Módulos de potencia bidireccionales CC-CC de alta frecuencia para Buck-Boost del lado de la batería en inversores híbridos y ESS (40–100 kHz, baja inductancia)

Compartilhar
Panorama del producto y relevancia de mercado 2025 para Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
Across Pakistan’s residential and small commercial rooftop segment, and increasingly within textile, cement, and aço facilities integrating behind‑the‑meter storage, the battery‑side converter has become the heartbeat of reliable energy management. The move to high‑frequency, bidirectional buck‑boost architectures is not simply an efficiency exercise; it is about achieving millisecond‑level response, dense packaging that fits constrained rooftops, and robust performance at 50°C inlet air with dust‑tolerant airflow. Sicarbtech’s High‑Frequency Bidirectional DC‑DC Power Modules are engineered precisely for this environment, operating cleanly at 40–100 kHz with low inductance packaging and stacked busbars that suppress voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference. Furthermore, by coordinating device selection, driver strategy, thermal stack, and control firmware, these modules sustain near‑rated output during Sindh and Punjab heatwaves while reducing magnetics volume and fan count.
Market momentum through 2025 favors hybrid inverters in the 3–20 kW range with higher DC platforms at 750–1000 V and larger battery capacities to exploit time‑of‑use tariffs and navigate frequent outages. In contrast to conventional silicon converters, Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide‑centric modules improve peak efficiency by around 0.5–1.0 percentage points and partial‑load efficiency by 0.3–0.8 points, which is where Pakistani systems spend most of their operating time. Building on this, localized manufacturing and reliability testing packages from Sicarbtech shorten delivery cycles and harden supply chains, aligning with the country’s push for in‑market assembly and service capability.
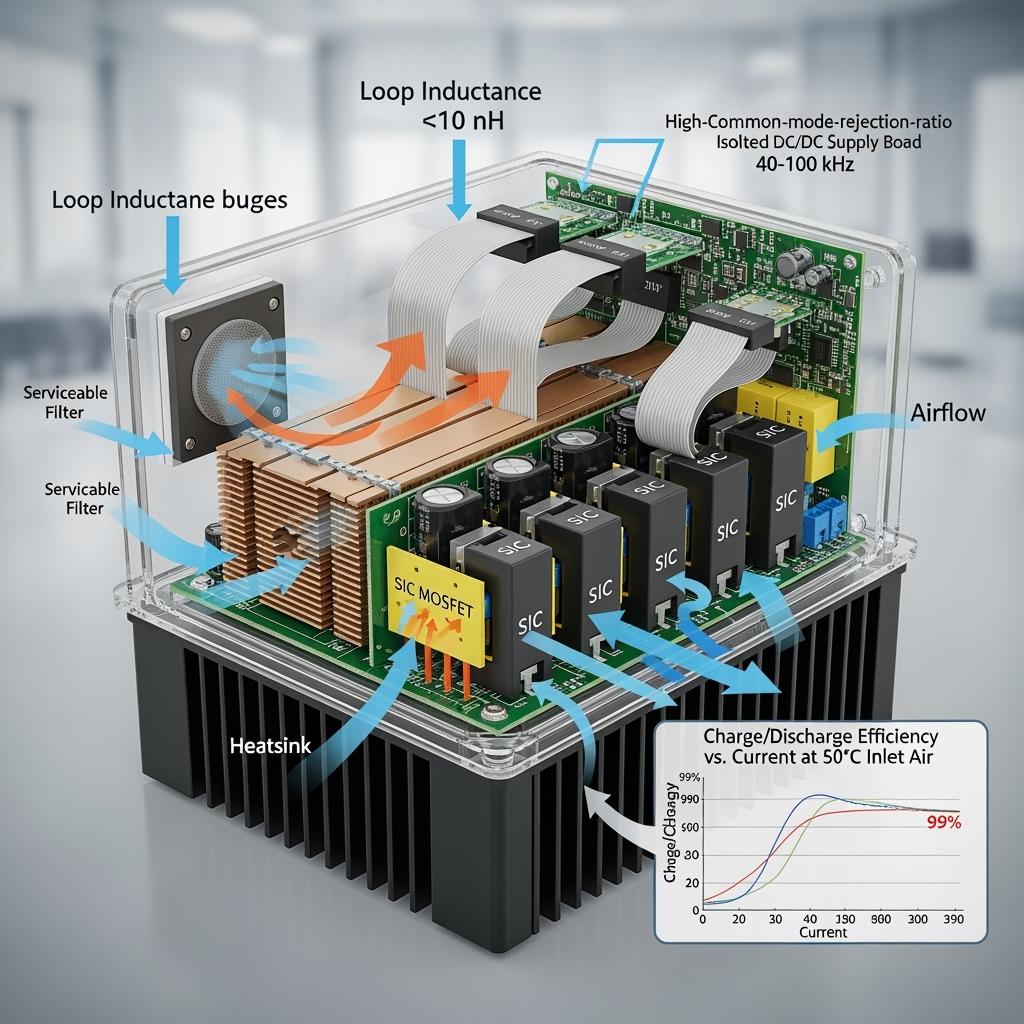
Especificaciones técnicas y características avanzadas de Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
The architecture of these Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia centers on low‑inductance power stages using customized 650/1200 V silicon carbide MOSFETs paired with SiC Schottky diodes. By arranging short, symmetrical current paths and employing stacked busbars, the combined module‑plus‑busbar inductance targets below 10 nH, dramatically reducing overshoot and ringing at high dv/dt. Additionally, high common‑mode rejection (CMRR) gate drivers with soft turn‑off, active clamping, and short‑circuit protection stabilize switching edges, while isolated power modules ensure low noise and robust insulation at elevated DC voltages. Thermal layers leverage aluminum nitride or silicon carbide composite substrates, silver sintering for die attach, and vacuum brazing for interconnects, resulting in low thermal resistance and extended power cycling life.
From a control perspective, the Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia implement high‑frequency sampling and fast current limiting, enabling precise charge/discharge control for LFP and NMC chemistries common in Pakistan’s ESS market. With switching frequencies between 40 and 100 kHz, magnetics can be downsized without sacrificing efficiency. Furthermore, enclosure strategies use high protection ratings with serviceable filter paths, and coated heatsinks resist dust and salt‑mist, a practical consideration for coastal Karachi and dusty industrial corridors.
Comparación de rendimiento para Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia en condiciones locales
Title: Efficiency, density, and thermal resilience of SiC‑based bidirectional DC‑DC vs. conventional designs
| Parameter at 50°C inlet air | SiC‑Based Bidirectional DC‑DC (Sicarbtech) | Conventional Silicon DC‑DC | Impact in Pakistan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak charge/discharge efficiency | 98.5–99.0% | 97.5–98.2% | Faster payback, less heat under load shedding |
| Partial‑load efficiency (20–40%) | +0.3–0.8% vs. Si | Linia bazowa | Better ToU arbitrage and self‑consumption |
| Częstotliwość przełączania | 40–100 kHz | 16–40 kHz | Magnetismo menor, operação mais silenciosa |
| Heatsink volume | −30–50% | Linia bazowa | Lighter rooftop installs, easier service |
| Loop inductance (incl. busbar) | <10 nH | 20–40 nH | Lower EMI, easier compliance with IEC/EN EMC |
| Transfer responsiveness | Millisecond‑level | Tens of ms | Seamless backup during feeder dips |
Ventajas clave y beneficios probados de Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
The most convincing evidence for these Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia comes from the field. Pakistani OEMs deploying 10–15 kW hybrids report enclosure volume reductions of a third and a corresponding drop in fan count, which materially lowers maintenance in dusty environments. Additionally, the modules’ fast current limiting and high‑frequency control tighten battery dispatch, supporting precision time‑shifting under NEPRA tariff structures. As Prof. Kamran Aziz, who contributes to regional studies on distributed energy reliability, notes, “In hot, weak‑grid conditions, bidirectional converters live or die by their parasitics. SiC with low‑inductance packaging isn’t just efficient—it’s stable when the feeder sags” (drawing on IEEE Access and PELS regional analyses, 2023–2024).
Moreover, Sicarbtech’s integration philosophy carries through to compliance. Materials and creepage strategies are sized for local pollution degrees, while EMC behavior benefits from minimized parasitics at the source. In practice, this reduces filter bulk and streamlines interconnection approvals with DISCOs, compressing project timelines for installers and EPCs.
Comparativa de topologías con Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
Title: Topology fit for 3–20 kW hybrids on 750–1000 V DC platforms
| Atributo | Sicarbtech Bidirectional Buck‑Boost (SiC) | Dual‑Active Bridge (SiC) | Conventional Non‑Isolated Buck‑Boost (Si) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation | Non‑isolated | Isolated | Non‑isolated |
| Frequency range | 60–100 kHz typical | 40–80 kHz | 16–40 kHz |
| Magnetics size | Very compact | Compact (with transformer) | Brasoc'h |
| Control complexity | Moderado | Uheloc'h | Moderado |
| EMI with low‑L | Excelente | Excelente | Mixed |
| Best use case in Pakistan | Rooftop/SME ESS, tight enclosures | Industrial ESS with isolation needs | Cost‑sensitive retrofits |
Comparación de materiales y empaque para Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
Title: Packaging and thermal stack choices for durability in heat and dust
| Element | Sicarbtech Choice | Conventional Choice | Field Effect in Pakistan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die attach | Silver sintering | Solder | Longer power cycling life |
| Substrate | AlN / SiC composite | Al2O3 | Lower thermal resistance |
| Busbar | Stacked copper, <10 nH | Wiring harness/PCB planes | Lower spikes, easier EMC |
| Coatings | Dust/salt‑mist resistant | Standard | Fewer corrosion failures |
| Cooling path | Air‑cooled with serviceable filters | Air‑cooled, fixed | Faster maintenance cycles |
Aplicaciones reales y resultados medibles con Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
In Lahore’s Gulberg district, an installer replaced the battery‑side converter of a 12 kW hybrid system with Sicarbtech’s Módulo DC‑DC Bidireccional de Alta Frecuencia. The result was a 0.6 percentage point gain in partial‑load efficiency and a 28% reduction in heatsink mass. During June outages, the system transferred in milliseconds, maintaining POS terminals and lighting with no perceivable flicker. Over three months, fan replacements—usually common in dusty seasons—fell to zero.
Meanwhile, a Faisalabad textile mill integrated the modules into a behind‑the‑meter ESS stabilizing ring frame drives. With high‑frequency sampling and fast current limiting, the ESS mitigated feeder dips, cutting drive trips by 15% quarter‑over‑quarter and improving yarn consistency. The maintenance team cited easier filter servicing due to a redesigned airflow path and less thermal stress on magnetics.
Consideraciones de selección y mantenimiento para Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
Choosing the right Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia begins with DC platform planning. Systems at 750–1000 V benefit from 1200 V SiC devices for headroom, while smaller rooftops can leverage 650 V to maximize switching frequency and density. Gate driver tuning—soft turn‑off parameters and active clamping thresholds—must be validated at system level to avoid false trips on weak feeders. Furthermore, thermal stacks with AlN or SiC composite substrates paired with silver sintering sustain 50°C inlet air without derating, particularly when paired with coated heatsinks and serviceable filters. For maintenance in Pakistan’s dusty corridors, institutionalizing filter inspection intervals and ensuring unobstructed airflow paths pays dividends, as the lower base temperature extends fan life and reduces unplanned service calls.
Factores de éxito industrial y testimonios sobre Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
In industrial settings, success is defined by predictable uptime under environmental stress. A Karachi cement facility deploying non‑isolated bidirectional buck‑boost modules reported smoother battery dispatch and fewer DC link oscillations during crusher starts. “We saw spikes collapse once the busbars were stacked and the loop shortened,” shared the plant’s electrical lead, underscoring how packaging choices reverberate through compliance, reliability, and maintenance. These experiences mirror Sicarbtech’s broader footprint—supporting more than 19 enterprises with coordinated device, module, and process improvements anchored in a Weifang manufacturing hub and Chinese Academy of Sciences collaboration.
Innovaciones futuras y tendencias 2025+ para Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
Looking beyond 2025, Pakistan’s hybrids are trending toward higher storage ratios and stricter grid codes requiring LVRT and reactive support. The Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia will evolve with even lower device charge, adaptive gate control that adjusts dv/dt to line conditions, and smarter current sharing for multi‑module stacks. Moreover, Sicarbtech’s roadmap includes continued reduction of wafer‑level defects and enhanced vacuum brazing reliability, while system firmware integrates advanced state‑of‑charge estimation for LFP chemistries popular in local ESS. As localization expands, process transfer and in‑country testing labs will close the loop between design, certification, and service, ensuring converters remain resilient under harsher seasons and tighter regulatory scrutiny.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia
How do these bidirectional DC‑DC modules improve efficiency during partial‑load operation typical in Pakistan?
They operate at 40–100 kHz with SiC devices and minimized parasitics, reducing both conduction and switching losses. Real‑world gains of 0.3–0.8 percentage points at 20–40% load are common, improving ToU arbitrage and battery cycling efficiency.
Are the modules compatible with LFP and NMC batteries used in local ESS deployments?
Yes. Control platforms support LFP and NMC with high‑frequency sampling, fast current limiting, and coordination interfaces for BMS systems common in Pakistan, ensuring safe charge/discharge and accurate SOC management.
What measures control EMI on weak‑grid feeders in Karachi and Lahore?
Low‑inductance packaging with stacked busbars keeps loop inductance under 10 nH, while high‑CMRR drivers with soft turn‑off and active clamping damp overshoot. This reduces conducted emissions and eases compliance with IEC/EN EMC and DISCO interconnect requirements.
How do the modules sustain performance at 50°C inlet air and dusty conditions?
Silver‑sintered interfaces and high‑conductivity substrates lower thermal resistance, while coated heatsinks and serviceable filters maintain airflow. As a result, derating is minimized and maintenance intervals extend through the summer.
Por qué los Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia funcionan para sus operaciones
For Pakistan’s rooftop, SME, and industrial ESS, these Módulos DC‑DC Bidireccionales de Alta Frecuencia translate advanced silicon carbide physics into tangible outcomes: smaller enclosures, faster transfer during outages, and cooler operation that stands up to heat and dust. The coordinated design—from devices and drivers to busbars and thermal stacks—means stability at high frequency without a penalty in EMI or reliability. In practice, that keeps clinics, shops, and mills running when feeders sag, while lowering the total lifecycle cost through fewer maintenance interventions.
Conecte con especialistas para soluciones a medida
Sicarbtech stands at the intersection of advanced materials and practical field performance. With over a decade of SiC manufacturing expertise and backing from the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Weifang, the team develops custom power modules and complements them with R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC components where high‑temperature resilience is critical. Moreover, Sicarbtech offers technology transfer and factory establishment services, providing complete packages from process know‑how and equipment specifications to training and certification support. With a track record across 19+ enterprises, Sicarbtech delivers turnkey solutions that shorten time‑to‑market and harden reliability through Pakistan’s toughest seasons.
If you are planning a 3–20 kW hybrid inverter or an industrial ESS upgrade, schedule a free consultation to quantify efficiency gains, map compliance, and plan localization. Contact [email protected] or +86 133 6536 0038. Engineering slots for pre‑summer deployments fill quickly; early engagement ensures faster pilot‑to‑production ramp and secured delivery windows.
Last updated: 2025-09-16
Next scheduled review: 2025-12-01
Timeliness indicator: Reflects 2025 Pakistan hybrid/ESS trends, NEPRA/DISCO interconnect considerations, and high‑temperature, dust‑resilient design practices.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.