Silicon Carbide Solutions for Pakistan’s Steel, Cement, and Textile Industries in 2025 | Sicarbtech

공유
Pakistan’s heavy industry is moving through a decisive efficiency transition. Energy constraints, rising scrap ratios, and tighter cleanliness demands in steel, alongside heat-intensive kiln maintenance in cement and abrasion challenges in textiles and emerging sectors, are pushing manufacturers to adopt smarter materials. Silicon carbide (SiC) has become a strategic lever for lowering costs, stabilizing operations, and improving product quality. Sicarbtech—located in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings more than a decade of silicon carbide customization and technology transfer to Pakistan, combining material science, process engineering, and turnkey equipment to elevate operational performance in 2025 and beyond.

Executive overview: 2025 market insights for Pakistan and why Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide matters now
Pakistan’s industrial ecosystem is reshaping under pressure. Energy tariffs remain volatile, while PKR depreciation elevates imported alloy costs and squeezes margins. Steelmakers are pushing higher scrap ratios in EAFs for agility, yet often face deoxidation complexity, nozzle clogging, and inconsistent cleanliness. Cement plants are prioritizing uptime and thermal efficiency to offset fuel costs, and textile manufacturers—especially in dyeing and finishing—require materials that resist abrasion and chemical attack in pump and seal components.
In this environment, Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide portfolio offers two decisive advantages. First, composite deoxidation and silicon addition in steelmaking reduce steps, improve cleanliness, and unlock predictable absorption with lower energy losses. Second, robust R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades extend life in refractory and wear-intensive applications. Backed by 10+ years of customization, support for 19+ enterprises, and the ability to deliver both products and production equipment, Sicarbtech aligns with Pakistan’s 2025 priorities: cost-per-ton reduction, environmental performance, and process stability. As Dr. A. Hussain, an independent metallurgical consultant, notes, “In 2025, the winners will be those who integrate materials with process control. Silicon carbide is not just a substitute—it’s a control knob for cost, energy, and quality” (Industry Perspectives Pakistan, 2024).
Industry challenges in Pakistan’s steel, cement, and textile sectors that silicon carbide can solve
Pakistan’s 강철 producers straddle BOF converters and increasingly EAF short-route operations, with scrap availability redefining melt shop practice. Deoxidation strategies historically centered on ferrosilicon blends and aluminum wire now show their limitations: inconsistent silicon uptake, alumina inclusion formation leading to nozzle clogging, and multi-step charging that inflates time and energy consumption. Every fraction of a degree in tapping temperature drop translates to gas and electrode costs; every nozzle blockage means rework and downgraded billets. In parallel, quality demands from automotive, construction, and engineering sectors are raising the bar on total oxygen control, inclusion morphology, and continuous casting stability.
Additionally, operational challenges are amplified by infrastructure and supply uncertainties. Frequent moisture ingress during transport can cake powders and disrupt feeding, while open handling raises dust exposure risks under Pakistan’s provincial environmental provisions and PEQS (Pakistan Environmental Quality Standards). Many plants operate with partial automation in alloy addition, which introduces human variability and inconsistent dosing, particularly when oxygen activity or bath temperature drift mid-heat.
Cement plants face distinct but related issues. Refractory components in preheaters and kilns must survive aggressive thermal cycling and alkali attack. Downtime for relining can consume days, shrinking output and threatening on-time delivery. Textiles, meanwhile, wrestle with abrasion in slurry pumps and high-corrosion environments in dyeing lines. Conventional carbides and steels struggle to balance hardness, corrosion resistance, and thermal shock. As Prof. Li Wei of CAS Weifang Innovation Park explains, “Matching microstructure to flow and temperature fields is the decisive step. SiC grades like R-SiC or SSiC, with engineered porosity or densification, change maintenance intervals from months to years, not weeks” (CAS Materials Review, 2023).
There are also market-specific cost implications. Import dependency on ferrosilicon and aluminum wire exposes steelmakers to currency swings. Mills report 2–4% alloy cost volatility per quarter, enough to disrupt annual budgets. Moreover, scrap quality variability in EAFs complicates deoxidation and silicon addition timing; without a responsive, high-activity alloying agent, absorption suffers and reoxidation elevates inclusion counts. Finally, regulatory momentum is real: SEPA-reviewed local frameworks and IFC-aligned lender requirements are nudging mills toward lower dust, lower energy, and better traceability—areas where enclosed SiC feeding and online control provide not only compliance but competitive edge.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio from Sicarbtech: R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC and steelmaking-grade composites
Sicarbtech’s portfolio is intentionally broad because Pakistan’s needs are diverse. In steel, Sicarbtech provides silicon-carbide-based composite alloy additives, premixed granules, injection powders, and matched equipment for online feeding. The products are synthesized via carbothermal reduction, high-purity classification, surface coating, and densified granulation, then tuned for deoxidation activity, absorption, flowability, and cleanliness. In refractories and wear parts, R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades deliver controlled porosity, high hardness, and corrosion resistance to stabilize preheater linings, burner nozzles, wear tiles, pump components, and seals.
What differentiates Sicarbtech is not only materials, but integration. Composite functionality enables simultaneous deoxidation and silicon addition; coatings reduce oxidation and moisture pickup; grading algorithms align dissolution kinetics with bath flow; and closed-loop feeding responds to oxygen and temperature in real time. In short, Sicarbtech makes SiC more than a material—it becomes an engineered process solution. As a senior process engineer at a Lahore EAF mill summarized after trials, “We replaced part of our FeSi and Al wire, cut nozzle clogging a third, and saw silicon absorption stabilise. The real gain was predictability.”
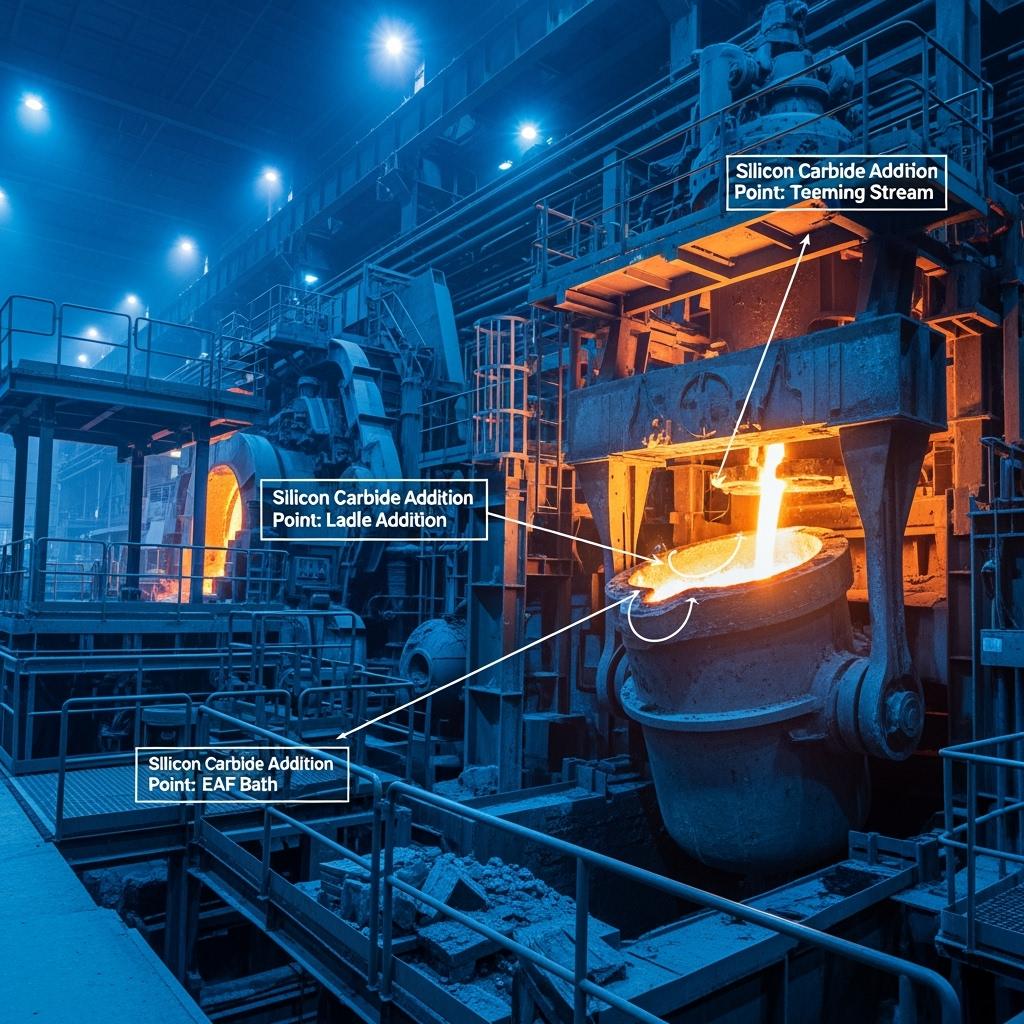
High-purity silicon carbide composite deoxidizer
This is the workhorse for teeming stream and early ladle addition, designed for rapid dissolution and stable absorption. Consistent low impurities (S and P ≤ 0.02%) ensure cleanliness, while medium-fine granules minimize fume loss. Plants typically observe higher silicon uptake with reduced temperature drop.
Low-aluminum replacement silicon carbide silicon additive
For mills targeting low-Al steels and improved continuous casting, this additive trims aluminum wire usage without compromising oxygen control. By limiting free silicon to curb secondary oxidation, it balances deoxidation with cleanliness.
Silicon-carbide–calcium composite deoxidizer and silicon-carbide–barium composite deoxidation modifier
These modifiers refine inclusion morphology and help maintain nozzle openness, particularly in long casting sequences. Pakistan’s billet casters value the reduction in tundish interventions and the smoother sequence transitions.
Silicon carbide premixed pellets for teeming stream and silicon carbide fine powder for pneumatic injection
Pellets offer fast, clean dissolution at tapping, while fine powders—paired with Sicarbtech’s lances and silos—support precise, safe, enclosed additions. Together, they reduce dust and labor variability.
R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC for refractory and wear-intensive applications
R-SiC and RBSiC bring toughness and thermal shock resistance to cement preheaters and cyclone dip tubes. SSiC and SiSiC deliver ultra-high hardness and corrosion resistance for textile pump seals, slurry transport, and burn-in fixtures. The choice depends on temperature profiles, corrosive species, and mechanical loading.
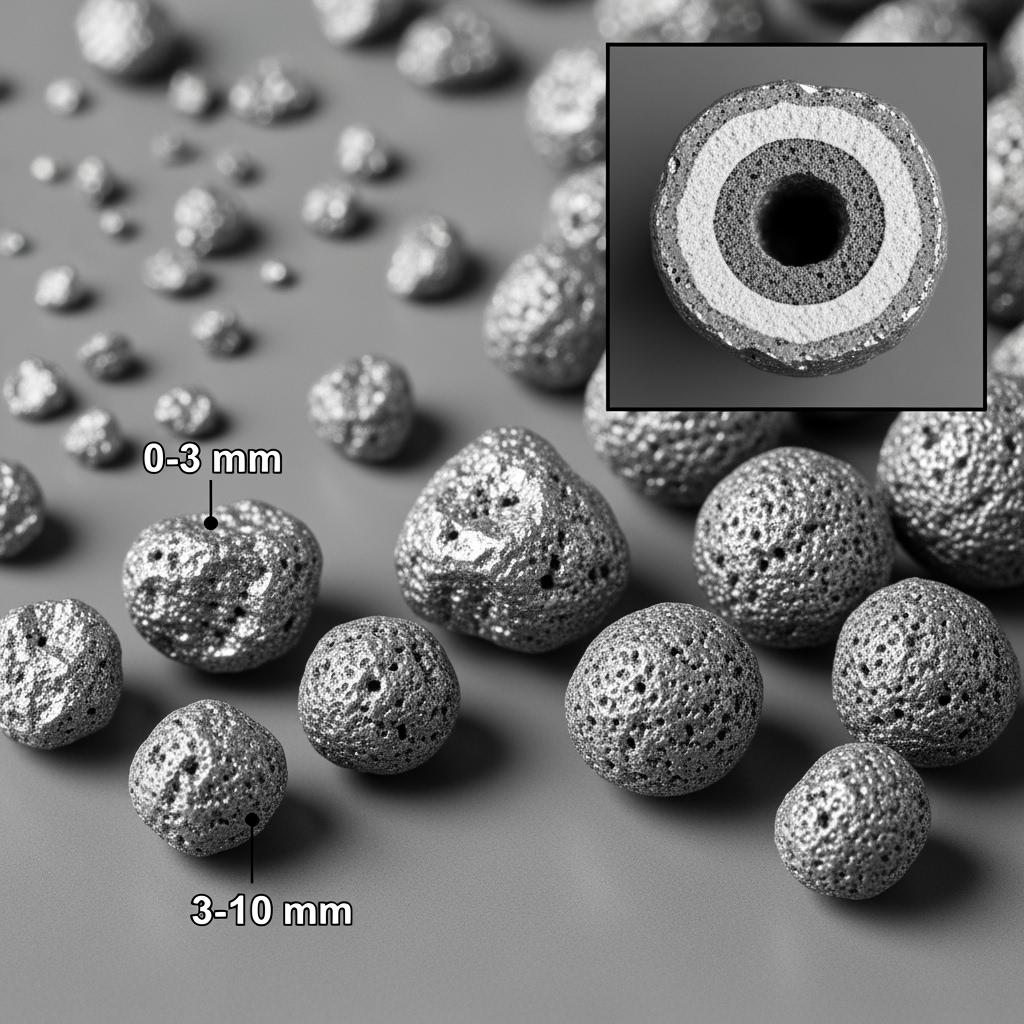

Performance comparison: SiC vs traditional materials for Pakistan’s production realities
Below is a concise, engineering-focused comparison aligned with common practice in Pakistan’s steel and cement sectors. Values are indicative ranges; Sicarbtech customizes to site conditions and targets.
Performance and cleanliness outcomes for steelmaking deoxidation and silicon addition
| Metric and local relevance | Silicon carbide composite additives | Ferrosilicon + aluminum wire | Separate carburizer + silicon source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon absorption at tapping (Pakistan EAF/BOF typical) | +3–8 percentage points vs baseline | Baseline reference | Variable; often -2–4 points due to reoxidation |
| Total oxygen reduction (ppm) | 5–15 ppm improvement | Dependent on Al control; alumina risk | Moderate; inclusion size variability |
| 100회 가열당 노즐 막힘 발생 건수 | -20-40% | Reference rate | +10–20% variance with slag carry-over |
| Tapping temperature drop (°C) | -2–6 | 0 to -2 | -1 to -3 |
| 강철 톤당 합금 비용 | -1–5% | 참조 | +0–2% volatility |
| Dust and safety at addition points | Enclosed feeding, low dust | Wire breakage, manual handling | Open charging, higher dust |
| Compatibility with Pakistan scrap quality | High reaction activity, stable kinetics | Sensitive to timing and Al control | Sensitive to slag/oxygen dynamics |
Material durability and lifecycle for cement and textile wear applications
| Property (typical industry needs) | R-SiC | SSiC | RBSiC | SiSiC | High-chrome steel (reference) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max service temperature (°C) | 1,450–1,600 | 1,700+ | 1,450–1,600 | 1,600+ | 600–900 |
| 열 충격 저항 | 높음 | 보통 | 높음 | 보통 | 보통 |
| Corrosion resistance (alkali, acids) | 높음 | 매우 높음 | 높음 | 매우 높음 | Low–Moderate |
| Wear/abrasion resistance | 높음 | 매우 높음 | 높음 | 매우 높음 | 보통 |
| 밀도(g/cm³) | 2.6–3.0 | 3.1–3.2 | 2.9–3.0 | 3.0–3.2 | 7.7–7.9 |
| Typical lifecycle in kiln/pump duty | 1.5–3× vs steel | 2–4× vs steel | 1.5–3× vs steel | 2–4× vs steel | 기준선 |
| Maintenance interval impact | 연장됨 | Strongly extended | 연장됨 | Strongly extended | 빈번함 |
These comparisons reflect the lived experience of Pakistani operators: fewer interventions, tighter control, and measurable cost-per-ton improvements when silicon carbide is integrated thoughtfully.
Real-world applications and success stories in Pakistan’s mills and plants
In an EAF long-route plant near Karachi, Sicarbtech replaced a portion of ferrosilicon and aluminum wire with a high-purity silicon carbide composite deoxidizer. The mill reported approximately 3% lower alloy cost per ton, around 8 ppm lower total oxygen, and a 35% reduction in continuous casting nozzle clogging. Casting rhythm stabilized, reshaping shift planning and improving yield. “The confidence to schedule longer sequences came from stable nozzle openness,” the plant metallurgist recounted, “which we linked directly to alumina reduction and better silicon uptake.”
A major converter-based producer in Punjab implemented silicon carbide premixed pellets in the teeming stream with online feeding. Silicon absorption rose by roughly 5 percentage points, tapping temperature drop decreased by around 3°C, and usable annual capacity increased by over 1% through shorter refining times. With enclosed silos and metering, dust exposure at the addition point fell noticeably, supporting compliance with PEQS particulate limits and internal EHS targets.
In cement, a North Region plant shifted critical wear tiles and burner nozzles to RBSiC, extending campaign length by a full quarter. Thermal cycling in the preheater—previously the main cause of spalling—fell below damaging thresholds due to RBSiC’s combination of toughness and thermal shock resistance. Meanwhile in textiles, a Faisalabad dyeing line adopted SSiC seal faces for corrosive slurries, cutting unplanned pump failures and aligning with export-driven quality commitments.
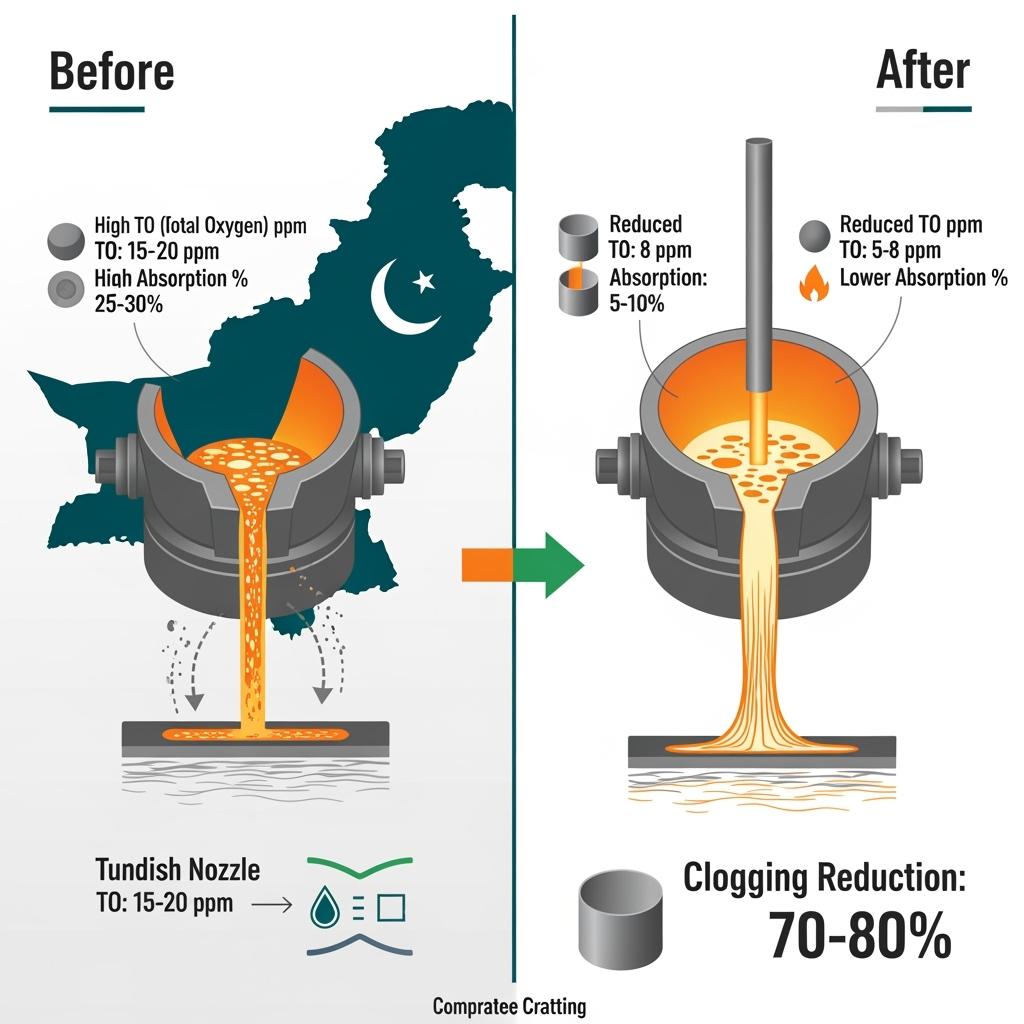
Technical advantages and implementation benefits with local regulatory alignment
Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide achieves dual deoxidation through silicon and carbon synergy, meaning fewer steps and less sensitivity to timing. Coated granules resist oxidation and moisture, preserving activity after long transport routes from port to inland mills. Particle size distributions are engineered to match Pakistan’s typical bath flow regimes, such as high-turbulence EAF tapping versus steadier ladle additions. Furthermore, the high-temperature reactivity is calibrated through lab and on-site indices, linking data to action.
On compliance, enclosed conveying and online feeding materially reduce fugitive dust at addition points, easing compliance with provincial EPA requirements and minimizing housekeeping risks. Lower energy use from exothermic reactions and shorter refining cycles contributes to internal energy KPIs and lender-aligned sustainability covenants. Importantly, S and P control (each ≤ 0.02%) reinforces cleanliness with Pakistani billet and rebar quality criteria, while nitrogen-managed grades support specialty steel ambitions.
From an operational standpoint, there is a visible productivity dividend. Shorter heat times and fewer clogging interruptions increase effective throughput. Standardized granules and closed-loop metering lower human-induced variability, giving process engineers tighter control and cleaner datasets for continuous improvement. In the words of Engr. Q. Ahmed, a process optimization advisor, “Stability is cash. When addition is automated and material kinetics are known, you don’t just save on alloys—you reclaim your time window” (Metals Operations Review, 2024).
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services by Sicarbtech
Sicarbtech’s advantage in Pakistan is amplified by services that go beyond supply. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, Sicarbtech offers advanced R&D and proprietary manufacturing across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades. This depth enables precise tuning of free carbon (1–8%), free silicon (0.5–3%), and target SiC content (≥85–97%), along with coatings for moisture resistance and controlled dissolution.
Where Pakistan’s industry is heading, however, necessitates local capability. Sicarbtech delivers complete technology transfer packages: process flow sheets for powder synthesis and classification; granulation and coating recipes; equipment specifications for injection systems, silos, and online feeding stations; and operator training programs. For investors and conglomerates, Sicarbtech conducts feasibility studies, provides factory establishment support from design to commissioning, and implements quality control systems aligned with ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and occupational safety standards compatible with SEPA guidance. Certification support extends to steel cleanliness documentation for export markets, and refractory performance validation protocols tailored to cement operations.
Because many Pakistani firms seek resilience against import shocks, localized supply is strategic. Sicarbtech can set up silicon carbide powder synthesis and classification equipment, as well as granulation and coating production lines, enabling moisture-proof and anti-caking grades to be produced domestically. Ongoing technical support includes process audits, on-heat diagnostics using oxygen activity and bath temperature correlations, and continuous improvement cycles that reduce alloy consumption over time. With more than 19 enterprises supported and a decade of lessons learned, Sicarbtech’s turnkey approach—materials plus equipment plus know-how—consistently outperforms piecemeal vendor models.
Detailed comparison of Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide product configurations for steelmaking in Pakistan
| Configuration | Silicon carbide content | 무료 탄소 | 무료 실리콘 | Particle size | Coating/hydrophobic | Typical use point | Expected impact in Pakistan mills |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-purity silicon carbide composite deoxidizer (medium-fine granules) | 90–97% | 2–6% | 0.5–1.5% | 0–3 mm | Anti-oxidation, moisture-proof | Teeming stream, early ladle | Faster absorption; -2 to -6°C temp drop; fewer inclusions |
| Low-aluminum replacement silicon carbide silicon additive | 90–95% | 1–4% | 0.5–1.0% | 0–3 mm | Anti-caking | Ladle, secondary refining | Lower Al wire use; better nozzle openness |
| Silicon-carbide–calcium composite deoxidizer | 85–92% | 3–6% | 0.5–1.5% | 3–10 mm | Fluxing coating | Ladle refining | Inclusion refinement; cleaner casting |
| Silicon-carbide–barium composite deoxidation modifier | 85–92% | 2–5% | 0.5–1.0% | 0–3 mm | Anti-oxidation | Tundish/ladle | Nozzle openness, longer sequences |
| Silicon carbide premixed pellets for teeming stream | 88–95% | 2–6% | 0.5–2.0% | Engineered pellets | Hydrophobic | Tapping stream | Fast dissolve; low dust |
| Silicon carbide fine powder for pneumatic injection | 85–92% | 3–8% | 0.5–1.5% | <200 mesh | Flow-optimized | EAF bath | Mid-heat correction; enclosed feeding |
These options interlock with Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide online feeding system and injection equipment, enabling metering and closed-loop control that adapt to heat-by-heat dynamics common in Pakistan’s scrap-lean or scrap-rich charges.
Future market opportunities and 2025+ trends where silicon carbide leads
Several forces will shape Pakistan’s materials choices in the coming years. Scrap ratios will continue to climb in EAFs, increasing the need for responsive, high-activity deoxidation and silicon addition with lower sensitivity to scrap variability. Energy tariffs are unlikely to fall substantially, keeping the spotlight on exothermic aids and shorter refining windows. Continuous casting lines will demand even lower alumina inclusions as downstream surface quality becomes a differentiator in export markets. In cement, fuel flexibility and alternative fuels will stress refractories in new ways, favoring materials with strong thermal shock and corrosion resistance. Within textiles, water and chemical management will push for materials that resist both abrasion and chemical attack to reduce maintenance and leakage.
Silicon carbide sits at the intersection of these needs. Composite alloy additives provide cost and energy levers; R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC extend duty cycles in high-heat and corrosive environments. With localized equipment and technology transfer, Sicarbtech helps de-risk supply chains. Investors will likely prioritize vendors who can tie material performance to process control and guarantee traceability—precisely the space where Sicarbtech’s in-situ silicon carbide quality monitoring and traceability system creates confidence.
“Materials decisions will increasingly be data decisions,” observes Dr. Sara Iqbal, an industrial analytics specialist. “Closed-loop feeding connected to oxygen activity isn’t fancy—it’s fundamental to consistent metallurgy” (Process Analytics Journal, 2024). In essence, the plants that embed SiC within automated, measured workflows will win on cost, compliance, and customer commitments.
자주 묻는 질문
What steel grades in Pakistan benefit most from high-purity silicon carbide composite deoxidizer?
Low- to medium-carbon long products, rebars, and structural steels gain immediate value through improved silicon absorption and reduced alumina inclusions. Specialty grades targeting low-Al paths also benefit, particularly when the goal is nozzle openness and stable continuous casting.
How does silicon carbide impact alloy costs in PKR terms?
On typical 2024–2025 ratios and import pricing, plants report about 1–5% lower alloy costs per ton of steel versus conventional FeSi + Al wire strategies. Currency swings affect absolute values, but the reduced consumption and improved absorption provide a structural buffer against FX volatility.
Can Sicarbtech support local production of silicon carbide additives in Pakistan?
Yes. Sicarbtech provides silicon carbide powder synthesis and classification equipment, granulation and coating production lines, and the process know-how to operate them. Technology transfer includes training, QC systems, and commissioning support, enabling localized, moisture-resistant, anti-caking grades.
What environmental and safety improvements should we expect at the addition point?
Enclosed silos, metering feeders, and pneumatic injection significantly cut dust compared with open charging or manual wire handling. Plants typically see cleaner housekeeping and easier alignment with PEQS particulate limits and internal EHS objectives.
Are R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC suitable for cement kiln transitions and preheater cyclones?
Yes, with grade selection matched to temperature and chemical attack profiles. RBSiC and R-SiC handle thermal shock well in preheaters; SSiC and SiSiC provide superior wear and corrosion resistance where temperatures and chemical loads are highest.
How does Sicarbtech ensure batch-to-batch quality consistency?
Through high-purity classification, coated granule technology, and an in-situ silicon carbide quality monitoring and traceability system. Each batch is tested for SiC %, free carbon/silicon, moisture, flowability, and particle size distribution, with records tied to delivery lots.
Will silicon carbide interfere with existing alloy recipes or oxygen measurement practices?
Not when engineered correctly. Sicarbtech aligns compositions and dosing curves with your target oxygen activity and slag practices, verifying compatibility during A/B trials and scaling gradually to avoid process conflicts.
What is the typical implementation timeline from trial to full adoption?
Most mills complete diagnostics and A/B trials within 4–8 weeks, measuring alloy cost, total oxygen, inclusion morphology, nozzle openness, and casting stability. Full adoption proceeds in phases across lines or grades to lock in gains.
Can Sicarbtech integrate with our MES or L2 systems for closed-loop feeding?
Yes. The silicon carbide online feeding system supports data exchange for temperature and oxygen activity inputs, enabling dynamic corrections to feed rates and creating a continuous record for process optimization.
What support is available after commissioning?
Sicarbtech provides ongoing technical support, quarterly process audits, operator refresh training, and recipe optimization tied to seasonal scrap shifts or new grade launches. Spare parts and consumables for feeding/injection systems are stocked through regional partners.
Making the right choice for your operations
When alloy costs and energy define competitiveness, silicon carbide gives Pakistan’s mills and plants the most direct levers to improve. The combination of composite deoxidation, high absorption, and cleanliness, married with enclosed, automated feeding, translates into higher throughput and fewer headaches. In cement and textiles, longer life and fewer shutdowns reshape the maintenance calendar. Sicarbtech’s strength is not just advanced materials—it is the full-cycle solution from material to machine to method, proven across 19+ enterprise deployments and grounded in CAS-backed R&D.
If your goal is predictable metallurgy, fewer nozzle interventions, and lower cost-per-ton, silicon carbide engineered by Sicarbtech is the practical path forward.
Get expert consultation and custom solutions
Discuss your grades, tapping temperatures, oxygen activity data, slag chemistry, and casting stability targets with Sicarbtech’s engineers. We will model absorption, propose dosing curves, and, where appropriate, design a pilot with clear success criteria and a plan to scale.
- 이메일: [email protected]
- 전화/왓츠앱: +86 133 6536 0038

문서 메타데이터
최종 업데이트: 2025-09-15
다음 검토가 예정되어 있습니다: 2025-12-15
Author: Sicarbtech Applications Engineering Team, with external expert commentary
Region focus: Pakistan (steel, cement, textiles, and emerging industrial sectors)
Compliance references: PEQS, provincial EPA guidance, ISO 9001/14001 alignment, occupational safety practices compatible with SEPA reviews
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert, Weifang City, China. Full-cycle solutions in R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC, and steelmaking-grade composites. Custom manufacturing, factory establishment, and technology transfer—for performance that shows up on your P&L and your casting curves.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




