Specifieke sinterapparatuur voor verpakking van SiC-voedingsapparaten: Ag-sinteren, verlijmen onder druk en leegtecontrole

Haalbare toleranties en maatnauwkeurigheid:
Productoverzicht en relevantie voor de markt in 2025
Speciaal ontworpen sinterapparatuur, speciaal ontwikkeld voor de verpakking van siliciumcarbide (SiC) vermogensapparatuur, maakt betrouwbare die-attach en substraatbinding mogelijk met behulp van zilver (Ag) sinter- en drukgeassisteerde processen met geavanceerde void-controle. Voor de Pakistaanse textiel-, cement- en staal sectoren—waar de omgevingstemperaturen de 45°C kunnen overschrijden en elektrische ruimtes gevoelig zijn voor stof—is de robuustheid van de verpakking net zo cruciaal als de selectie van het apparaat. Ag-sintering creëert een thermisch geleidende, metallurgische verbinding met een hoog smeltpunt die beter presteert dan solderen bij thermische cycli, vermogenscycli en langetermijnstabiliteit, en direct de efficiëntie van omvormers van ≥98,5% ondersteunt, de vermogensdichtheid tot 2× verhoogt en MTBF-doelen van 200.000 uur haalt.
In 2025 breiden middenspannings- (11–33 kV) PV-aansluitingen en zware aandrijvingen zich uit over industrieparken in zuidelijke regio's. Lokaal beleid voor productie en technologie-introductie opent de deur voor binnenlandse verpakkingen, modulemontage en investeringen in apparatuur. Sinterplatforms met programmeerbare druk-, temperatuur- en atmosfeerprofielen stellen Pakistaanse OEM's, EMS-leveranciers en joint-venturepartners in staat SiC-modules te produceren met een lagere thermische weerstand, minder storingen in de beginfase en een verbeterde betrouwbaarheid in het veld bij hitte en stof.
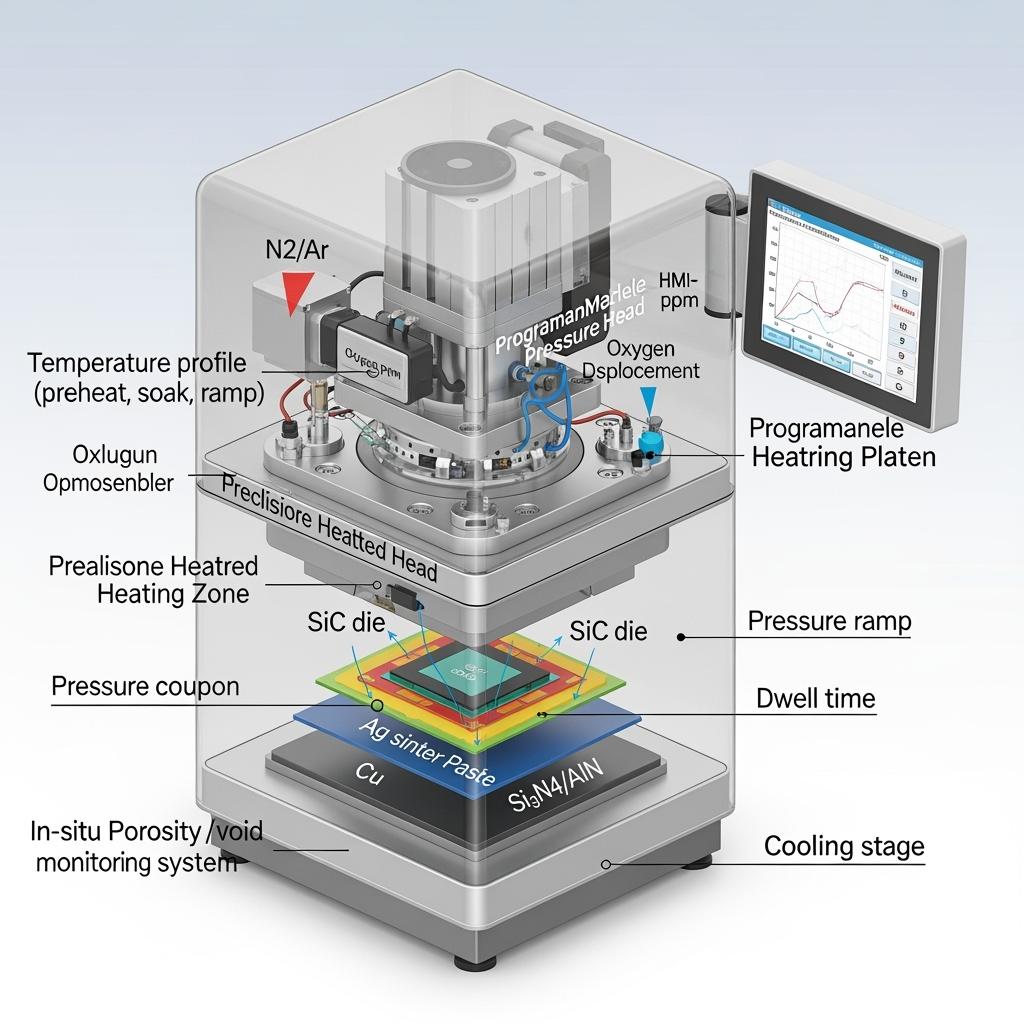
Technische specificaties en geavanceerde functies
- Procesmogelijkheden:
- Temperatuurbereik: 150–300°C (programmeerbare multi-zone uniformiteit ±2°C)
- Drukbereik: 1–40 MPa (closed-loop controle, <±2% fout)
- Atmosfeercontrole: Vacuüm ≤1 mbar; N2/Ar-spoeling met rest-O2-monitoring
- Tijdprofielen: Voorverwarmen, ontgassen, opwarmen, verblijven en gecontroleerd afkoelen
- Ondersteunde materialen:
- Ag-sinterpasta's en -folies voor die-attach en DBC-naar-grondplaat-verbinding
- Cu-, Ag-, Ni-metallisaties; compatibiliteit met Si3N4- en AlN-DBC-substraten
- Holtecontrole en -monitoring:
- In-situ ultrasone/akoestische impedantiecontroles voor porositeitstrenddetectie
- Post-proces röntgen- en SAM (scanning acoustic microscopy) integratieworkflow
- Doorvoer en herhaalbaarheid:
- Receptgestuurde batch- of semi-continue werking met SPC-datalogging
- Fixture-systemen voor multi-up panelen en uniforme lastverdeling
- Kwaliteit en traceerbaarheid:
- Volledige MES-connectiviteit, barcode/RFID-tracking en elektronische batchrecords
- Procesvergrendelingen voor temperatuur-, druk- en alarmsignalen voor de atmosfeer
- Veiligheid en betrouwbaarheid:
- Vergrendelde deuren, E-Stop, over-temp- en over-druk-beveiligingen
- Preventieve onderhoudsverzoeken op basis van cyclustellingen en sensordrift
Beschrijvende vergelijking: Ag Sinter versus soldeer met hoge temperatuur voor SiC-verpakking
| Criterium | Ag-sinter met drukondersteunde verbinding | Hoogtemperatuur soldeerverbinding |
|---|---|---|
| Thermische geleidbaarheid van de verbinding | Hoog (maakt lage Rth en koelere verbindingen mogelijk) | Matig (hogere Rth) |
| Smelt-/verzachtingsgedrag | Metallurgische verbinding; geen verzachting tijdens gebruik | Gedefinieerd smelten; kruiprisico bij hoge temperatuur |
| Robuustheid van het vermogenscycleren | Superieur; minder scheuren/delaminatie | Lager; soldeerfatigue komt vaak voor |
| Bedrijfstemperatuur | Stabiel tot +175°C junctie en hoger | Marginaal bij hoge junctietemperaturen |
| Holtegehalte | Controleerbaar tot zeer lage niveaus met procesafstemming | Doorgaans hoger; holtes blijven bestaan |
| Veld betrouwbaarheid (stof/warmte) | Hoge veerkracht; langere MTBF richting 200.000 uur | Kortere levensduur op zware locaties |
Belangrijkste voordelen en bewezen resultaten met citaat van experts
- Lagere thermische weerstand: Ag-sinterverbindingen geleiden warmte efficiënt, wat compacte koeling ondersteunt met ongeveer 40% reductie in het volume van de koelvin.
- Hogere betrouwbaarheid bij cycleren: Drukondersteund sinteren vermindert grensvlakscheuren, waardoor een lange levensduur wordt gehandhaafd bij frequente belastingsverschijnselen die typisch zijn voor staal- en cementaandrijvingen.
- Stabiliteit bij verhoogde temperatuur: Behoudt mechanische integriteit tot +175°C junctie, cruciaal voor de omgevingstemperatuur in het zuiden van Pakistan.
- Holtecontrole: Geavanceerde profielen en in-situ monitoring bereiken lage holtefracties, waardoor consistente prestaties en opbrengst worden gewaarborgd.
Deskundig perspectief:
"Zilver sinteren is een hoeksteen voor de volgende generatie SiC-vermogensmodules, die een hoge thermische geleidbaarheid combineert met uitstekende thermomechanische betrouwbaarheid bij zwaar cycleren." - IEEE Power Electronics packaging insights (ieee.org)
Praktijktoepassingen en meetbare succesverhalen
- Modules voor PV-omvormers met gemiddelde spanning: De overgang van soldeerverbinding naar Ag-sinter verminderde de thermische weerstand van junctie naar behuizing met 15–25%, waardoor de omvormer een efficiëntie van ≥98,5% bereikte en bijdroeg aan een reductie van 30–40% in het koelvolume.
- Cementoven-ventilatoraandrijvingen: Modules die met drukondersteund sinteren werden verpakt, behielden stabiele thermische prestaties bij stoffige cycli met hoge belasting, waardoor ongeplande stilstanden werden verminderd en de onderhoudsintervallen werden verlengd.
- Textiel-VFD's: Gesinterde die-attach verbeterde de thermische marges in de zomer, waardoor thermische derating-gebeurtenissen werden verminderd en de productiviteit op hogesnelheidslijnen werd gehandhaafd.
Overwegingen voor selectie en onderhoud
- Selectie van procesrecepten: Pas de temperatuur- en drukrampen aan op de specificaties van de leverancier van pasta/folie en de metallisatiestack. Valideer ontgassingsfasen voor consistente porositeitscontrole.
- Fixture-ontwerp: Gebruik vlakheidsgecontroleerde, conforme fixtures om een uniforme druk over multi-up panelen en verschillende modulegeometrieën te garanderen.
- Atmosfeerbeheer: Handhaaf lage zuurstofniveaus om oxidatie te voorkomen; valideer de vacuümintegriteit en spoeltijden voor herhaalbare verbindingen.
- Inspectiestrategie: Combineer in-situ akoestische controles met post-proces röntgen/SAM op statistisch significante monsters; voer SPC-gegevens in voor continue verbetering.
- Onderhoud: Kalibreer temperatuur- en druksensoren periodiek; inspecteer afdichtingen, platen en uitlijningskenmerken om de procesmogelijkheden te behouden.
Succesfactoren in de industrie en getuigenissen van klanten
- Gelokaliseerde procesmogelijkheden: Het inzetten van sintercapaciteit in Pakistan vermindert de importafhankelijkheid en de doorlooptijden voor module-reparatie- of uitbreidingsprojecten.
- Geïntegreerde training: Procesingenieurs en operators die zijn getraind in receptcontrole, fixturing en NDT bereiken een snellere opbrengst en een stabiele output.
Feedback van klanten:
"Na de overstap op drukondersteund Ag-sinteren daalden de hotspot-temperaturen van onze module en verdwenen de thermische cyclustoringen. We verhoogden vol vertrouwen de schakelfrequentie zonder oververhitting." - Manufacturing director, regionale omvormer OEM
Toekomstige innovaties en markttrends
- Hogere doorvoerpersen met multi-station architecturen voor schaalbare SiC-moduleproductie
- Real-time porositeitsinferentie met behulp van machine learning op ultrasone handtekeningen
- Nieuwe Ag-composietpasta's voor sinteren bij lagere temperaturen met behoud van een hoge geleidbaarheid
- Groei van het lokale ecosysteem in DBC-substraten, grondplaten en NDT-diensten ter ondersteuning van de uitbreiding van de MV-omvormermarkt in Pakistan
Veelgestelde vragen en antwoorden van experts
- Welke druk- en temperatuurbereiken zijn typisch voor Ag-sinteren in SiC-modules?
Typische bereiken zijn 10–30 MPa en 200–250°C, waarbij de exacte waarden afhankelijk zijn van de chemie van de pasta/folie en de metallisatiestacks. - Hoe verbetert sinteren de betrouwbaarheid ten opzichte van solderen in de hete, stoffige omgevingen van Pakistan?
Ag-sinterverbindingen zijn bestand tegen kruip en fatigue bij hoge temperaturen, waardoor een lage thermische weerstand wordt gehandhaafd en delaminatie bij thermisch/vermogenscycleren wordt voorkomen. - Kan de apparatuur zowel die-attach als DBC-naar-grondplaat-verbinding ondersteunen?
Ja, met de juiste fixtures en recepten kan hetzelfde platform beide lagen aan, wat de flexibiliteit van de lijn verbetert. - Hoe wordt het holtegehalte geregeld en gemeten?
Ontgassingsfasen, drukramp-profielen en atmosfeercontrole verminderen holtes. In-situ akoestische controles en post-proces röntgen/SAM verifiëren de porositeitsniveaus. - Wat is de verwachte impact op de prestaties op systeemniveau?
Lagere Rth en een verbeterde cycleringsweerstand maken hogere schakelfrequenties mogelijk, kleinere koeling en dragen bij aan MTBF-doelstellingen van 200.000 uur.
Waarom deze oplossing werkt voor uw activiteiten
Ag-sinteren en drukondersteunde verbinding pakken de operationele realiteit van Pakistan rechtstreeks aan - hoge omgevingstemperaturen, stof en frequent cycleren - door robuuste, thermische interfaces met lage holtes te produceren die de juncties koeler houden en de modules betrouwbaar. Het resultaat is tastbaar: hogere omvormer- en aandrijvingsefficiëntie, kleinere koelhardware en minder onderhoudsinterventies, waardoor een betrouwbare inzet bij 11–33 kV-verbindingen en in veeleisende industriële lijnen mogelijk is.
Neem contact op met specialisten voor oplossingen op maat
Versnel uw verpakkingsmogelijkheden met een partner die het volgende biedt:
- 10+ jaar expertise in siliciumcarbideproductie en verpakkingsknowhow
- Innovatie ondersteund binnen een toonaangevend onderzoeksecosysteem voor snelle procesoptimalisatie
- Maatwerkontwikkeling voor R-SiC-, SSiC-, RBSiC- en SiSiC-materiaalsystemen en -substraten
- Technologieoverdracht en fabrieksoprichtingsdiensten - van haalbaarheid en lay-out tot inbedrijfstelling
- Kant-en-klare oplossingen van materialen en apparaten tot apparatuur, kwalificatie en opschaling
- Bewezen resultaten in 19+ bedrijfsopdrachten die een meetbare ROI opleveren
Vraag een gratis consultatie en een op maat gemaakt voorstel voor het sinterproces aan:
- Email: [email protected]
- Telefoon/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Artikelmetadata
Laatst bijgewerkt: 2025-09-10
Volgende geplande update: 2026-01-15

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




