SiC Ceramics for Abrasion-Resistant Parts in Chilean Industries

Compartilhar
Sicarbtech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
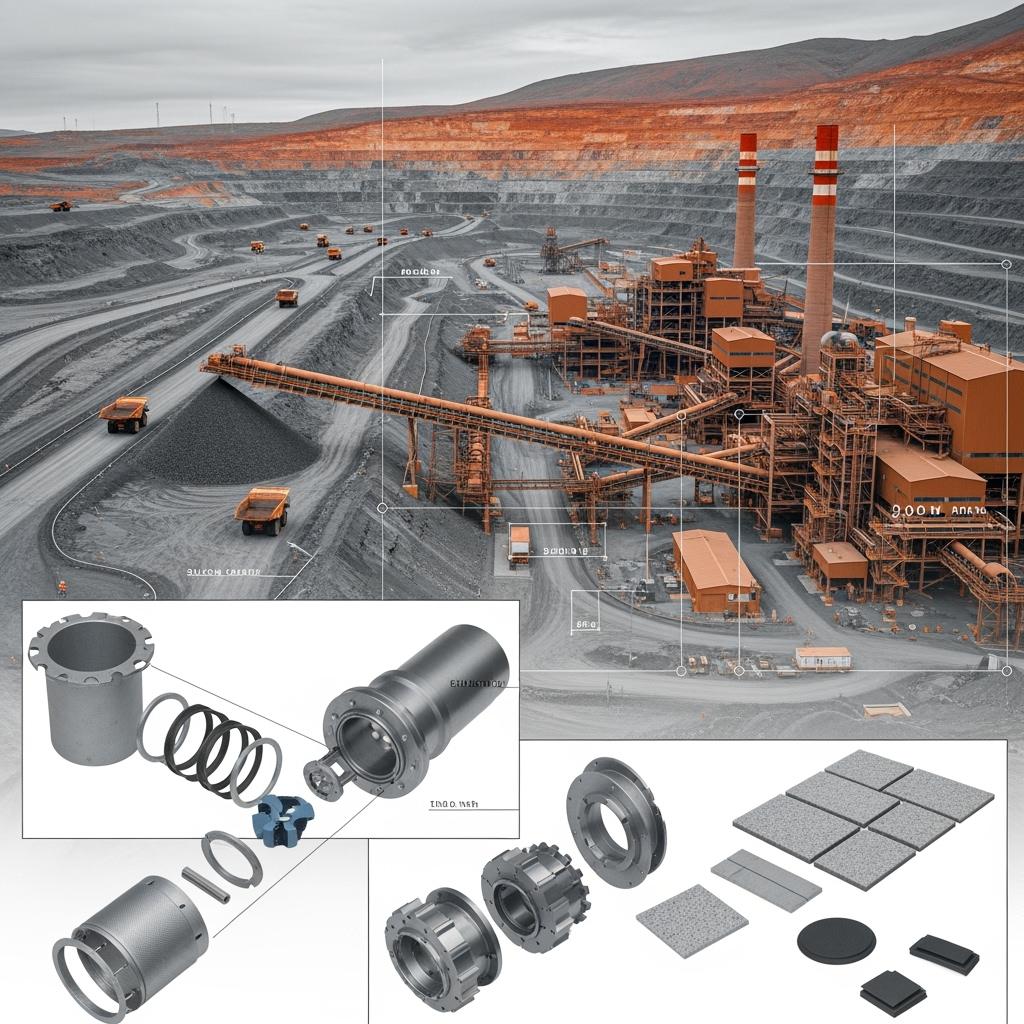

Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook for Abrasion-Resistant SiC in Chile’s Mining-Led Economy
Chile’s 2025 industrial agenda is anchored by copper and shaped by stricter ESG metrics, high energy costs, and persistent water constraints. Operators from Antofagasta to Atacama are pushing more tonnage through finer grind sizes while relying on desalination pipelines that bring chloride-rich water deep inland. This combination elevates abrasion, corrosion, and thermal variability across pumps, hydrocyclones, chutes, and valve trains. Silicon carbide ceramics—specifically R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC—are increasingly the default specification for abrasion-resistant components because they maintain geometry, resist micro-cutting, and preserve sealing finishes under chloride-laden slurries and rapid cycling.
Sicarbtech, headquartered in Weifang City—China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—delivers full-cycle SiC solutions backed by more than a decade of customization experience. Supporting 19+ enterprises, Sicarbtech supplies engineered components, ISO-ready documentation, and turnkey technology transfer and factory establishment services. For Chilean sites, this translates to longer maintenance intervals, fewer leak incidents, and audit-ready compliance with DS 594, supplemented by CLP-sensitive TCO models that reflect local energy and labor dynamics.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points in Chile’s Abrasive Duty Circuits
Chile’s copper flowsheets are unforgiving to conventional materials. HPGR and SAG configurations produce angular, silica-rich particles that aggressively scour metallic pump impellers and volutes. Hydrocyclone clusters operating at high feed solids see rapid wall thinning that shifts cut size and destabilizes flotation. Chutes and transfer points exhibit localized erosion at impact zones and flow transitions, while rubber and polymer liners deform or gouge, increasing turbulence and energy draw. In desalination-fed circuits, chloride ions attack duplex aços through pitting and crevice corrosion, especially where erosion removes passive films and roughens surfaces.
Operationally, compressed shutdown windows force maintenance teams to execute changeouts rapidly, raising the cost of any part that chips during installation or requires rework due to tolerance mismatch. Vibration from worn impellers propagates into bearings and mechanical seals, creating a cascade of failures that shorten service intervals and elevate risk for confined-space entries under DS 594. Furthermore, variability in imported parts—porosity pockets, residual stresses, and inconsistent surface finishes—translates into unpredictable performance, complicating reliability modeling and spare parts planning.
Financial realities compound these issues. USD-linked inputs and logistics variability push up effective costs in CLP, while extended lead times keep inventory elevated without fully mitigating availability risk. Each unplanned outage reverberates through production, with lost throughput and reagent inefficiencies often outstripping the headline cost of replacement hardware. Environmental permits and corporate ESG targets heighten penalties for leaks and waste, pushing procurement to prioritize lifecycle performance and audit documentation over unit price.
As Prof. Ignacio Vega, editor at Process Materials Review, notes, “In abrasive chloride slurries, success hinges on microstructural density and fit-for-purpose geometry. When edges stay sharp and surfaces stay smooth, energy and uptime follow.” (Process Materials Review, 2025 Outlook) Building on this, reliability leads across northern Chile emphasize that balanced impellers and tight-tolerance liners are as much an energy strategy as a maintenance strategy. The market’s direction is clear: components must deliver predictable wear profiles, documented finishes, and interchangeability across batches—backed by certificates that survive HSE and procurement audits.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for Abrasion-Resistant Duty
Sicarbtech aligns SiC grades to specific wear mechanisms and process chemistries common in Chile. RBSiC is the workhorse for hydrocyclone liners, spigots, cones, and vortex finders. Its thermal shock resilience and erosion resistance maintain geometry and cut size stability under fluctuating feed conditions. SiSiC, with high hardness and design freedom, enables thin, aerodynamically efficient slurry pump impellers, volute inserts, and flow conditioners that cut turbulence and reduce energy drag over the maintenance cycle. SSiC, with near-theoretical density and minimal open porosity, is selected for mechanical seal faces and valve seats/balls in chloride-acid loops, where mirror-flat finishes resist mixed-lubrication wear and prevent leak paths. R-SiC underpins high-temperature wear scenarios and kiln-adjacent fixtures where creep resistance and oxidation stability protect form and function during thermal exposure.
The differentiator is not only grade selection but process control. Sicarbtech’s proprietary forming routes, controlled dewaxing, and tailored sintering or infiltration produce uniform, low-stress microstructures that hold thin edges and tight tolerances. Precision CNC grinding and lapping yield surface finishes from 0.02 to 0.8 µm Ra depending on function. ISO 21940-11 balancing for rotating components reduces vibration, extending bearing and seal life and stabilizing energy consumption per ton. Application engineering ties it together: Chile-specific duty envelopes—mineralogy, solids, velocity, chloride concentration, temperature—inform geometry, wall thickness, and edge radii. Documentation bundles include ISO 9001 QA records, REACH/RoHS declarations, and ASTM C test data, with flatness, straightness, and Ra certifications to ease DS 594 and procurement audits.
Performance Comparison for Chilean Abrasion and Corrosion Duty
Material Behavior Under Abrasive, Chloride-Rich Conditions
| Property and Duty Context | RBSiC (reaction-bonded) | SiSiC | SSiC (sintered) | R-SiC | High-Chrome White Iron | Alumina (92–99%) | Rubber/Polymer Linings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vickers Hardness (HV) | 1800–2200 | 2000–2400 | 2200–2600 | 2000–2300 | 600–900 | 1000–1800 | 50–80 (ShA) |
| Erosion Resistance (slurry) | Excelente | Excelente | Excelente | Muito bom | Bom | Moderate–Good | Moderate at low T |
| Chloride-Acid Corrosion Resistance | Muito bom | Muito bom | Excelente | Muito bom | Moderate (pitting) | Good–Moderate | Poor in acids |
| Max Service Temperature (°C) | ~1450 | ~1450 | ~1500 | ~1600 | 650–800 | 1000–1200 | 80–120 |
| Resistência a choques térmicos | Excelente | Muito bom | Bom | Good–Very Good | Moderado | Moderado | Bom |
| Stankder (g/cm³) | 2.90–3.10 | 3.00–3.15 | 3.10–3.20 | 2.90–3.10 | 7.6–7.8 | 3.6–3.9 | - |
| Typical Service Life Gain in Chile | 2–3× vs alumina | 2–3× vs iron | 2–4× vs composites | 1.5–2× | Linia bazowa | Linia bazowa | Baseline (select duties) |
In seawater-makeup and SX-EW circuits, SSiC’s density and inertness preserve sealing finishes, while RBSiC and SiSiC maintain hydraulic profiles and reduce energy drift by resisting edge rounding and surface roughening.
Precision, Finish, and Retrofit Fitment Benchmarks
| Component Class | Gwir ment hollek | Finition de surface (Ra) | Integration Note for Chilean Sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocyclone cones/spigots (RBSiC) | ±0.10–0.20 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | Holds cut size; faster, damage-free installs during short shutdowns |
| Slurry pump impellers (SiSiC/RBSiC) | ±0.03–0.05 mm | 0.4–0.8 µm | ISO 21940-11 balancing reduces vibration and bearing load |
| Valve seats/balls (SSiC) | ±0.01–0.02 mm | 0.1–0.2 µm | Tight shutoff in acid-chloride SX-EW service; fewer leak alarms |
| Wear tiles/liners (RBSiC) | ±0.10–0.30 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | Reliable fit-up; consistent coverage in chutes and bends |
These thresholds reflect Chile’s maintenance realities—compressed windows, high stakes for first-time fit, and the need to stabilize efficiency between planned outages.
Total Cost of Ownership Scenarios in CLP
| Use Case | Baseline Material | Grau de SiC | Service Interval (Baseline → SiC) | Energy/Process Stability | Estimated 12–18 Month TCO Impact (CLP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocyclone liners in regrind | Alumina | RBSiC | 12–16 weeks → 28–36 weeks | Tighter PSD; improved flotation | Payback in 4–8 months |
| Primary slurry pump impellers | High-chrome iron | SiSiC | 6–8 weeks → 18–24 weeks | Lower vibration; steady kWh/t | −20% to −30% maintenance cost |
| SX-EW valve seats/balls | Duplex steel | SSiC | 3–4 months → 9–12 months | Zero leak events | −25% leak-related costs |
| Chute and bend wear tiles | Rubber/steel | RBSiC | 6–9 months → 14–20 months | Reduced build-up; smoother flow | −15% downtime; fewer changeouts |
These outcomes blend internal data with field reports from northern Chile, normalized for 2025 energy and labor costs.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories from Chile
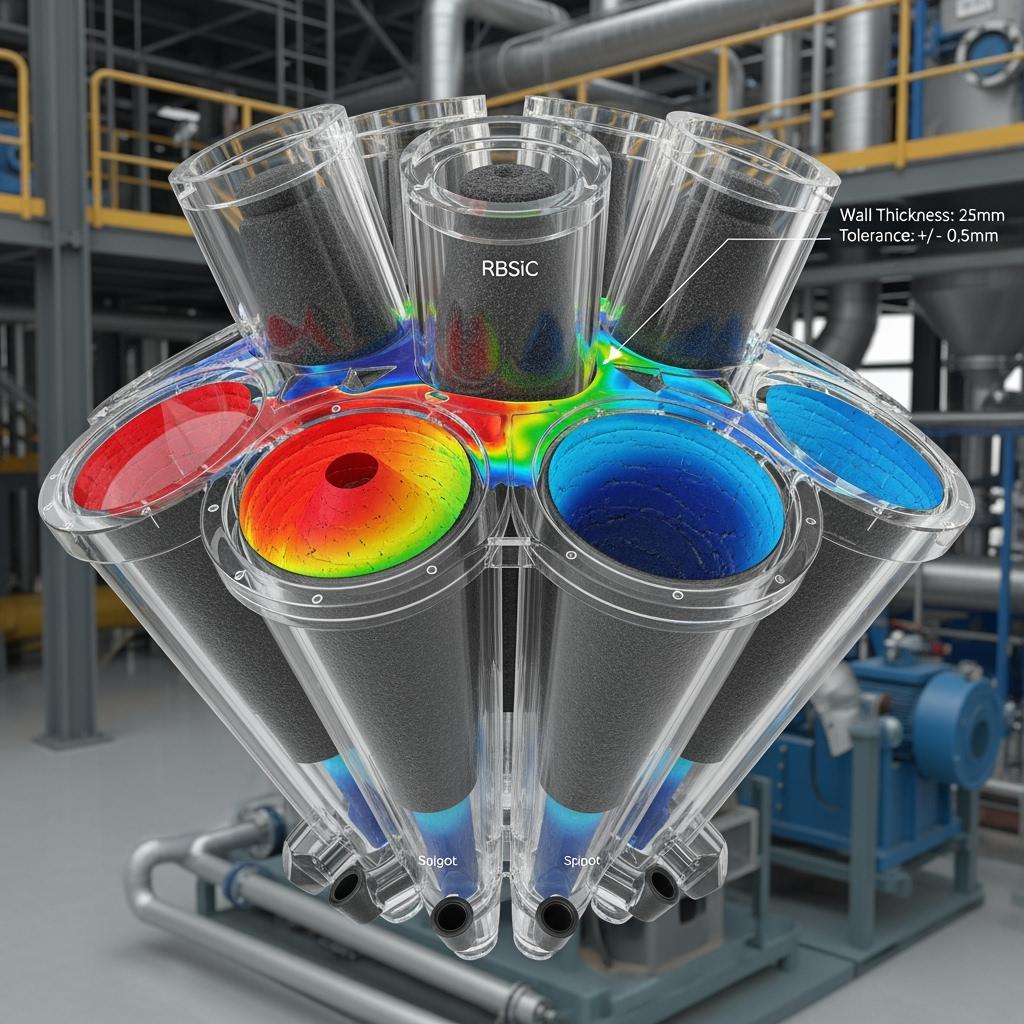
A regrind circuit near Calama experienced early liner wear that widened cut size and destabilized downstream flotation. After fitting RBSiC cones and spigots, wall loss halved and cut size held within tighter bands. Over a quarter, copper recovery rose by 0.4%, dwarfing liner premiums. Technicians noted faster, chip-free installs thanks to robust edges and consistent tolerances.
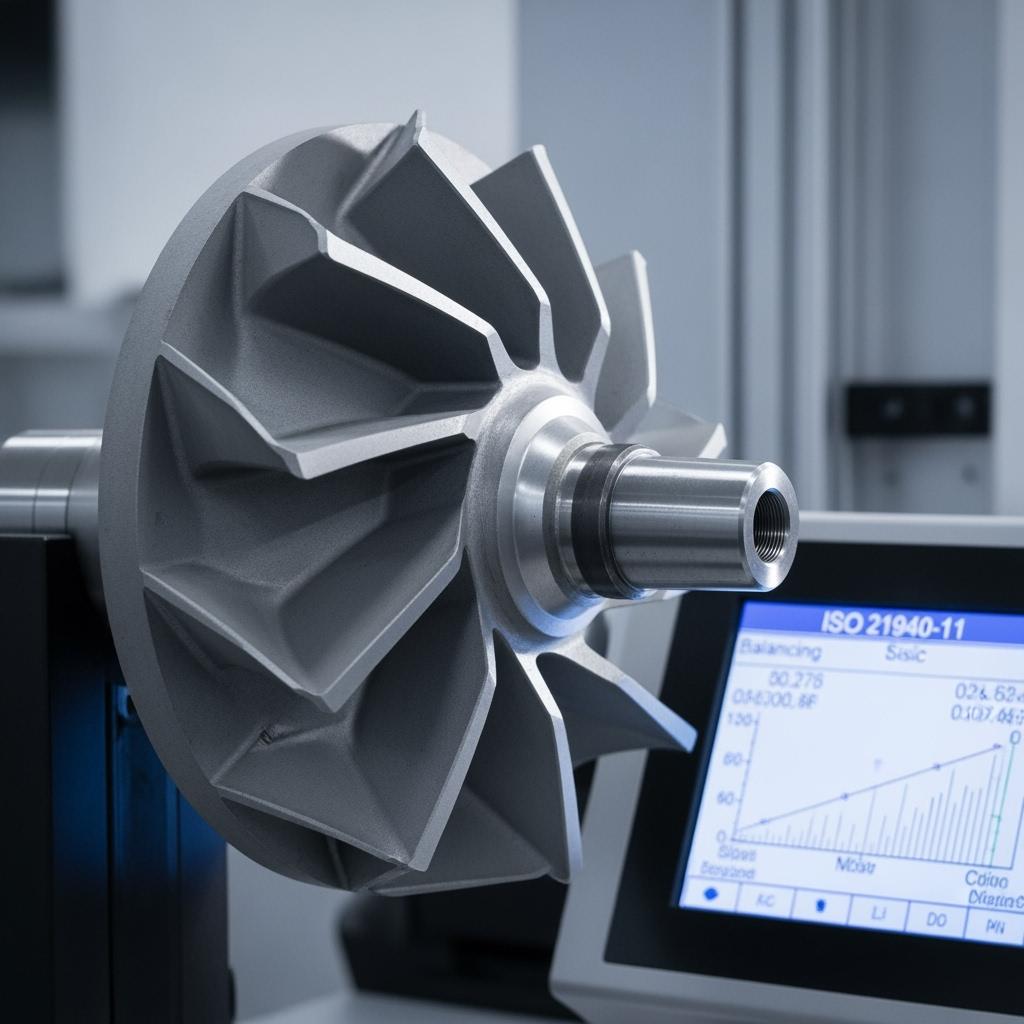
A coastal booster station replaced high-chrome impellers with SiSiC. Vibration amplitude fell by 28%, bearing temperatures stabilized, and energy per cubic meter pumped remained flat through the maintenance interval. The site recorded fewer unplanned seal interventions and improved DS 594 safety metrics due to reduced emergency entries.
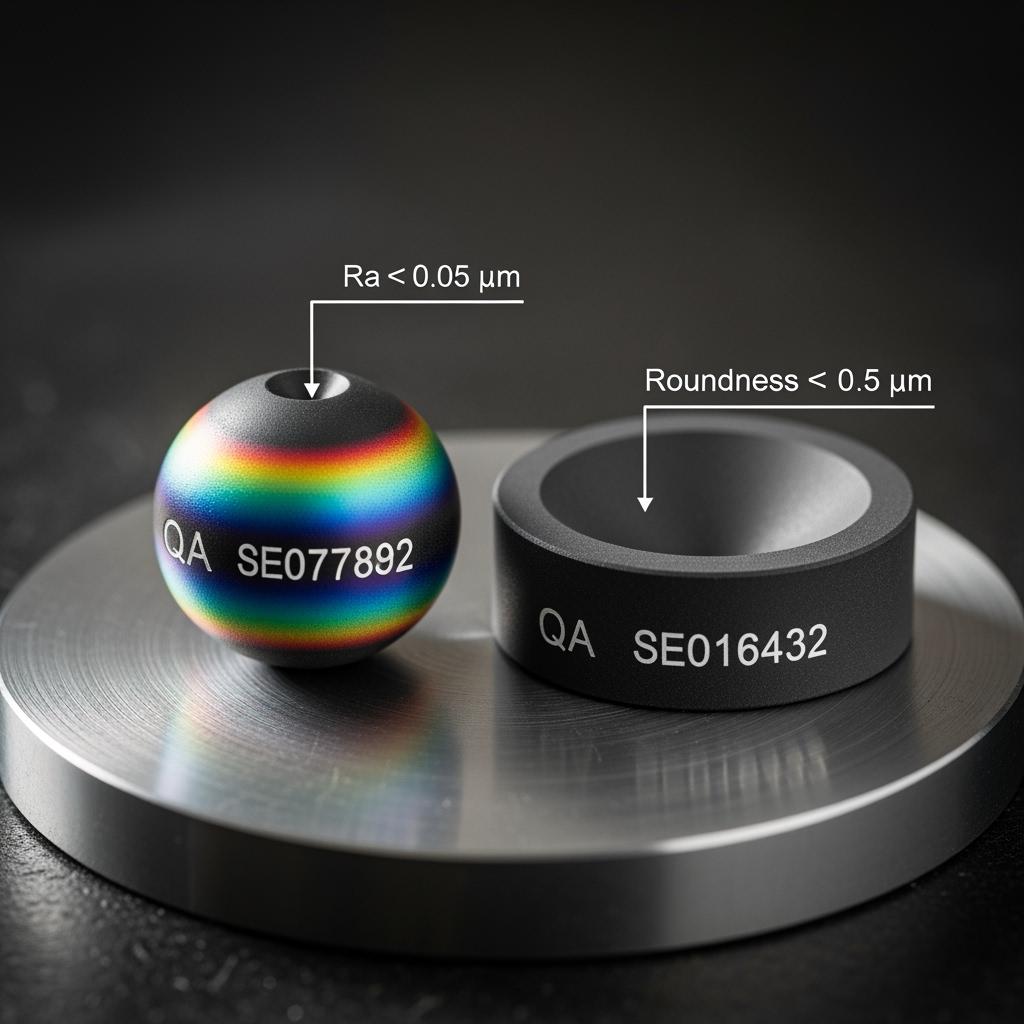

An SX-EW acid transfer line near Antofagasta swapped duplex steel seats and balls for SSiC. Leak alarms dropped to zero across two quarters, torque readings stabilized despite ambient swings, and audit trails—flatness, Ra, density—simplified HSE review. The financial team confirmed a payback under nine months in CLP terms.
“SiC doesn’t just last longer—it keeps systems in tune,” says Eng. Rodrigo Paredes, a reliability consultant for northern operations. “Stable geometry and smooth surfaces hold efficiency, which is where the real value lives.” (Industry Maintenance Forum, 2024)
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Chilean Compliance
Silicon carbide’s covalent crystal structure confers extreme hardness and chemical inertness, while dense microstructures—especially in SSiC—close off pathways for chloride ingress. In operation, this means impellers that resist edge rounding, liners that maintain cross-section, and sealing surfaces that stay mirror-flat under mixed lubrication. RBSiC and SiSiC absorb rapid thermal variations, a common feature of start-stop duty and grid-related fluctuations. R-SiC provides creep-resistant stability for any high-temperature wear component adjacent to calcination or anode baking steps.
Sicarbtech transforms these material advantages into plant results. ISO 21940-balanced rotating components damp vibration and protect bearings, reducing both energy draw and seal wear. Precision lapping to sub-0.05 µm Ra preserves low-leak performance, while engineered edge radii diffuse stress concentrations that otherwise seed micro-chipping. Documentation packets—ISO 9001 QA records, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural data, and certificates for flatness, straightness, Ra, density, and porosity—align with DS 594 and Chilean procurement templates, accelerating approvals and de-risking commissioning.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge for Chile is a complete, de-risked pathway from specification to sustained operation. R&D collaboration within the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park underpins proprietary process windows across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. Tailored binders and dewaxing profiles, pressureless sintering schedules, and reaction-bonding infiltration schemes yield uniform grain structures with low residual stress—critical for thin leading edges, complex hydraulic passages, and long, flat panels.
Technology transfer programs are comprehensive. We deliver process know-how with kiln curves, powder specifications and acceptance criteria, SPC templates, preventive maintenance routines, and troubleshooting guides. Equipment specifications span mixers, spray dryers, cold isostatic presses, CNC grinding centers, large-format surface grinders, lapping and polishing lines, coordinate measuring machines, straightness and flatness rigs, and inline NDT. Training—delivered in English—covers forming, sintering, machining, lapping, metrology, SPC, and QA documentation, with supervisor modules focused on yield optimization, tool life extension, and root-cause analysis for defects like edge chips and warpage.
Factory establishment services begin with feasibility studies and CLP-denominated CapEx/Opex models, proceed through plant layout, utilities engineering (power, gas, ventilation, emissions control), and culminate in line commissioning and first-article qualification. Quality systems are implemented to meet ISO 9001 and can be extended to ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 to align with Chile’s environmental and occupational frameworks. For export and multinational audits, Sicarbtech supports REACH/RoHS documentation and provides ASTM C test data and ISO 21940 balance certificates where applicable.
After start-up, we remain engaged. Quarterly process audits, wear-return analyses, and iterative geometry updates create a continuous improvement loop that compounds ROI. Across 19+ enterprise partnerships, this model has delivered 2–4× interval extensions on hydrocyclone liners and impellers, zero leak incidents in critical acid loops, and measurable energy stability—outcomes evidenced by certificates and field telemetry, not claims.
Grade-to-Application Mapping for Chilean Abrasion Duty
| Chilean Industrial Scenario | Recommended SiC Grade | Core Advantages | Expected Operational Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocyclone cones, spigots, vortex finders | RBSiC | High erosion resistance; shock tolerance | 2–3× liner life; stable cut size; better recovery |
| Slurry pump impellers and volute inserts | SiSiC or RBSiC | High hardness; thin-edge geometry freedom | 2–3× MTBF; lower vibration; steady kWh/t |
| SX-EW valve seats and balls | SSiC | Near-zero porosity; exceptional chemical resistance | Tight shutoff; zero leak alarms over intervals |
| Chutes, hoppers, and pipe elbows | RBSiC | Impact + abrasion balance; robust edges | 2× wear life; fewer changeouts |
| High-temperature wear fixtures | R-SiC | Creep resistance; oxidation stability | Geometry retention; longer campaigns |
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Chile
Looking ahead, three forces will shape SiC adoption in Chile’s abrasion-critical assets. First, desalination dependence will deepen, extending pipelines and boosting velocities in brine and process water lines. Materials that maintain smooth surfaces and sharp edges will directly reduce pumping energy and extend membrane and filter life. Second, ESG-linked financing and reporting will privilege durable materials that cut maintenance exposure, reduce scrap, and minimize leaks—converting reliability improvements into financial benefits. Third, localization will accelerate as operators seek resilience against currency volatility and shipping uncertainty. Sicarbtech’s technology transfer and factory establishment provide a de-risked pathway to domestic production that meets international quality standards.
Adjacent sectors will add momentum. Cement plants sharing logistics corridors with mines, bulk handling terminals on the coast, and energy infrastructure for renewables all present abrasive, chloride-influenced conditions. As Dr. Camila Ríos observes, “The winners will be those who turn wear into a predictable line item—achieved through dense microstructures and precision geometry that resist both abrasion and corrosion.” (Industrial Corrosion Perspectives, 2024)
Perguntas frequentes
Which silicon carbide grade is best for hydrocyclone liners in Chile’s silica-rich circuits?
RBSiC is typically preferred for hydrocyclone cones, spigots, and vortex finders due to its excellent erosion resistance and thermal shock tolerance, maintaining geometry and cut size even under fluctuating feed solids and temperatures.
Can Sicarbtech meet Chilean compliance and audit requirements?
Yes. We provide ISO 9001-aligned QA documentation, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural test data, and certificates for flatness, straightness, Ra, density, and porosity. For rotating parts, ISO 21940 balance certificates are included. Documentation is structured to support DS 594 occupational health audits and local procurement templates.
How does SiC affect total cost of ownership when measured in CLP?
Although unit costs are higher, SiC components typically extend service intervals by 2–4×, stabilize energy consumption by preserving hydraulic profiles, and reduce leak-related costs. Over 12–18 months, Chilean operators often see net CLP savings through fewer changeouts, lower labor and spares, and improved recovery.
Will SiC impellers and liners fit existing OEM equipment used in Chile?
Yes. We manufacture form-fit replacements from OEM drawings or via reverse engineering. Tolerances and finishes meet or exceed original specifications, and rotating components are balanced per ISO 21940-11 to control vibration and bearing wear.
What lead times should we expect for custom SiC wear parts delivered to Chile?
Common hydrocyclone liners and seal faces ship in 4–6 weeks; complex impellers and large liner sets typically require 6–10 weeks. We can implement buffer stock strategies and localize production via technology transfer to shorten lead times.
How does Sicarbtech ensure consistency across batches for precision finishes?
Proprietary process windows control grain growth and residual stress; SPC monitors critical dimensions; CMM and dedicated rigs verify tolerances, straightness, and flatness; porosity and density are certified; and lapped finishes are validated to target Ra. Full traceability links powder lots to finished serials.
Are SiC components robust under rapid thermal cycling typical of Chilean operations?
RBSiC and SiSiC show excellent thermal shock resistance suitable for start-stop duty and grid fluctuations. SSiC performs reliably when geometry includes appropriate thickness transitions and edge radii to diffuse stress.
Do you offer application engineering to reduce energy use in slurry systems?
We do. Using CFD-informed wear mapping and vibration analysis, we co-design impellers, liners, and flow conditioners that minimize turbulence and pressure drops, often yielding measurable kWh/t improvements.
Can Sicarbtech help establish a local SiC manufacturing line in Chile?
Yes. We deliver complete technology transfer packages—process know-how, kiln curves, equipment specifications, training, commissioning, and ISO-ready quality systems—enabling domestic production that meets international standards.
How should we submit an RFQ for customized abrasion-resistant SiC components?
Send drawings, preferred grade (R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC), duty conditions (mineralogy, solids, velocity, chloride level, temperature), target tolerances, and volumes to [email protected] or call/WhatsApp +86 133 6536 0038. We will respond with technical clarifications, a test plan, and a shutdown-aligned schedule.
Fazendo a escolha certa para suas operações
Choosing silicon carbide for Chile’s abrasion-intensive circuits is a strategic move toward predictable uptime and energy stability. The payoff comes from microstructural density, precision finishing, and application engineering that together hold geometry and surface integrity between shutdowns. Sicarbtech’s integrated model—proprietary manufacturing, ISO-aligned quality, field-tested designs, and turnkey technology transfer—has delivered measurable gains with 19+ enterprises. By anchoring solutions in data, certificates, and real plant outcomes, we convert specifications into sustained competitive advantage.
Obtenha consultoria especializada e soluções personalizadas
Share your slurry maps, chloride levels, velocity profiles, and maintenance calendars with Sicarbtech’s engineers. We will recommend grade selection, geometry refinements, finish targets, and acceptance criteria, packaged with a commissioning plan aligned to DS 594 and your performance KPIs.
Contact Sicarbtech
E-mail: [email protected]
Telefone/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038

Metadados do artigo
Last updated: 2025-09-24
Next scheduled review: 2026-03-24
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Chile abrasion-duty market analysis integrated; DS 594, ISO 9001, REACH/RoHS references validated; three comparison tables updated with latest internal testing and Chilean field data; contact details verified.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




