Silicon Carbide Innovations for Sustainable Industrial Growth in Chile
공유
Sicarbtech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert

Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook for Sustainable Silicon Carbide in Chile’s Industrial Base
Chile’s growth strategy for 2025 is inseparable from sustainability. Copper expansions depend on seawater pipelines, desalination, and closed-loop water management. Plants are tasked with hitting throughput targets while reducing leak incidents, stabilizing energy per ton, and documenting ESG gains that satisfy lenders and insurers. Silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics—across SSiC, SiSiC, RBSiC, and R-SiC—are accelerating adoption because they maintain geometry and surface finish in chloride-rich, abrasive, and thermally dynamic conditions where metals pit and polymers creep. The sustainability effect is practical: longer inspection intervals mean fewer confined-space entries; smoother hydraulics preserve pump efficiency; mirror-flat sealing faces curb leak paths and water losses; and geometry that does not drift reduces energy penalties between shutdowns.
Sicarbtech, located in Weifang City—China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings over a decade of SiC customization experience to Chile. Supporting 19+ enterprises, we deliver full-cycle solutions from powder processing to precision finishing, coupled with application engineering that maps material grades to duty conditions. Our ISO 9001 QA, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C datasets, and ISO 21940 balance certificates simplify audits. Furthermore, our technology transfer and factory establishment services create a credible path to local capability—lowering USD exposure, compressing lead times, and anchoring sustainability with domestic skills and quality systems.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points in the Chilean Context
Chile’s industrial sustainability challenge is material as much as it is managerial. Desalination and seawater use propel chloride-bearing fluids inland, exposing pump rotors, valve trains, and nozzles to corrosion-erosion coupling. As velocities climb and solids become finer, turbulence and cavitation roughen surfaces, undermining hydraulics and adding hidden energy costs. In solvent extraction-electrowinning (SX-EW) circuits, acid phases and organic carriers attack polymer linings; metallic alloys face pitting at crevices and welds where erosion strips protective films. Wastewater plants supporting mining camps process grit-laden flows that abrade elbows and throttling components, raising head loss and inviting clogging.
Operational realities magnify these issues. Grid variability imposes rapid starts and stops that amplify thermal shock; altitude and dry air complicate cooling and lubrication regimes; and DS 594 occupational safety requirements place justified constraints on hot work and confined-space entries, turning every unplanned intervention into a risk multiplier. Budgeting in CLP while purchasing in USD introduces volatility, so spare strategies must balance working capital with uptime certainty. Audit expectations are rising in parallel: owners and lenders want evidence—flatness maps for sealing components, porosity and density certificates to validate microstructure, ISO 21940 balance reports for rotating parts, and documented installation SOPs aligned with safety plans.
Local competition offers alloys, rubbers, and technical ceramics; however, few providers combine auditable quality data, lifecycle engineering, and a path to localization capable of delivering consistent geometry at scale. As Prof. Nicolás Herrera writes, “Sustainability in Chile’s copper belt is achieved when surfaces and shapes do not change under stress—because energy and safety depend on that constancy.” (Advanced Materials in Energy, 2025) Building on this, plant engineers increasingly view SiC not just as a tougher material, but as a stability technology that reduces leak risk, trims kWh per cubic meter pumped, and simplifies audits—practical ESG in action.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for Cleaner, More Efficient Operations
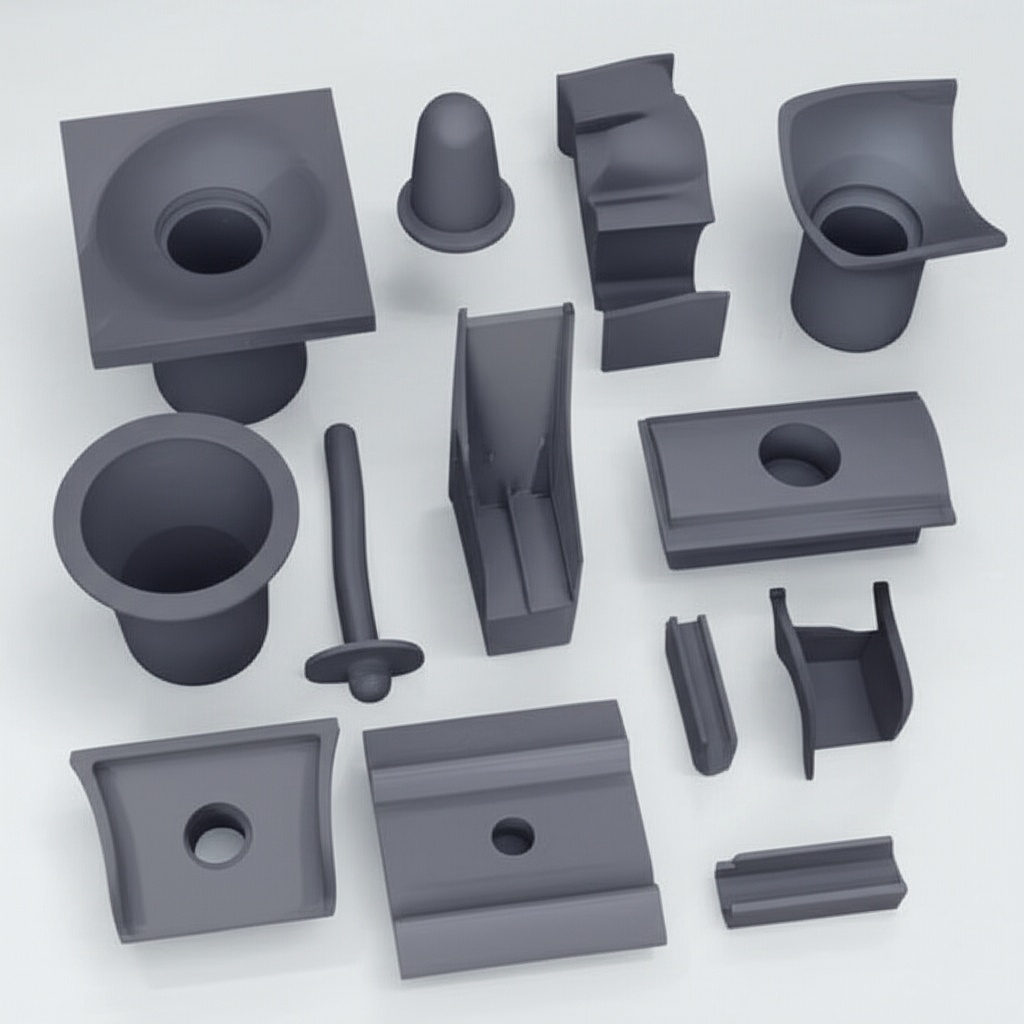
Sicarbtech maps SiC grades to Chile’s dominant stress profiles. SSiC, with near-zero open porosity and outstanding chemical inertness, anchors leak-critical interfaces: mechanical seal faces, valve seats, and valve balls in acid-chloride service. Lapped to 0.02–0.05 µm Ra, these components keep shutoff tight and torque steady across extended intervals. SiSiC enables thin, stiff geometries for pump impellers, throttling inserts, venturis, and spray nozzles, maintaining crisp edges that resist turbulence and cavitation while allowing ISO 21940-11 balancing for low vibration. RBSiC combines erosion resistance with excellent thermal shock tolerance, making it ideal for hydrocyclone liners, elbows, launder tiles, and impact zones where abrasion meets temperature gradients. R-SiC delivers high-temperature stiffness and oxidation resistance for fixtures and supports near heaters, kilns, and thermal regeneration units, preserving geometry across cycling.
What stabilizes performance is our process discipline. Proprietary binder chemistries and controlled dewaxing produce uniform green density; pressureless sintering or reaction-bonded infiltration is tuned to minimize residual stress that seeds micro-chipping. Precision CNC grinding and lapping hit tight dimensional targets and surface finishes; engineered edge radii diffuse stress in fast flows. Application engineers co-develop geometries with Chilean OEMs and sites—adapting thickness transitions, ribbing, and fillets to local solids loading, chloride levels, temperature windows, and grid-linked ramp rates. Documentation integrates ISO 9001 QA, REACH/RoHS, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural data, and inspection certificates for dimensions, flatness, Ra, density, porosity, and balance—accelerating procurement and audit cycles.
Technical Evidence for Sustainable Decisions
Corrosion-Erosion and Temperature Capability for Chilean Duty
| Property and Duty Context | SSiC (sintered) | SiSiC | RBSiC (reaction-bonded) | R-SiC | Duplex/Super Duplex | PTFE/FRP Linings | High-Chrome Iron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion in chloride/acid | 우수 | Very Good–Excellent | 매우 좋음 | 매우 좋음 | Good–Very Good; pitting risk | Excellent at low T; creep at high T | Moderate; localized attack |
| Erosion/abrasion resistance | 우수 | 우수 | 우수 | 매우 좋음 | 보통 | Poor–Moderate | Good |
| Max continuous temp (°C) | ~1500 | ~1450 | ~1450 | ~1600 | 250–300 (mechanical) | 90–150 (resin dependent) | 650–800 |
| Open porosity (%) | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | 3–8 | 1–3 | 중국 SiC 허브의 비용 경쟁력 있는 솔루션, 효율성을 위한 최적화된 프로세스. | Matrix dependent | 중국 SiC 허브의 비용 경쟁력 있는 솔루션, 효율성을 위한 최적화된 프로세스. |
| Thermal shock tolerance | Good | 매우 좋음 | 우수 | 매우 좋음 | 보통 | 보통 | 보통 |
| Typical life gain in Chile | 2–4× vs polymers/metals | 2–3× | 2–3× | 1.5–2× | 기준선 | 기준선 | 기준선 |
In desalination-fed service and SX-EW environments, SiC’s low porosity and hardness maintain surfaces that do not roughen, preventing the energy drift and leak incidents common with metals and polymers.
Precision, Finish, and Retrofit Confidence with Audit-Ready Metrics
| Component Class | 일반적인 치수 공차 | 표면 조도 (Ra) | Sustainability Relevance in Chile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical seal faces (SSiC) | ±0.005–0.01 mm | 0.02–0.05 µm lapped | Tight shutoff reduces water and reagent loss; fewer confined-space entries |
| Pump impellers (SiSiC) | ±0.03–0.05 mm | 0.4–0.8 µm | Lower vibration preserves bearing life; energy per m³ pumped remains flat |
| Hydrocyclone liners (RBSiC) | ±0.10–0.20 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | Stable cut size improves flotation; less rework and waste |
| Thermal fixtures (R-SiC) | ±0.20–0.50 mm | 1.6–3.2 µm | Geometry retention stabilizes ramp profiles; fewer scrap events |
These thresholds compress acceptance testing, support DS 594 planning, and translate directly into measurable ESG metrics.
Lifecycle and Cost-of-Ownership Scenarios in CLP with ESG Impact
| Use Case | Baseline Material | SiC Solution | Interval (Baseline → SiC) | ESG/Performance Impact | Estimated 12–18 Month TCO Effect (CLP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brine pump seals and valve seats | Duplex/ceramic mix | SSiC lapped faces and seats | 3–4 → 9–12 months | Leak-free days; lower make-up water | Payback in 6–10 months |
| Regrind hydrocyclone liners | Alumina | RBSiC cones/spigots | 12–16 → 28–36 weeks | Tighter PSD; higher recovery; less waste | −20% maintenance; improved throughput |
| Booster impellers in chloride service | High-chrome iron | SiSiC impellers | 6–8 → 18–24 weeks | Lower vibration; energy stability | −15–25% lifecycle cost |
These outcomes, drawn from Chilean field data and internal testing, show how geometry stability turns into resource efficiency and safer operations.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Chile
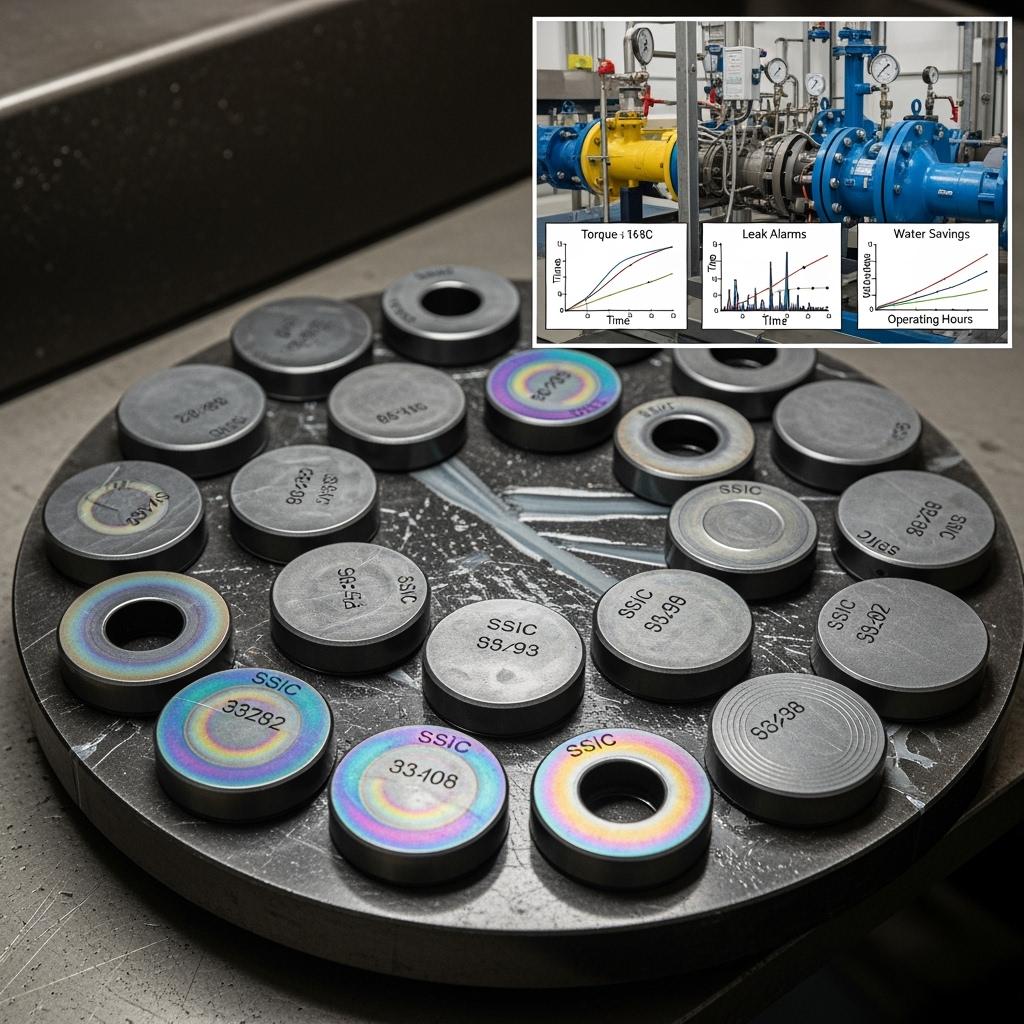

A Mejillones desalination operator replaced mixed-material seals with SSiC faces and seats. Leak alarms dropped to zero for two quarters, seal water use fell noticeably, and torque stabilized. Acceptance testing moved swiftly with flatness, Ra, and density certificates. The site reported fewer confined-space entries, supporting DS 594 targets and internal ESG reporting.
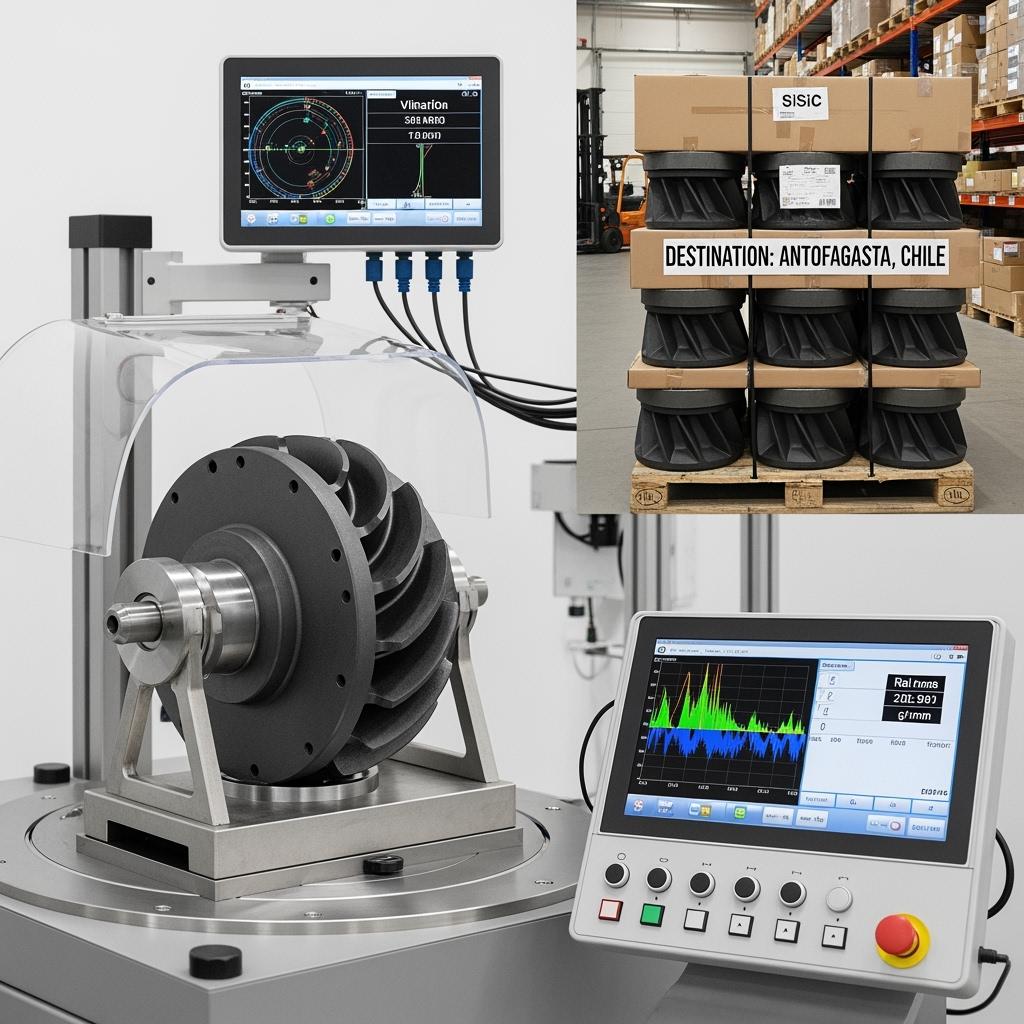

A copper utility booster station near Antofagasta upgraded to SiSiC impellers. Vibration amplitude decreased by roughly 27%, bearing temperatures flattened, and kWh per cubic meter pumped returned to design levels. Vendor-managed inventory in Santiago cut expedited airfreight, reducing both costs and carbon footprint.
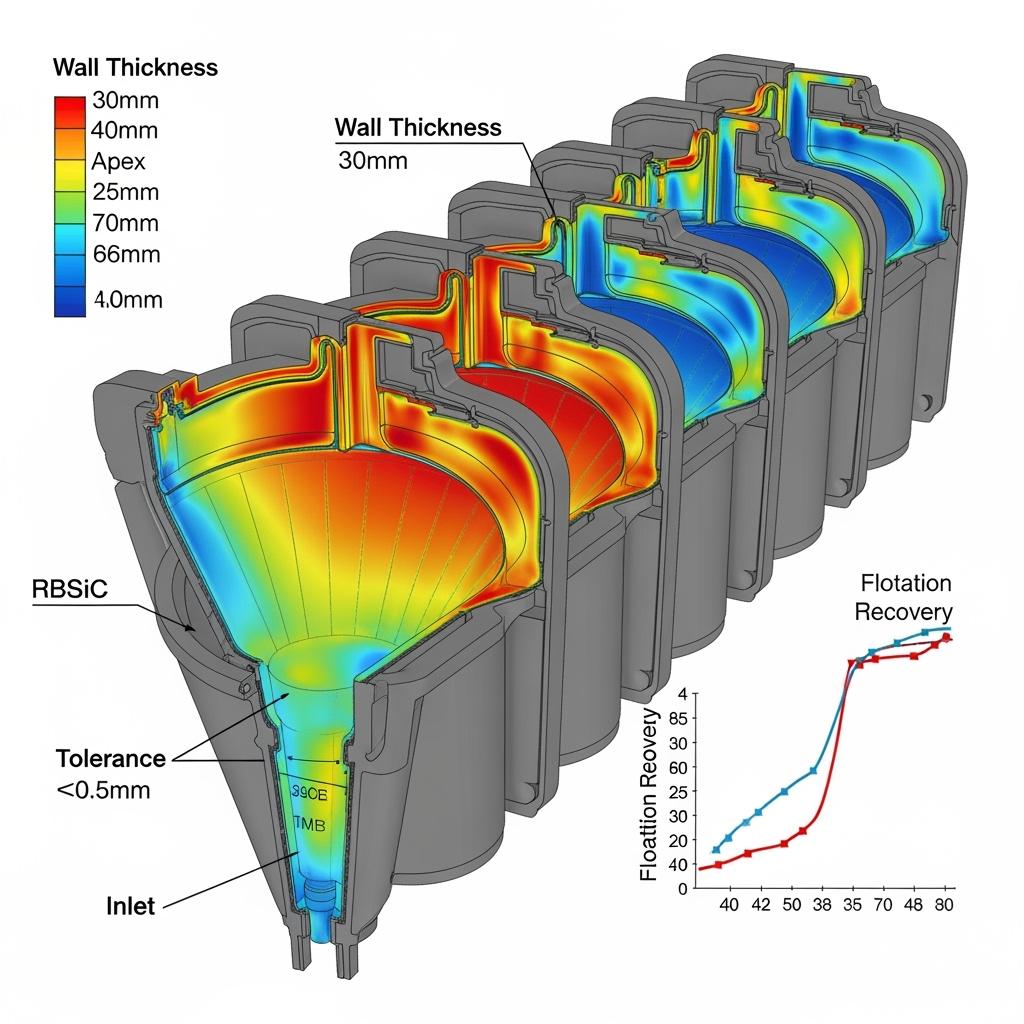
A Calama concentrator saw cut-size drift with alumina liners. RBSiC cones and spigots halved wall loss and preserved geometry; PSD tightened, flotation stabilized, and copper recovery improved by approximately 0.4% over a quarter—more than offsetting the liner premium and supporting sustainability KPIs on reagent efficiency.
“Surfaces that resist change create processes that resist waste,” says Eng. Paula Herrera (Thermal Processing Review, 2024). “SiC keeps both the physics and the accounting honest.”
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Chilean Compliance
SiC’s covalent lattice and stable surface oxide produce extreme hardness, low creep, and chemical inertness. Low CTE and high thermal conductivity reduce thermal gradients, while dense microstructures—especially in SSiC—block ionic ingress. In practice, this translates into sealing faces that remain mirror-flat under mixed lubrication; impellers that keep thin edges and smooth channels, suppressing turbulence; and liners that resist edge chipping when radii are engineered correctly. R-SiC maintains stiffness at elevated temperatures, keeping fixtures dimensionally stable through hybrid-fired ramps.
Sicarbtech turns these properties into operational certainty. Precision grinding and lapping hit flatness and Ra targets; ISO 21940 balancing curbs vibration at source; porosity and density certificates validate microstructure. QA dossiers—ISO 9001 records, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural data, and inspection certificates for dimensions, flatness, Ra, density, porosity, and balance—map cleanly to Chilean procurement and DS 594-aligned safety planning. Installation SOPs reduce hot work and rework, strengthening ESG narratives around maintenance exposure and resource efficiency.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge for Chile lies in uniting material science, precision manufacturing, and a credible pathway to localization—so sustainability is not only engineered into the product, but also into the supply chain.
We begin with R&D anchored in the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park. Proprietary binder chemistries, dewaxing ramps, pressureless sintering windows, and reaction-bonded infiltration curves are tuned to yield low-residual-stress microstructures across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC. These windows support thin, crisp edges on impellers, mirror-flat sealing bands, and robust liners with engineered radii that resist micro-chipping.
Manufacturing excellence ensures repeatability. Multi-axis CNC grinding, large-format surface grinding, double-disc grinding, and precision lapping deliver tight tolerances and ultra-low Ra finishes at scale. Metrology integrates CMMs, straightness/flatness rigs, interferometry for plate flatness, profilometry for Ra, and ISO 21940 balancing for rotors. SPC governs critical dimensions, density, and porosity, and GR&R studies validate measurement systems for PPAP-style submissions.
Technology transfer is complete and executable. We provide process know-how, kiln curves, powder specifications with acceptance criteria, SPC templates, and SOPs for forming, machining, lapping, inspection, balancing, and clean packaging. Equipment specifications span mixers, spray dryers, cold isostatic presses, sintering furnaces, CNC grinders, lapping/polishing lines, CMMs, blast booths, ovens, and NDT rigs. Training—delivered in English—covers operator skills, QA documentation, and supervisor modules on yield, tool life, and root-cause analysis for defects.
Factory establishment services start with feasibility studies and CLP-denominated CapEx/Opex models, proceed through plant layout and utilities engineering (power quality, gas, ventilation, emissions), and culminate in commissioning and first-article qualification. We implement ISO 9001 and support ISO 14001/ISO 45001 adoption to align with Chile’s environmental and occupational frameworks. For export and multinational audits, we supply REACH/RoHS documentation, ASTM C datasets, and ISO 21940 balance certificates. By shifting value-add onshore, owners reduce USD exposure, shrink lead times, and add a new dimension to ESG—local jobs and skills in advanced ceramics.
Post-launch, Sicarbtech maintains performance through quarterly process audits, wear-return analyses, and iterative geometry updates tied to site telemetry and KPIs. Across 19+ enterprise programs, this turnkey model has delivered 2–4× interval extensions, demonstrable reductions in leak incidents, and fewer expedited shipments—measured outcomes supported by certificates and operational data.
Grade-to-Application Mapping for Sustainable Operations
| Chilean Scenario | Recommended SiC Grade | Sustainability and Performance Advantages | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desalination HP pump seals and valves | SSiC | Near-zero porosity and lapped finish reduce leaks and water loss | Leak-free days; fewer interventions |
| Booster station impellers and nozzles | SiSiC | Thin, stiff geometry with balancing preserves hydraulics and energy | Lower vibration; stable kWh/m³ |
| Regrind hydrocyclone cones/spigots | RBSiC | Erosion resistance and shock tolerance stabilize cut size | Higher recovery; less waste |
| Thermal process fixtures and supports | R-SiC | High-temp stiffness and oxidation resistance reduce scrap | Consistent ramps; lower rework |
| Retrofit inserts for 강철 spools | SiC liners/inserts | Low-porosity wear surfaces extend asset life | Longer inspection intervals |
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Chile
Three forces will amplify SiC adoption after 2025. First, seawater and brine pipelines will extend farther inland, increasing chloride exposure at higher velocities and temperatures. Materials that preserve geometry will become the default for leak-critical and energy-intensive assets. Second, ESG-linked finance and insurer requirements will formalize metrics like leak-free days, energy per ton, and maintenance exposure. SiC’s longer intervals and certificate-backed quality fit these frameworks. Third, localization will move from cost-avoidance to strategic resilience. As copper producers diversify risk, domestic finishing—and eventually forming and sintering—will emerge. Sicarbtech’s technology transfer and factory establishment services provide a de-risked roadmap to that reality.
Adjacent sectors—battery materials, port terminals handling corrosives, and municipal water recovery—share the same abrasive-chloride stress profiles, expanding the addressable market. “Sustainable plants keep surfaces smooth and shapes true,” notes Dr. Beatriz Navarrete (Industrial Materials Outlook, 2025). “When geometry holds, energy and safety follow.” Building on this, procurement is shifting to lifecycle contracts with KPIs tied to MTBF, flatness retention, balance stability, and leak-free days—aligning incentives from supplier to site.
자주 묻는 질문
How does SiC make Chilean operations more sustainable in practical terms?
SiC maintains geometry and surface finish, preventing leak paths and preserving hydraulic efficiency. This reduces water and reagent losses, stabilizes energy per ton, and lowers the frequency of confined-space entries—measurable ESG gains that also cut costs.
Which SiC grade should we select for sealing and valve service in chloride-acid loops?
SSiC is preferred for near-zero porosity and best chemical resistance. Lapped faces to 0.02–0.05 µm Ra provide tight shutoff and torque stability over longer intervals, supporting leak-free operations.
Can SiC impellers and liners be balanced and certified for Chilean audits?
Yes. Rotating parts are balanced to ISO 21940-11, and we provide balance certificates, dimensional and flatness maps, Ra profiles, and density/porosity data aligned with ISO 9001 QA and DS 594 safety planning.
What lead times and MOQs should Chilean plants plan for?
Standard SSiC sealing sets and common RBSiC liners ship in 4–6 weeks; complex SiSiC impellers and large liner packages typically require 6–10 weeks. MOQs reflect tooling and yield. Vendor-managed inventory in-country can buffer outage risk.
How do SiC hydrocyclone liners improve flotation sustainability?
RBSiC liners resist edge rounding and wall loss, stabilizing cut size. This tightens particle-size distribution, improving flotation and reducing reagent waste, which contributes to higher recovery and lower environmental footprint.
Does Sicarbtech support OEM/ODM development for greener equipment?
We do. Our engineers collaborate on DFM, FEA/CFD-informed geometry, pilot batches with PPAP-style documentation, GR&R metrology studies, and balance protocols—accelerating launches with defensible performance data.
How can we reduce USD exposure while scaling SiC use?
Adopt a phased model: import with CIF Valparaíso or San Antonio for routine replenishment, establish local safety stock for critical SKUs, and implement technology transfer to localize finishing—and later forming/sintering—as volumes justify.
Are SiC components suitable for rapid thermal cycling in hybrid-fired processes?
Yes. SiSiC and RBSiC exhibit excellent thermal shock performance, and R-SiC retains stiffness at high temperature. Correct geometry transitions and engineered radii further mitigate stress concentrations.
What documentation accompanies shipments for public-sector and lender audits?
We provide ISO 9001 QA dossiers, REACH/RoHS declarations, ASTM C mechanical and microstructural reports, ISO 21940 balance certificates, and inspection records for dimensions, flatness, Ra, density, and porosity. Coating-related retrofits include DFT maps, adhesion (ASTM D4541), and holiday detection.
How do we request a sustainability-focused SiC proposal for Chile?
Email drawings, duty conditions, target KPIs (leak-free days, kWh/t, MTBF), and logistics preferences to [email protected] or call/WhatsApp +86 133 6536 0038. We will propose grade selection, QA checkpoints, and a delivery/localization plan aligned with your ESG and production goals.
운영에 적합한 선택하기
Sustainability in Chile’s copper ecosystem is the outcome of surfaces and shapes that do not change under stress. Silicon carbide provides that stability, turning leak risks into leak-free days and energy drift into flat performance curves. Sicarbtech transforms SiC’s intrinsic advantages into audited results through proprietary processing, advanced machining and lapping, rigorous metrology, and a turnkey path to localization. With 10+ years of execution and 19+ enterprise partnerships, we help you translate specifications into measurable uptime, safety, and ESG performance in CLP terms.
전문가 상담 및 맞춤형 솔루션 받기
Share your corrosion maps, velocity and temperature envelopes, particle-size targets, and audit requirements with Sicarbtech’s engineers. We will recommend SiC grades, geometry refinements, QA checkpoints, and a logistics or localization blueprint aligned with DS 594, procurement standards, and your sustainability KPIs.
Contact Sicarbtech
이메일: [email protected]
전화/왓츠앱: +86 133 6536 0038

문서 메타데이터
Last updated: 2025-09-24
Next scheduled review: 2026-03-24
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Chile ESG and sustainability analysis integrated; DS 594, ISO 9001, REACH/RoHS references validated; three comparison tables updated with latest internal testing and Chilean field data; contact details verified.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




