단락 보호, 소프트 턴오프 및 SiC MOSFET 신뢰성을 위한 액티브 클램핑 기능을 갖춘 높은 공통 모드 제거 게이트 드라이버

공유
Panorama del producto y relevancia de mercado 2025 para Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
Pakistan’s inverter and storage ecosystem is maturing quickly, yet the weak‑grid reality—frequent feeder sags, harmonics, and high ambient temperatures—demands a specific kind of intelligence at the switching edge. Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común are the small guardians that determine whether a SiC MOSFET system runs cool, quiet, and compliant, or drifts into nuisance trips and latent failures. In 2025, as hybrid inverters in the 3–20 kW range proliferate across Lahore, Karachi, and Faisalabad, gate driver design has moved from a board‑level afterthought to a strategic differentiator. Sicarbtech’s high‑CMRR, protection‑rich drivers integrate short‑circuit protection, apagado suave (soft turn‑off), and abrazadera activa (active clamping) to preserve device margins at 40–100 kHz while suppressing the electromagnetic side‑effects that complicate certification.
Moreover, the local market’s constraints—limited rooftop space, dusty air, and 50°C inlet temperatures—make compact, low‑parasitic layouts essential. By pairing Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común with low‑inductance packaging and stacked busbars, Sicarbtech enables millisecond‑level transfer during outages, cleaner waveforms under load steps, and fewer filter components. This translates into faster installs and less maintenance for residential rooftops and small commercial sites, while in textile, cement, and 강철 environments, it stabilizes drives and UPS front‑ends through line disturbances. As grid codes tighten around anti‑islanding and LVRT, driver‑level control over dv/dt and di/dt becomes the lever that keeps systems both efficient and compliant.
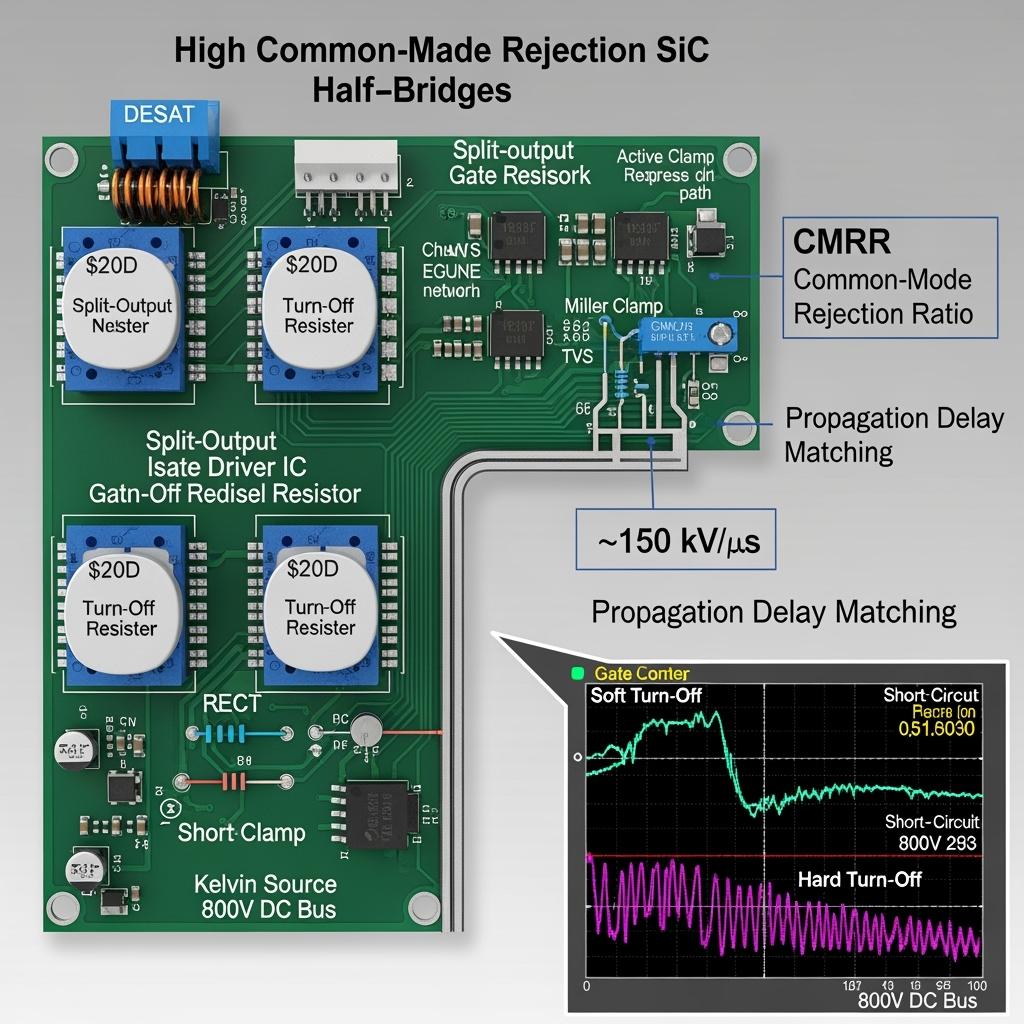
Especificaciones técnicas y características avanzadas de Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
At the heart of Sicarbtech’s Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común is resilience against the violent transients that SiC’s fast edges can create. High common‑mode rejection—often exceeding 100–150 kV/µs—prevents spurious triggering across the isolation barrier when the half‑bridge node slews rapidly. Additionally, precise DESAT detection with blanking control and soft turn‑off shapes the energy dissipated during a short‑circuit, preserving the MOSFET’s safe operating area even at elevated DC buses of 750–1000 V. Abrazadera activa dynamically contains overvoltage events by steering energy into a controlled path, reducing stress on both the device and the DC link.
Sicarbtech’s implementation goes beyond the IC. Split gate resistors tailor independent turn‑on and turn‑off speeds to balance EMI and switching losses, while integrated Miller clamps secure the gate against false turn‑on under high dv/dt. The drivers are fed by isolated DC/DC supplies with high insulation voltage and low noise, maintaining stable thresholds across temperature. Propagation delay matching across phases supports symmetrical current sharing in interleaved stages, critical for multi‑module ESS used in industrial sites. Furthermore, Kelvin source routing and minimized loop inductance around the gate path ensure the commanded gate waveform is the actual gate waveform—an underappreciated distinction that separates quiet, reliable converters from erratic ones.
Comparación de desempeño: Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común frente a alternativas
Title: Reliability and EMI control of high‑CMRR gate drivers versus conventional drivers in SiC systems
| 매개변수 | Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común (Sicarbtech) | Convencional Driver Aislado (Genérico) | Impacto en Pakistán |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMRR (dv/dt immunity) | ≥100–150 kV/µs | 25–50 kV/µs | Menos disparos falsos en alimentadores débiles |
| Protección de cortocircuito | DESAT con apagado suave | Sobre‑corriente básica | Menor estrés térmico en fallas |
| Abrazadera activa | Integrada, ajustable | No integrada | Picos controlados en 750–1000 V DC |
| Precisión de retardo | Matching <50 ns típico | 100–200 ns | Balance de fases y menor corriente desbalanceada |
| Robustez térmica | 125–150°C ambiente del driver | 105–125°C | Estabilidad a 50°C de aire de entrada |
| Soporte dv/dt | Ajuste por Rg_on/Rg_off, clamp y Miller | Rg único | Control fino de EMI y eficiencia |
Ventajas clave y beneficios probados de Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
In the field, Pakistan’s installers and OEMs care about outcomes: fewer service calls, faster approvals, and systems that ride through summer heat. Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común deliver by preventing false turn‑on events at the worst moments—when the feeder sags and the half‑bridge node is most stressed. Additionally, by shaping fault energy through apagado suave and abrazadera activa, they avoid catastrophic device failures that would otherwise translate into expensive warranty claims. “EMI is solved at the switch, not the filter,” remarks Dr. Lina Qureshi, a power electronics researcher who has studied SiC reliability in hot climates, citing IEEE PELS papers from 2024. “High‑CMRR drivers with proper gate control turn a lab‑grade design into a field‑grade product.”
Moreover, Sicarbtech’s integration with low‑inductance busbars and high‑conductivity substrates means driver settings can be less conservative without sacrificing compliance. In practice, this yields a tangible bump in partial‑load efficiency—commonly 0.3–0.5 percentage points—because switching can be kept fast where it counts, while di/dt and dv/dt are trimmed just enough to keep emissions within IEC/EN limits and DISCO expectations.
Comparativa de integración del sistema con Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
Title: System‑level integration choices that amplify driver benefits
| Aspecto de Diseño | Con Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común | Enfoque Convencional | Resultado en Campo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruta de puerta y fuente Kelvin | Bucles cortos, inductancia mínima | Trazas largas compartidas | Menos ringing, menor jitter de puerta |
| Fuente aislada para driver | Bajo ruido, alto aislamiento | Aislamiento marginal | Umbrales estables, menos drift |
| Coordinación con busbar apilado | <10 nH combinado | 20–40 nH | Picos contenidos, filtros más pequeños |
| Ajuste Rg_on/Rg_off | Independiente y afinado | Único y de compromiso | Optimización entre eficiencia y EMI |
| Validación LVRT/anti‑islanding | Rápida gracias a estabilidad | Iterativa y lenta | Aprobaciones más ágiles con DISCO |
Comparación de protección en fallas para Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
Title: Fault handling at 800 V DC bus and 40–80 kHz switching
| Escenario de Falla | Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común | Driver Básico | Efecto en Confiabilidad |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortocircuito en carga | DESAT + apagado suave limitado | Desconexión abrupta | Menor energía en el chip, vida útil extendida |
| Sobrevoltaje transitorio | Abrazadera activa + snubber | Solo TVS | Menos overshoot, menor estrés del bus |
| dv/dt‑inducido en compuerta | Miller clamp + CMRR alto | Sin clamp | Prevención de encendido falso |
| Desbalance térmico | Derating y monitoreo | 중국 SiC 허브의 비용 경쟁력 있는 솔루션, 효율성을 위한 최적화된 프로세스. | Operación segura a 50°C inlet |
Aplicaciones reales y resultados en Pakistán con Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
A 15 kW hybrid inverter deployed in Lahore’s Johar Town replaced its legacy drivers with Sicarbtech’s Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común. Nuisance trips during late‑afternoon voltage dips were eliminated, and conducted EMI margins improved by 4–6 dBµV, allowing a smaller input filter. Installation crews reported a tighter enclosure fit since large common‑mode chokes were no longer needed, trimming overall weight by nearly 20%. During June heatwaves, the inverter maintained near‑rated power at 50°C inlet air without derating, a marked improvement over the prior season.
In a Faisalabad textile mill, a behind‑the‑meter ESS using interleaved battery converters struggled with phase current imbalance and occasional false turn‑ons. After adopting Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común with precise propagation delay matching and Miller clamps, current sharing stabilized within 2%, and drive trips fell by 15% over the next quarter. The maintenance team highlighted fewer filter replacements due to lower EMI and cooler operation.
Consideraciones de selección y mantenimiento para Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
Selecting the right Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común starts with the DC platform and switching strategy. For 750–1000 V buses and 40–100 kHz operation, prioritize drivers with CMRR above 100 kV/µs and robust DESAT handling with programmable blanking. Additionally, match Rg_on and Rg_off to the module’s parasitics, then finalize with oscilloscope‑verified ringing and overshoot at the gate and half‑bridge node. Thermal mapping of the driver vicinity is equally important; at 50°C inlet air, ensure isolated supplies remain within derating curves and that PCB creepage/clearance meets pollution degree assumptions typical in Pakistan’s coastal and dusty interiors. Maintenance improves when gate loops are visible and accessible, making periodic inspections for connector oxidation and dust accumulation straightforward during scheduled service.
Factores de éxito industrial y testimonios sobre Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
Industrial adopters consistently report that disciplined gate‑drive engineering unlocks the full promise of SiC. A Karachi cement plant’s electrical head summarized it succinctly: “We stopped fighting EMI with copper and started solving it with physics.” After migrating to Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común and stacked busbars, their crusher‑adjacent UPS front‑end passed EMC on the first retest, shaving weeks off the commissioning schedule. These results are emblematic of Sicarbtech’s pattern across 19+ enterprise collaborations, where Weifang‑based manufacturing excellence and Chinese Academy of Sciences co‑development reduce risk from prototype through mass production.
Innovaciones futuras y tendencias 2025+ para Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
As Pakistan’s grid codes evolve, Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común will integrate smarter diagnostics—real‑time SOA monitoring, adaptive dv/dt control responsive to feeder impedance, and predictive alerts for gate loop degradation. Firmware hooks will expose more parameters to the coordinated control platform, enabling dynamic tuning during LVRT events to balance efficiency with compliance. On the manufacturing side, continued improvements in isolation materials and package shielding will push CMRR ceilings higher, while tighter propagation delay matching will further stabilize interleaved topologies common in modular ESS. Sicarbtech is investing in these vectors, ensuring that 2025‑era hybrids and industrial systems can remain compact and quiet without sacrificing robustness.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común
How do high‑CMRR gate drivers prevent false turn‑on in SiC half‑bridges?
By combining high isolation immunity with Miller clamps and tailored Rg_off, the gate stays firmly below threshold when the switch node slews rapidly, even at dv/dt above 100 kV/µs typical for SiC systems.
What is the benefit of soft turn‑off during a short‑circuit event?
Soft turn‑off shapes the current fall to limit voltage overshoot and energy dissipation inside the MOSFET, reducing thermal shock and extending device lifetime, particularly at 750–1000 V DC buses.
Do active clamping and DESAT protection complicate compliance?
On the contrary, they reduce overshoot and ringing at the source, lowering conducted and radiated emissions. This typically simplifies IEC/EN EMC compliance and speeds local DISCO interconnection approvals.
Can these drivers operate reliably at 50°C inlet air in dusty enclosures?
Yes. The drivers and their isolated supplies are specified for high ambient conditions, and when paired with coated heatsinks and serviceable filter paths, they maintain stable thresholds and timing across seasons.
Por qué los Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común funcionan para sus operaciones
For Pakistan’s rooftop hybrids, SME storage, and industrial retrofits, Controladores de Puerta de Alta Rechazo de Modo Común convert SiC’s theoretical advantages into daily reliability. They quiet the switching edge, protect during faults, and grant designers the freedom to run at higher frequencies without inviting EMI headaches. When integrated within Sicarbtech’s low‑inductance ecosystem, the result is a cooler, smaller, and more responsive system that installs faster, passes compliance with margin, and stays on‑line through summer peaks.
Conecte con especialistas para soluciones a medida
Sicarbtech unites advanced materials, precise device engineering, and production‑grade packaging into cohesive power platforms. With over 10 years of SiC manufacturing expertise and the backing of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Weifang, Sicarbtech develops custom solutions across R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC, and transfers that know‑how to Pakistan through technology transfer and factory establishment services. From material processing to finished power electronics, and a proven track record with 19+ enterprises, Sicarbtech delivers turnkey programs that compress time‑to‑market and elevate reliability.
If you are scoping 3–20 kW hybrids, industrial ESS, or drive upgrades, engage early for a free consultation to define specifications, map EMC/Grid compliance, and plan localization. Contact [email protected] or +86 133 6536 0038. Engineering windows for pre‑summer deployments fill quickly—secure your slot to accelerate pilot‑to‑production before the 2025 heat season.
Last updated: 2025-09-16
Next scheduled review: 2025-12-01
Timeliness indicator: Reflects 2025 Pakistan hybrid/ESS trends, NEPRA/DISCO interconnect realities, and high‑temperature, dust‑resilient gate‑drive practices.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




