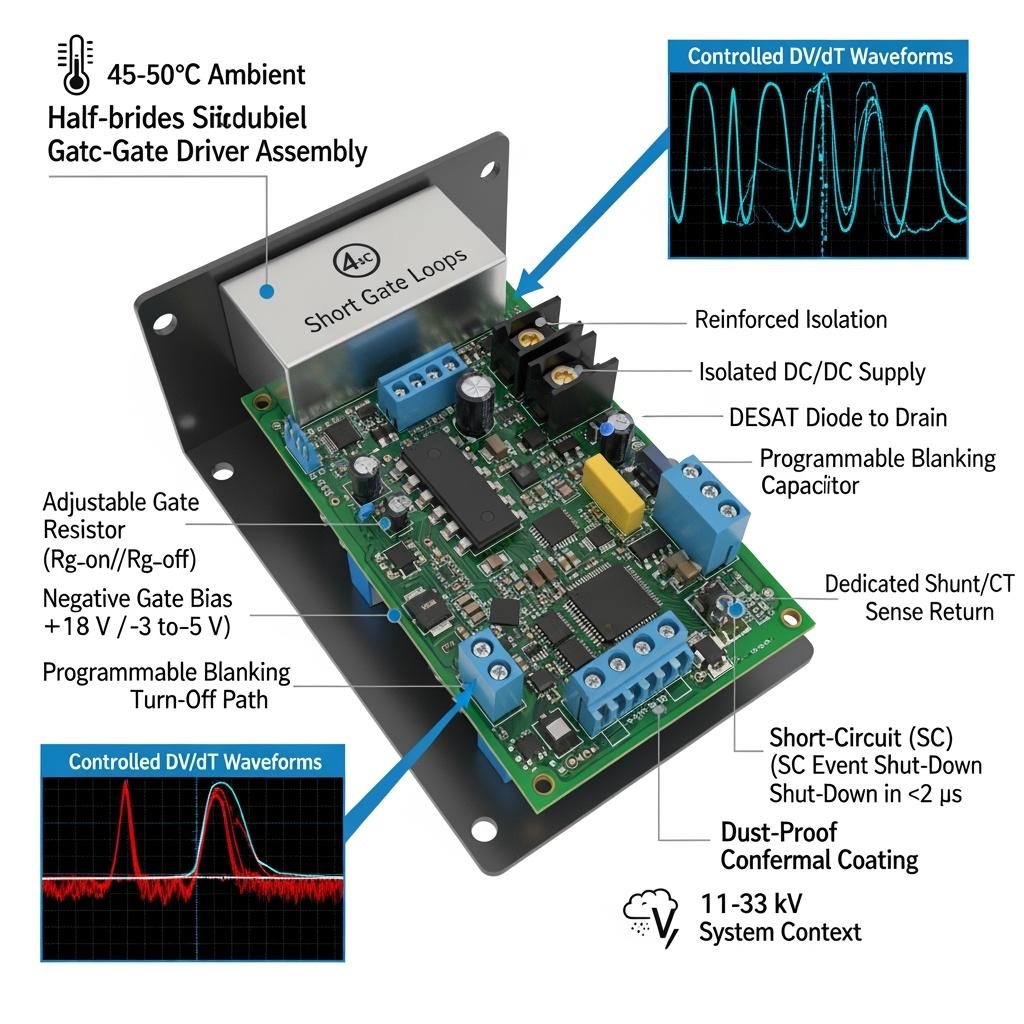
Technical Specifications and Advanced Features
- Drive and isolation
- Gate voltage: +15 to +20 V turn-on; -3 to -5 V turn-off (configurable)
- Peak source/sink current: 6–30 A classes to drive large SiC modules
- Isolation rating: Reinforced insulation for system MV compliance; CMTI ≥ 100 V/ns
- Isolated DC/DC: Low common-mode capacitance, tight regulation, undervoltage lockout (UVLO)
- Switching control
- dv/dt management: Independent Rg_on/Rg_off, optional split-gate drive, and active Miller clamp
- Two-level turn-off (TLO): Soft turn-off path to limit VDS overshoot during fault events
- Slew-rate shaping: Gate current shaping networks to balance loss and EMI
- Protection and diagnostics
- DESAT sensing: Fast short-circuit detection with programmable blanking time and soft-shutdown; <2 µs reaction typical
- Overtemperature input, overcurrent via shunt or Rogowski/CT, and fault latching with fault bus signaling
- Gate monitoring: Open-wire detection, gate-source short detection, and UVLO with deterministic fault handling
- Communications and control
- Interfaces: PWM with deadtime enforcement; optional SPI/UART for telemetry (faults, temperature, event counts)
- Redundant disable lines for safety; watchdog/reset integration
- Environmental and reliability
- Conformal coating options, corrosion-resistant finishes, and extended temperature operation
- Mechanical: Low-inductance gate loop footprints, Kelvin source connectivity, and robust connectors for field service
Descriptive Comparison: SiC-Optimized Gate Drivers vs Conventional IGBT/Silicon Drivers
| Criterion | SiC-optimized gate driver with dv/dt control and DESAT | Conventional IGBT/silicon gate driver |
|---|---|---|
| Switching frequency support | 50–150 kHz with precise dv/dt shaping | 5–20 kHz typical; limited dv/dt control |
| CMTI and EMI robustness | ≥100 V/ns with Miller clamp and negative bias | Lower CMTI; higher susceptibility to false turn-on |
| Short-circuit protection | DESAT with <2 µs reaction and soft shut-down | Slower detection; higher stress during faults |
| Efficiency impact | Lower switching loss, stable operation at high ambient | Higher losses; more derating at temperature |
| Integration with SiC modules | Kelvin source, split gate resistors, fast protection | Often lacks SiC-specific layout and timing |
Key Advantages and Proven Benefits with Expert Quote
- Efficiency and density: dv/dt control and high CMTI enable higher switching frequencies (50–150 kHz), cutting passive size and supporting ≥98.5% efficiency with compact filters and cooling.
- Robust protection: DESAT with TLO prevents catastrophic failures under short-circuit or shoot-through events, reducing downtime and warranty risk.
- EMI-resilient operation: Negative gate bias and Miller clamp mitigate false turn-on, maintaining stability in dusty, hot electrical rooms with long cable harnesses.
- Faster time-to-market: Pre-validated layouts, parameter libraries, and diagnostic telemetry reduce integration effort for 11–33 kV PV and industrial drives.
Expert perspective:
“Gate driver design is pivotal in realizing the advantages of wide bandgap devices; high CMTI isolation, controlled dv/dt, and fast short-circuit protection are indispensable for reliable SiC power stages.” — IEEE Power Electronics Society application guidance (ieee.org)
Real-World Applications and Measurable Success Stories
- Distribution-level PV inverters (southern Pakistan): SiC drivers with DESAT and TLO cut fault-related module damage, while dv/dt shaping yielded THD margin and ≥98.5% efficiency. Systems realized ~40% cooling volume reduction due to stable junction temperatures.
- Textile mill VFDs: Negative bias and split gate resistors eliminated false turn-on during fast transients, reducing nuisance trips and improving loom uptime in 45–50°C ambient conditions.
- Cement and steel drives: Short-circuit ruggedness improved through sub-2 µs DESAT action, reducing IGBT-era protection delays and associated collateral damage. Maintenance calls fell measurably over summer peak loads.
Selection and Maintenance Considerations
- Device pairing
- Match driver current and voltage swing to module gate charge and desired switching speed; ensure Kelvin source availability.
- Validate negative bias level to balance immunity and oxide stress limits.
- Protection tuning
- Set DESAT threshold and blanking time per module characteristics and expected stray inductance.
- Implement TLO resistor sizing to limit VDS overshoot without prolonging energy dissipation.
- PCB/layout
- Minimize loop inductance; segregate power and logic grounds; use dedicated return for DESAT and sense lines.
- Place DC/DC and isolator away from high di/dt nodes; enforce creepage/clearance appropriate for MV systems.
- Environmental hardening
- Apply conformal coating for dust; specify high-temperature components; verify operation at 45–50°C ambient.
- Verification
- Conduct double-pulse tests to tune dv/dt; short-circuit tests to validate TSC reaction; EMC pre-compliance for conducted/radiated emissions.
Industry Success Factors and Customer Testimonials
- Co-design with module packaging and LCL filter teams aligns dv/dt targets with EMI and THD goals, cutting redesign loops.
- Early mission-profile validation reduces over-engineering and cost while maintaining reliability.
Customer feedback:
“Integrating fast DESAT and two-level turn-off into our SiC half-bridges eliminated field failures from rare short-circuit events. dv/dt tuning improved EMI headroom without sacrificing efficiency.” — Lead power engineer, C&I PV integrator in Sindh
Future Innovations and Market Trends
- Digital gate drivers with adaptive dv/dt control based on real-time current and temperature sensing
- Integrated condition monitoring (SOH metrics) for gate charge and threshold drift tracking
- Higher CMTI isolation technologies and lower common-mode capacitance for multi-MW MV systems
- Reference designs tailored for Pakistan’s MV PV pipeline (>5 GW) with local manufacturing support
Common Questions and Expert Answers
- Why use negative gate bias with SiC MOSFETs?
To prevent false turn-on from Miller coupling at high dv/dt. Typical values are -3 to -5 V, selected per device limits and EMI targets. - How fast should DESAT protection be?
Target total reaction times under ~2 µs from fault onset to current interruption, with soft-shutdown to limit overvoltage stress. - What is two-level turn-off and why use it?
TLO introduces a controlled, softer turn-off during faults to reduce VDS overshoot and stray inductive ringing, protecting the module and gate oxide. - How do I tune dv/dt without losing efficiency?
Use split Rg_on/Rg_off, layout to reduce inductance, and optionally gate current shaping; iterate via double-pulse testing to balance EMI and switching loss. - Can these drivers operate reliably at 45–50°C with dust?
Yes. With conformal coating, derated components, and proper airflow or sealing, drivers maintain stability and protection performance.
Why This Solution Works for Your Operations
These SiC-focused gate driver circuits deliver the control precision and protection speed required for Pakistan’s MV interconnections and heavy-duty industrial drives. They enable higher switching frequencies for compact LCL filters, stabilize operation in hot, dusty environments, and guard against damaging faults—unlocking ≥98.5% efficiency, up to 2× power density, and long service life across textile, cement, and steel applications.
Connect with Specialists for Custom Solutions
Accelerate your SiC power stage with expert driver design and validation:
- 10+ years of SiC manufacturing expertise and application engineering
- Backing from a leading research ecosystem driving innovation in isolation, protection, and EMI control
- Custom product development across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC components influencing thermal and mechanical reliability
- Technology transfer and factory establishment services for local driver assembly and testing
- Turnkey solutions from devices and drivers to filters, cooling, and compliance
- Proven results with 19+ enterprises delivering efficiency, reliability, and faster time-to-market
Request a free consultation and a tailored gate driver specification package:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Book your 2025–2026 development slots now to secure co-design, EMC validation, and field pilots aligned with MV PV and industrial drive rollouts.
Article Metadata
Last updated: 2025-09-10
Next scheduled update: 2026-01-15

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




