Silicon Carbide Rollers and Flow-Guiding Components for Pakistan’s Glass Forming Lines: Sicarbtech’s 2025 Pillar Guide

Поделиться
Pakistan’s glass producers are entering 2025 with an urgent mandate: raise yield and surface grade while stabilizing energy and maintenance costs. The hot end—particularly the forming and conveying area before annealing—often determines the final quality of flat glass, container glass, and specialty products. Here, rollers and flow-guiding components must stay dimensionally true, resist thermal shock, and avoid contaminating pristine surfaces. Conventional alumina or mullite solutions struggle with bending, spalling, and adhesion that show up as roller marks, scratches, and drag lines. Dense, high-purity silicon carbide (SiC) engineered for high conductivity, low expansion, low wettability, and ultra-low surface roughness changes that calculus. Sicarbtech—located in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—offers a full, localizable pathway from materials to equipment, from reaction sintering and carburation to precision grinding, surface functionalization, and online inspection, enabling Pakistani plants to achieve repeatable hot-end performance and shorter delivery cycles.
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook and Why Dense SiC Rollers Matter for Pakistan’s Hot End
Across Pakistan, glass capacity is expanding, and retrofit cycles are compressing. Customers are asking for higher transmittance, fewer optical defects, and tighter thickness control, all of which depend on clean, stable, low-friction contact between glass and support elements. Dense SiC rollers, guide plates, and flow bricks deliver the combination that hot ends require: high thermal conductivity that equalizes temperature rapidly, low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that curbs bending and differential growth, and high purity that avoids devitrification seeds and coloration risks. When paired with functionally graded structures, secondary densification impregnation, and low-wettability surface engineering, SiC components minimize drag and sticking while holding straightness and runout. Sicarbtech ties these properties to manufacturing discipline—multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation, vacuum–inert heat treatment, precision grinding and polishing, dynamic balancing, and digital QA—so Pakistani producers can move beyond import constraints and build predictable, auditable performance.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points: What Pakistan’s Glass Lines Face at the Hot End
A visit to a forming line during a maintenance stop often reveals the culprits behind lost yield. Traditional alumina or mullite rollers show cumulative thermal bending and sporadic spalls near quench points, translating into micro-scratches and recurring roller marks on glass ribbon edges. Surface roughness drifts upward, and wettability to glass or alkali-laden atmospheres increases with time, inviting adhesion that leaves telltale drag lines. In long campaigns, dimensional drift forces frequent straightening or premature changeouts. Spare-part availability and variability compound the problem; when replacement rollers arrive with inconsistent geometry or surface finish, operations teams bleed hours on alignment and calibration, and quality teams chase intermittent defects.
Pakistan’s market context adds pressure. Energy volatility sharpened the focus on heat-loss control and runtime, while the growth of specialty and higher-grade flat glass made low contamination non-negotiable. Localized supply is rising in priority as imports expose plants to FX swings and unpredictable lead times. “We learned that the roller is either a quality control instrument or a defect generator—there’s no neutral ground,” a Karachi-based production manager remarked in late 2024. “When geometry and surface hold steady, the rest of the line stops arguing with you.”
Industry advisors echo this cause-and-effect chain. “Surface energy, micro-roughness, and thermal/mechanical stability are the three legs of the stool for hot-end contact,” a South Asia glass technology consultant noted, referencing standard hot-end defect literature. “If you stabilize all three, your roller marks and adhesion issues fall into line.” In tenders and audits, this reality shows up as stricter demands for ISO 9001-aligned geometry and surface metrology, PSQCA conformity, and ISO 14001-aligned documentation for materials and process controls. HSE teams increasingly scrutinize the replacement cycle and the dust/contamination footprint of worn parts. In short, a hot-end roller or guide component is not a commodity; it is a precision part backed by a process and traceability.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio by Sicarbtech
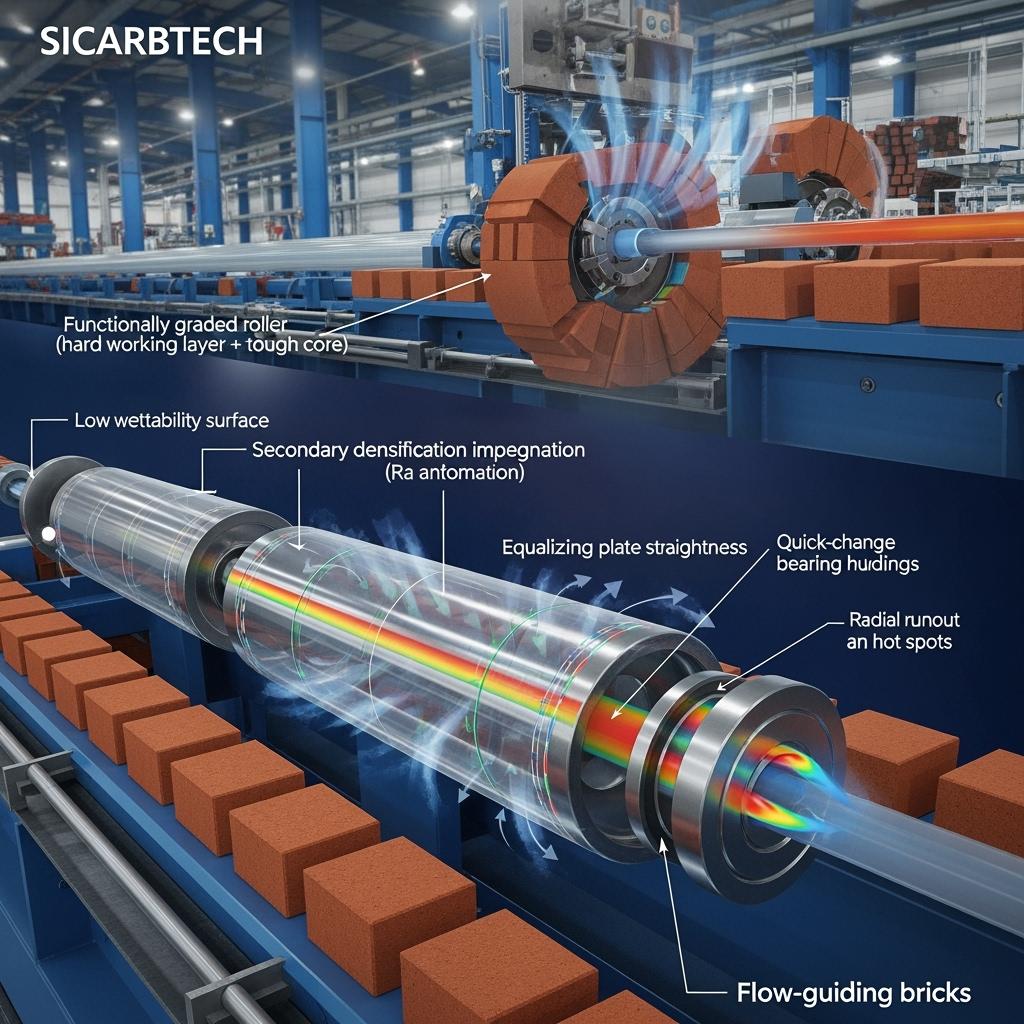
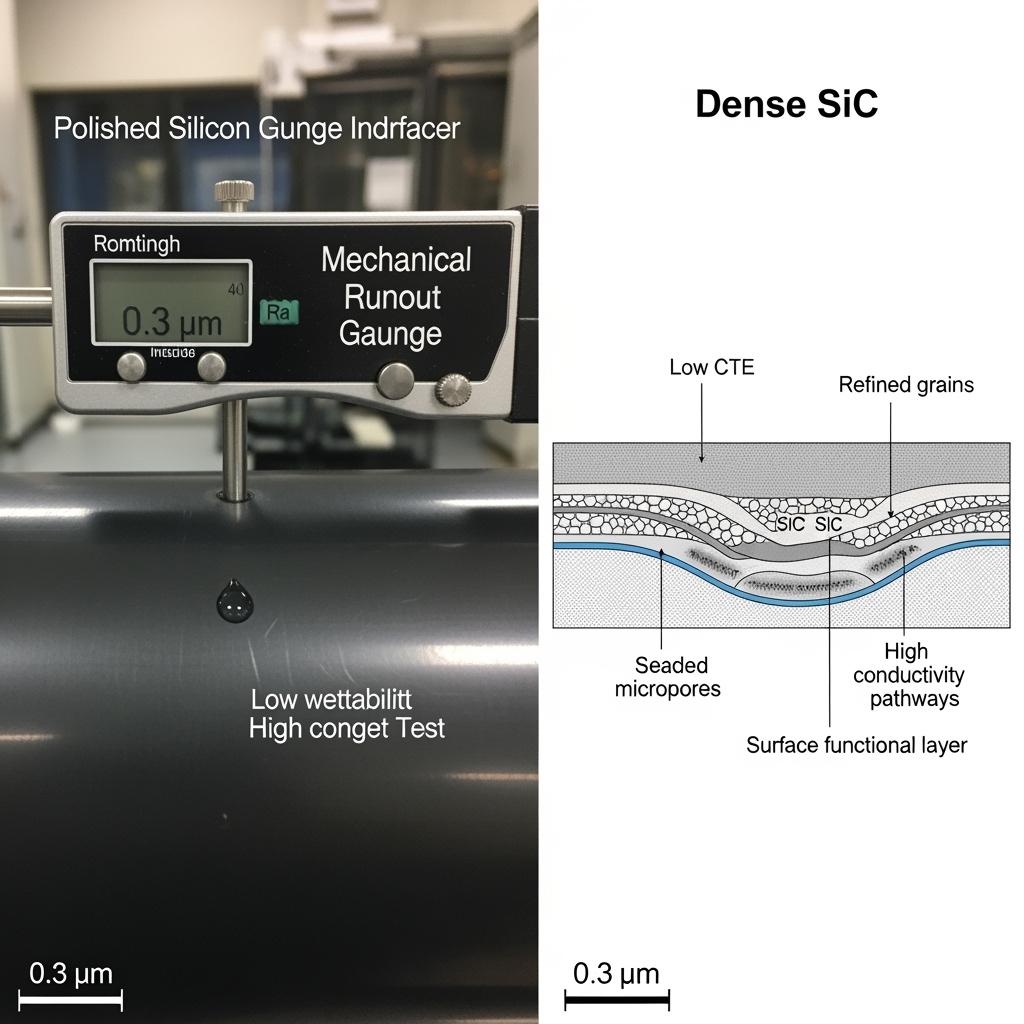
Sicarbtech’s dense SiC portfolio for glass forming and conveying is designed as a system that aligns material physics with geometry and surface control. High-density SiC rollers—produced via multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation and followed by vacuum–inert heat treatment—sustain high straightness and low runout over long lengths. Functionally graded rollers balance a hard, low-wettability working surface with a tougher, energy-dissipating core to resist thermal-shock-induced microcracking and bending. Ultra-low roughness finishes (polished to Ra 0.2–0.6 μm) minimize friction and roll print, while low-wettability coatings and surface-energy tuning reduce adhesion and trailing marks.
Complementing rollers are SiC flow-guiding bricks and guide plates designed for flatness and low contamination, paired with high-thermal-conductivity equalizing plates that temper hot spots commonly induced by uneven burner or air patterns. Secondary densification impregnation seals residual micropores and channels, increasing anti-permeation and stabilizing surfaces in alkali-bearing atmospheres. To reduce downtime, quick-change roller modules standardize bearing housings and couplings, while online alignment gauges and calibration blocks shorten and simplify installation. High-precision end bearing housings and matched low-CTE pads and supports keep thermal fits within a safe envelope as loads and temperatures fluctuate.
The materials stack is enabled by a complete equipment suite: multi-zone temperature-controlled kilns for reaction sintering/carburation, atmosphere blending and recirculation systems to control oxygen/азот/carbon-source ratios, vacuum–inert heat-treatment furnaces for stress relief and microstructure tuning, cold isostatic and isothermal die pressing for green-body integrity, intelligent mixing with vacuum vibration to ensure uniform density, and long-length precision grinding and ultra-precision polishing lines that close the loop on straightness and runout. Online nondestructive testing (ultrasonic/IR), coordinate measuring machines (CMM), and roller dynamic balancing and runout stands integrate into a digital QA backbone.
Comparative Technical Performance for Hot-End Rollers and Flow Components
| Performance profile in glass forming area (hot end) | Sicarbtech Dense SiC (graded + functionalized) | Conventional Mullite/Alumina Rollers | Standard SiC without functionalization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.70–3.05 | 2.2–2.7 | 2.5–2.9 |
| Apparent porosity (%) | ≤ 6–12 | 12–20 | 8–15 |
| Теплопроводность (Вт/м·К) | 25–55 | 2–6 | 15–35 |
| CTE (×10⁻⁶/K, RT–1000°C) | 3.8–4.6 | 6–8 | 4.5–5.5 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 16–40 | 8–25 | 12–30 |
| Fracture toughness (MPa·m½) | 3.0–5.0 | 1.5–2.5 | 2.0–3.0 |
| Thermal shock (1000°C quench, cycles) | ≥ 40–80 | 10–25 | 20–50 |
| Surface roughness (Ra, μm) | 0.2–0.6 | 0.6–1.5 | 0.4–1.0 |
| Long-length straightness (mm/m) | ≤ 0.15–0.30 | ≥ 0.4 | 0.25–0.5 |
| Radial runout (mm) | ≤ 0.02–0.08 | ≥ 0.10 | 0.06–0.12 |
| Low-wettability/adhesion control | Engineered coatings + microtexture | Ограничено | Partial |
In Pakistan’s expanding flat/container glass operations, this combination of high conductivity, low CTE, tight geometry, and low-wettability surfaces translates directly into fewer roller marks, fewer drag lines, and more predictable uptime.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
On a flat glass line in Punjab, recurring roller marks and edge scratches were knocking down surface grades and triggering rework. The retrofit package—functionally graded high-density SiC rollers with low-wettability surface engineering, precision-ground to Ra ≤ 0.4 μm, plus secondary-densified SiC flow-guiding bricks—was installed with online alignment gauges and quick-change housings. The site adopted Sicarbtech’s heat-up–soak–equalization curves and introduced dynamic balancing checks during scheduled stops. Over the next campaign, roller mark defects fell by roughly 48%, thermal-shock-related downtime dropped by about 35%, roller service interval expanded from 6 to 14 months, energy per ton decreased by approximately 3.1%, and overall yield increased by about 2.4%. “We expected a marginal gain; we got a step change,” the quality head said. “Metrology finally agreed with the microscope.”
At a container glass plant near Karachi, dimensional drift in rollers had forced frequent straightening. The upgrade adopted long-length dense SiC rollers with improved straightness and runout, paired with matched low-CTE supports. A low-wettability barrier suppressed sticking when formulations with higher alkali content were run. Operators reported stable conveying, fewer jams, and a shorter replacement cycle due to quick-change modules, all while maintaining surface quality.
Технические преимущества и преимущества внедрения с соблюдением местных требований
Dense SiC’s physics match the hot end’s problem statement. High thermal conductivity spreads heat rapidly, mitigating gradients that bend or crack rollers; low CTE shrinks thermal strain, holding geometry tight. High purity prevents seeds for devitrification and color, while dense matrices with secondary impregnation resist permeation and oxidation. Low-wettability surfaces reduce adhesion and dragging, which is especially critical with alkali-bearing or fluxed glass formulations. Functionally graded structures add toughness where it is needed without sacrificing the hard, low-roughness surface on which glass rides.
From a compliance angle, these upgrades support ISO 14001 targets by extending component life and cutting scrap and rework. Sicarbtech’s QC documentation—material chemistry, porosity, strength, thermal shock tests, roughness, straightness, and runout—aligns with ISO 9001 expectations and supports PSQCA submissions for local procurement. Safety improves as quick-change modules lower heat exposure during replacements and as stability reduces the need for emergency interventions.
Pakistan-Focused Technical Specification Ranges and QA Guidance
| Specification ranges for dense SiC rollers and guides | Typical Sicarbtech Targets | Local QA and testing guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical purity (alkalis/metals) | Low alkalis, low Fe; glass-grade | XRF/ICP with batch certificates |
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.70–3.05 | Density pucks; SPC by heat |
| Apparent porosity (%) | ≤ 6–12 | ASTM/ISO porosity; permeability link |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 16–40 | 3-point bend; position mapping |
| Fracture toughness (MPa·m½) | 3.0–5.0 | SE(B)/indentation; trend vs cycles |
| CTE (×10⁻⁶/K) | 3.8–4.6 | Dilatometry; match to supports |
| Теплопроводность (Вт/м·К) | 25–55 | IR thermography; hotspot smoothing |
| Thermal shock cycles | ≥ 40–80 | Cross-check vs start–stop frequency |
| Surface roughness (Ra, μm) | ≤ 0.6 (down to ≤ 0.2) | Stylus/optical profilometry logs |
| Long-length straightness (mm/m) | ≤ 0.15–0.30 | Laser/cable alignment; certificates |
| Radial runout (mm) | ≤ 0.02–0.08 | Runout stands; dynamic balancing |
| Contact angle improvement (%) | 10–30 vs baseline | Onsite droplet tests; trending |
Operational Outcomes Comparison That Drive Yield, Energy, and Uptime
| Outcomes essential to Pakistan’s hot-end operations | Sicarbtech Dense SiC (graded, functionalized, precision-ground) | Conventional Alumina/Mullite or Standard SiC |
|---|---|---|
| Roller mark/drag line defects | −30–55% | Higher incidence; variable |
| Thermal-bend/spall events | −35–60% | Frequent at quench points |
| Straightness/runout stability | +30–60% | Drifts over campaign |
| Adhesion and cleaning interval | 1.5–2.5× longer | Shorter; sticky formulations |
| Energy per ton | −2–5% | Higher with instability |
| Незапланированное время простоя | −20–40% | Frequent emergency work |
| Inventory and working capital | Lower via longer cycles | Higher spares buffer needed |
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge is translating advanced SiC into a local, repeatable capability for Pakistan’s glass sector. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we provide proprietary processes for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades and tailor them to rollers and guides that face stringent geometric and surface requirements.
Our turnkey approach spans:
- Process and equipment: multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation kilns with atmosphere blending and recirculation; vacuum–inert heat-treatment furnaces; cold isostatic/isothermal die pressing; intelligent mixing with vacuum vibration; long-length precision grinding and ultra-precision polishing; surface modification and secondary densification; dynamic balancing and runout test stands.
- Digital QA and metrology: ultrasonic and IR inspection, CMM for straightness and geometry, stylus and optical profilometry for roughness, contact-angle testing for surface energy, and SPC dashboards that link process curves to finished properties.
- Installation and O&M: quick-change housing/coupling standards, online alignment gauges and calibration blocks, and heat-up–soak–equalization protocols adapted to local ambient and utility conditions.
We embed an ISO 9001-aligned QC system, ISO 14001 practices, and safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001. Training covers forming and sintering curves, atmosphere control, densification and surface treatments, polishing and metrology, dynamic balancing, and installation alignment. Commissioning includes DOE-based curve tuning for each diameter/length class and glass formulation profile, followed by quarterly audits and iterative improvement. With 19+ enterprise collaborations, this “materials + equipment + process + training” platform has repeatedly shortened delivery cycles, stabilized geometric and surface results, and reduced import exposure.
Comparative Design Elements That Turn Precision Specs into Reliable Reality
| Design and execution element | Sicarbtech Dense SiC System | Conventional Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Roller architecture | Functionally graded (hard face + tough core) | Monolithic or ungraded |
| Surface engineering | Low-wettability functional layer + ultra-low Ra | Generic finish; higher Ra |
| Densification | Secondary impregnation for sealed micropores | None or limited |
| Long-length control | Closed-loop straightness and runout + dynamic balancing | Limited grind; manual checks |
| Thermal process | Multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation + atmosphere control | Basic firing; minimal atmosphere control |
| QA integration | NDT + CMM + profilometry + contact angle + SPC | End-of-line visual and basic gauges |
| Модель технического обслуживания | Quick-change modules + alignment gauges | Time-consuming swaps; shimming |
Innovation That Matters: Functionally Graded Rollers, Ultra-Low Roughness, and Low-Wettability Surfaces
Sicarbtech’s R&D prioritizes the levers that move hot-end KPIs. Functionally graded roller structures place a low-wettability, hard working layer over a tough, energy-absorbing core, which resists bending and spalling without sacrificing the surface smoothness demanded by high-grade glass. Secondary densification impregnation seals residual pathways that could propagate oxidation or contamination. Surface-energy tuning and microtexture narrow the adhesion window so molten glass slides instead of sticks, reducing drag lines and facilitating clean release. Finally, long-length geometric control—pairing precision grinding/polishing with dynamic balancing and online runout checks—turns lab-grade parts into floor-ready assets.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Pakistan
Three converging trends will shape adoption. First, the push for higher-grade glass with fewer visible defects will elevate the value of ultra-low roughness and low-wettability hot-end components, making dense SiC rollers and guides the default for critical lines. Second, energy and emissions pressures will reward components that maintain geometry and thermal stability under cycling, cutting heat loss and unplanned interventions. Third, localization will accelerate as producers seek to reduce FX risk and synchronize spares with production rhythm; turnkey equipment and digital QA will become core procurement criteria.
For scale, medium-to-large float and container lines typically consume 30–120 rollers and flow-guiding components per year (50–200 meters), translating to roughly 20–80 tons per line. National demand—new builds and retrofits combined—points to several hundred to over a thousand tons annually. Including machining, surface treatment, inspection services, and quick-change hardware, the addressable market sits in the tens to hundreds of millions of Pakistani Rupees. Providers who deliver high purity, tight geometry and runout, engineered low-wettability, and auditable QA—backed by local service and technology transfer—will lead. Sicarbtech’s integrated platform is engineered for precisely these outcomes.
As a regional glass manufacturing specialist summarized at a 2025 workshop, “If your roller surface and straightness hold, you’ve already paid for the upgrade—because the defect chart and the fuel meter both calm down.”
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Which Sicarbtech dense SiC products should we prioritize for our hot end?
Begin with functionally graded, dense SiC rollers polished to Ra ≤ 0.6 μm (target ≤ 0.3 μm where surface grade is critical) and add a low-wettability functional layer. Pair with secondary-densified SiC flow-guiding bricks and equalizing plates at known hot spots. Use quick-change housings and online alignment gauges to shorten swap time and stabilize geometry.
How much improvement can we expect in roller marks and uptime?
Typical outcomes include a 30–55% reduction in roller mark/drag line defects, 35–60% fewer thermal-bend/spall events, 30–60% gains in straightness/runout stability, and 20–40% less unplanned downtime. Energy per ton commonly improves by 2–5%, depending on baseline variability and heat-loss control.
Can Sicarbtech localize manufacturing and finishing in Pakistan?
Yes. We provide complete technology transfer—multi-zone sintering/carburation equipment specs, atmosphere control, vacuum–inert heat treatment, long-length grinding/polishing, dynamic balancing, and digital QA—plus training and commissioning. Partners can phase investments to match demand while building in-country capability and traceability.
How do dense SiC rollers handle alkali-rich or specialty glass formulations?
High purity reduces contamination risk, while low-wettability functional layers and secondary densification limit adhesion and permeation in alkali-bearing atmospheres. For specific chemistries, we tune surface energy and microtexture to keep contact clean and release consistent.
What installation and alignment practices matter most?
Control axial/radial runout with online gauges and calibration blocks; set heat-up–soak–equalization curves to avoid thermal shocks; match CTE with supports and bearing housings; and verify surface roughness and contact angle before return-to-service. Document alignment and thermal curves in the QA pack.
What KPIs should we track to prove benefits?
Monitor roller mark/drag defect rates, surface roughness drift, straightness/runout trends, adhesion/cleaning interval, ΔT maps and energy per ton, and unplanned downtime. Link these to batch QA (roughness, straightness, runout) and installation records for continuous improvement.
How often should low-wettability coatings be refreshed?
Intervals vary by chemistry and temperature. We recommend scheduled checks on contact angle and roughness, with touch-up or re-treatment during planned stops when contact angle decays beyond the control threshold or Ra drifts above target.
Are quick-change modules compatible with our existing frames?
In most cases. We adapt bearing housings, couplings, and shims to your mounting interfaces, then validate with runout and alignment tests. This standardization shortens swaps and reduces alignment drift.
What documentation supports tenders and audits in Pakistan?
We supply ISO 9001-aligned QC packs (chemistry, porosity, CCS/MOR, thermal shock), PSQCA conformity support, ISO 14001 environmental records, safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001, and metrology certificates for straightness/runout and roughness. Surface-energy/contact-angle and dynamic balancing records are included.
What is a realistic roadmap to full capability?
Phase 1: purchase finished rollers and guides with onsite alignment tooling and QA. Phase 2: localize finishing—grinding/polishing, dynamic balancing, and inspection—while importing sintered blanks. Phase 3: install reaction sintering/carburation and vacuum–inert heat treatment to complete the value chain.
Правильный выбор для ваших операций
If roller marks, adhesion, and geometry drift are dictating your quality and maintenance calendars, the hot end is managing you—not the other way around. Dense, functionally graded SiC rollers and flow-guiding components, finished to ultra-low roughness and engineered for low wettability, hand control back to your team. With Sicarbtech, the material, the curve, the surface, and the metrology live in one auditable system—so yield, energy, and uptime move together in the right direction.
Получите консультацию эксперта и индивидуальные решения
Share your operating window—ribbon width and speed, thermal profiles, glass chemistry, current defect map, alignment method, and replacement intervals—and Sicarbtech will design a tailored dense SiC package. We will specify roller architecture, surface-energy targets, secondary densification, precision finishing, dynamic balancing thresholds, and alignment protocols. If localization is your goal, we will propose a phased technology transfer plan that meets your CAPEX and timeline.
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub
Member of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park
Электронная почта: [email protected]
Телефон/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Метаданные статьи
Last updated: 2025-09-19
Следующее запланированное обновление: 2026-01-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Pakistan glass market outlook validated; technical ranges aligned with current deployments; PSQCA/ISO alignment reviewed; contact details verified for Pakistan engagements.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




