Industrial Silicon Carbide Solutions for Pakistan: Sicarbtech’s 2025 Pillar Guide for Kiln Cars, Setter Plates, and Roller Kilns

공유
Pakistan’s manufacturing base is expanding across refractories, glassware, advanced ceramics, and allied sectors that rely on thermal processing. In 2025, the mandate is clear: raise throughput, lower energy per ton, and protect quality while absorbing volatility in fuels, raw materials, and exchange rates. Kiln cars, setter plates, and roller kiln fixtures sit at the center of this challenge. They determine thermal mass, takt time, flatness, and defect rates, and they are punished daily by thermal cycling, scouring gas flows, and alkali–sulfur–chlorine volatiles. Industrial silicon carbide (SiC) has emerged as the enabling platform. With high specific strength, high thermal conductivity, low expansion, and exceptional wear and corrosion resistance—combined with honeycomb and thin-rib lightweight topologies—SiC fixtures cut heat capacity, stabilize geometry, and extend campaign life. Sicarbtech—based in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings over a decade of SiC customization, full-cycle manufacturing, and turnkey technology transfer that allows Pakistani partners to localize capability and control outcomes.
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook and Why Silicon Carbide Matters for Pakistan’s Thermal Processing
Across Pakistan’s ceramics, glass, and specialty materials lines, the economics of heat are decisive. Energy remains a volatile cost center, while delivery windows tighten and defect tolerance shrinks. Traditional high-alumina or mullite fixtures carry excess mass, heat and cool slowly, and warp under cyclic stress, which extends cycle times and erodes flatness and yield. By contrast, SiC boasts high thermal conductivity that equalizes temperature quickly and a low coefficient of thermal expansion that resists distortion. When engineered into honeycomb and thin-rib plates with functionally graded layers, SiC fixtures deliver high stiffness-to-weight ratios, low heat capacity, and stable flatness through start-stop and load swings. Surface engineering further reduces wetting by glazes and salts, cutting sticking and secondary contamination.
Sicarbtech aligns the entire chain—material formulation, lightweight structural design, densification process, surface engineering, prefabrication and onsite installation, plus inspection and O&M—into a closed-loop program. With technology transfer, Pakistani operators can internalize mixing, classification, prefabrication, coatings, and eventually reaction sintering, compressing lead times, lowering FX exposure, and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency even as ambient conditions shift. The outcome is a predictable, auditable method for winning the energy, quality, and uptime battle simultaneously.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points: The Reality on Pakistan’s Kiln Floors
A walk along a roller kiln in Punjab during peak production reveals the friction points. Heavy fixtures raise thermal mass, forcing longer heat-up and cool-down to protect product quality. That in turn squeezes takt time, makes scheduling brittle, and amplifies energy consumption. Frequent thermal cycling seeds warpage and corner chipping; once flatness drifts outside tolerance, yield drops and rework rises. Gas–solid scouring wears down work surfaces, while alkali–sulfur–chlorine volatiles condense at imperfectly insulated spots to create sticky films. Those films invite bottom adhesion and glaze defects that drain operator confidence and demand cleaning time.
On kiln cars, the mass of the top deck and supports often dominates the heat budget. Uneven stiffness or insufficient conductivity amplifies thermal gradients across large setters, encouraging bowing and print-through defects. Over long campaigns, oxidation and abrasion thin load-bearing sections, reducing capacity and raising the risk of sudden failures that force unplanned downtime. The stakes are higher when green bodies are larger or more complex: non-uniform heating and localized stress at supports can turn promising production runs into unpredictable defect cascades.
Pakistan’s operating context adds practical constraints. Mixed fleets of legacy and modern kilns, varied fuels and firing regimes, and seasonal humidity swings complicate bake-out, venting, and dimensional control. Local supplies of high-performance fixtures are limited; imported parts entail long and volatile lead times, tying up working capital and creating planning uncertainty. A Karachi-based operations manager captured the hidden cost well during a 2024 review: “We can calculate energy; we can’t calculate uncertainty. When flatness drifts or fixtures stick, the costs arrive as missed deliveries.” Industry advisors point back to fundamentals. “High conductivity reduces the gradient that causes stress; low expansion reduces the strain when it happens,” explained a regional refractory specialist, referencing standard materials and thermal shock literature. “If your microstructure also resists penetration and oxidation, the fixtures stop being the bottleneck.”
Regulatory and customer expectations elevate the bar. ISO 9001-aligned documentation, PSQCA conformity, and ISO 14001-aligned practices are increasingly referenced in tenders and audits. Safety targets discourage hot, reactive maintenance and encourage rapid, modular replacement. In short, success demands fixtures that are lighter, faster, flatter, and easier to maintain—backed by a method that Pakistani teams can repeat season after season.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio by Sicarbtech
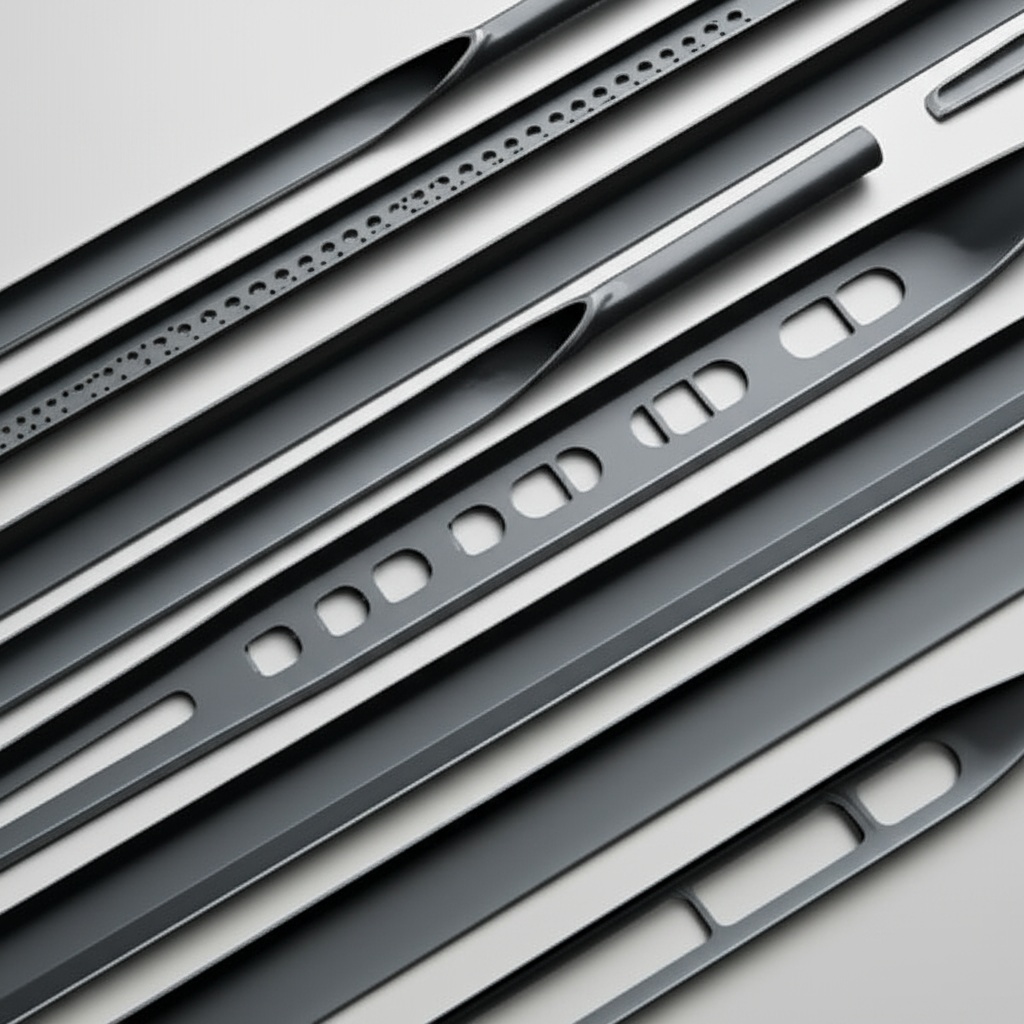
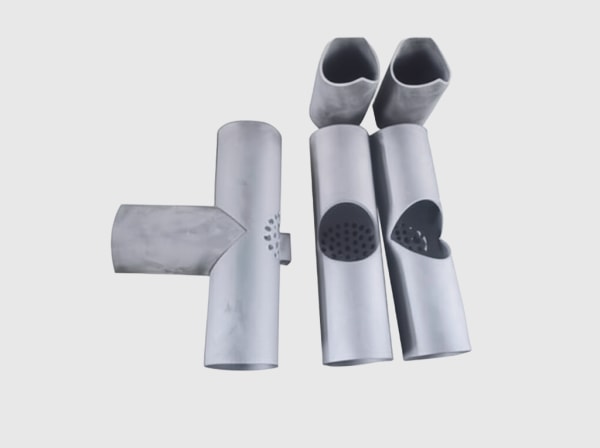
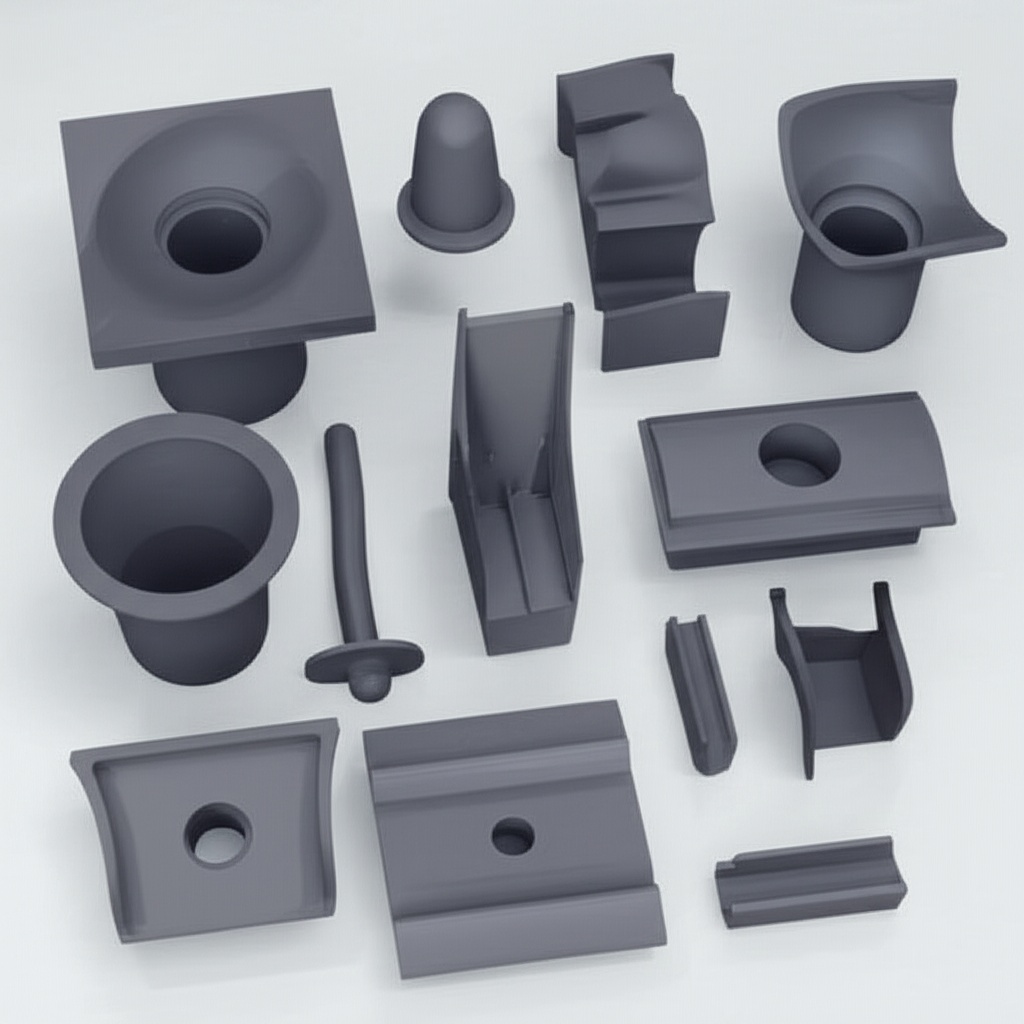
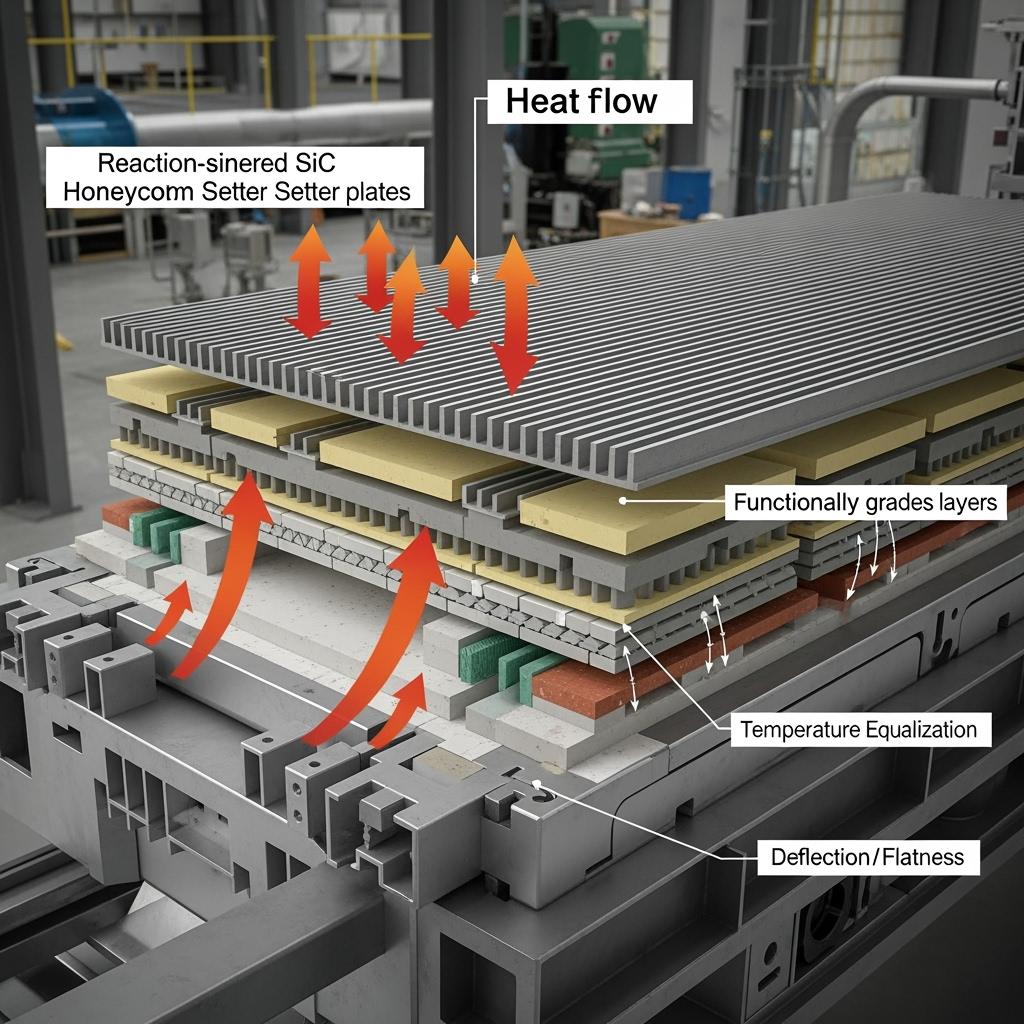
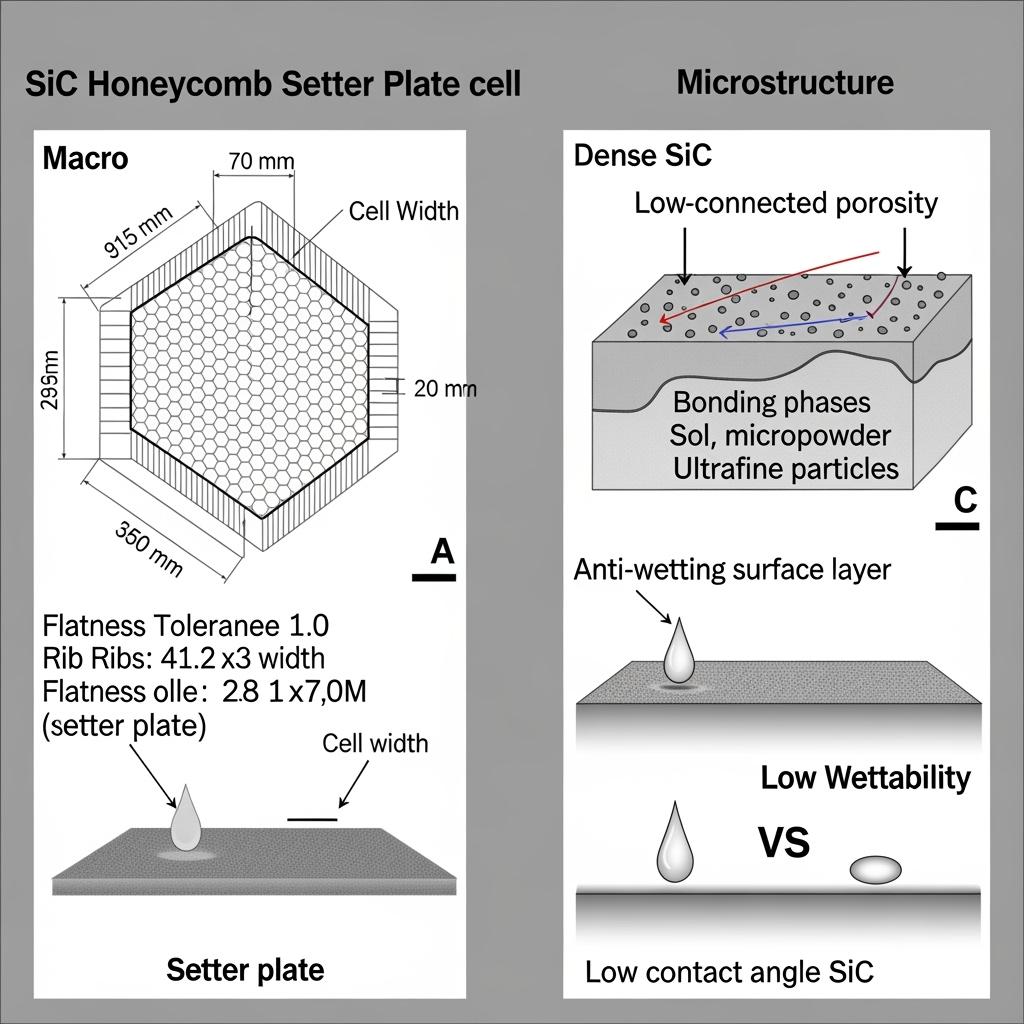
Sicarbtech’s portfolio for kiln cars, setter plates, and roller kilns is engineered to attack mass, gradients, and defects simultaneously. Reaction-sintered SiC honeycomb setter plates are the flagship: thin-wall cells deliver high stiffness with low mass, reducing heat capacity while maintaining flatness. For large flat setters, high-density SiC thin-rib plates add directional reinforcement that holds plane under cyclic loads. On kiln cars, SiC honeycomb top decks reduce thermal inertia, immediately lowering the energy budget for every heat and cool. High-thermal-conductivity SiC roller support blocks help equalize roller temperatures, stabilizing thermal balance in roller kilns.
Surface performance is handled via low-wettability, anti-fouling SiC coatings and microtextured layers that resist adhesion from glazes, salts, and powders. For tougher environments, SiC–mullite functionally graded fixtures place a high-hardness working face over a low-modulus transition layer to buffer stress and a supportive backing for insulation. SiC microporous equalizing pads fine-tune bottom temperature fields under sensitive bodies, while SiC wear-resistant columns and brackets create modular, replaceable supports. Ultra-low-cement SiC-bonded castable shims simplify leveling and insulation with short bake-out times, and SiC gunning and repair mortars enable rapid edge and crack fixes between runs.
Under the skin, multi-graded SiC aggregate packages and micropowder activation optimize packing, densification, and microstructure connectivity. SiC backing insulation composite boards tame shell temperatures on kiln cars; flexible joints and buffer shims control expansion mismatch to cut warpage. Modular locking and locating pieces enforce precise alignment and reduce changeover times. Where slip risk is a concern, an anti-slip microtextured surface layer raises friction and protects handling safety.
Critically, Sicarbtech supplies the equipment and process scaffolding to make these outcomes repeatable: reaction sintering and high-temperature densification kilns; cold isostatic and die-press forming; intelligent mixing and vacuum vibration for rheology control; precision classification and demagnetization for purity; CNC cutting, forming, and grinding/polishing for geometry and surface finish; and non-destructive testing plus dimensional inspection for traceability. “Fixtures fail in the factory long before they fail in the kiln if curves and grading aren’t right,” notes a Sicarbtech process lead. “We transfer the recipes, the curves, and the inspection gates so Pakistani plants can own the performance.”
Technical Comparison for Kiln Cars, Setter Plates, and Roller Kilns
| Performance profile for thermal processing fixtures | Silicon Carbide Fixtures (R-SiC/SSiC/RBSiC/SiSiC) | High-Alumina/Mullite Fixtures | Conventional Dense Plates/Metal-Containing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.60–3.05 | 2.2–2.8 | 2.6–7.8 (metals vary) |
| Apparent porosity (%) | 6–15 (dense parts ≤ 6) | 15–25 | Wide; metals none but oxidize |
| Thermal conductivity at RT (W/m·K) | 20–55 | 2–6 | 15–50 (metals high but oxidize/warp) |
| Cold crushing strength (MPa) | 120–240 (dense ≥ 260) | 80–160 | 100–250 (metals ductile) |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 14–35 (ribbed +20–40%) | 8–20 | 10–30 |
| Thermal shock (1000°C water quench) | ≥ 30–60 | 10–25 | 10–25 (metals deform) |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (×10⁻⁶/K) | ~4–5 | ~6–8 | 11–18 (강철s) |
| Anti-wetting/anti-fouling behavior | High with coatings | 보통 | Variable; oxide scale forms |
| Weight/heat capacity impact | Low; honeycomb/rib | Higher; solid mass | High for metals; heat sink risk |
The combination of high conductivity and low expansion makes SiC uniquely effective at limiting gradients and strain, while lightweight topologies cut heat capacity and time-to-temperature—both crucial to Pakistan’s energy and takt targets.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
On a structural ceramics line near Faisalabad, high thermal mass and warpage on large setters constrained takt time and produced flatness-related rejects. Sicarbtech introduced reaction-sintered SiC honeycomb setter plates with optimized cell geometry and thin ribs, backed by functionally graded layers and low-wettability surface engineering. The kiln car top deck was migrated to SiC honeycomb to drop heat capacity further, while flexible shims and modular locating locks strengthened alignment control. Within two quarters, fixture self-weight fell by about 32% and calculated heat capacity by roughly 24%. Heat-up and cool-down times shortened by approximately 15% and 18%, thermal shock life nearly doubled, and cleaning man-hours for sticking events dropped by almost half. Overall energy consumption fell by around 7% and unplanned fixture-related downtime shrank by about 28%. “Flatness stopped being the constraint,” the production engineer noted. “We planned for throughput instead of workarounds.”
A tile line in Sindh struggled with bottom adhesion and edge chipping under volatile firing schedules. The upgrade combined low-wettability, anti-fouling SiC coatings on set-down surfaces, SiC microporous equalizing pads under sensitive bodies, and SiC roller support blocks to stabilize roller temperature profiles. The site also adopted Sicarbtech’s staged bake-out curves and dimensional checks aligned with seasonal humidity. Bottom defects fell sharply, and the plant met a demanding delivery window without extraordinary overtime or excess scrap.
기술적 장점 및 현지 규정 준수 구현 이점
SiC’s physics map directly to KPIs. High thermal conductivity speeds temperature equalization, shrinking the gradient-driven stress that seeds warpage and cracks. Low expansion reduces strain accumulation during cycles; high modulus and tailored rib geometry keep planes true under load. Dense, low-connected porosity and grain-boundary purification resist oxidation and alkali–sulfur–chlorine attack, extending life. Low-wettability coatings and microtextures minimize adhesion of molten phases, curbing bottom sticking and cleaning time.
From a compliance perspective, longer life and fewer interventions support ISO 14001 goals by cutting energy and waste. Sicarbtech’s quality packs align with ISO 9001 and support PSQCA submissions where required. Installation SOPs—staged bake-out, moisture/venting control, adhesion testing, 3D coordinate and flatness checks—plug into CMMS workflows for auditable execution. Practically, that means safer operations, predictable performance through seasonal swings, and credible documentation for customers and regulators.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s differentiator is converting materials performance into a local, repeatable capability. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we deliver proprietary manufacturing routes for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades and their structural assemblies through staged technology transfer.
We begin with feasibility and factory layout aligned to Pakistani utilities, labor skills, and throughput targets. Equipment specifications cover reaction sintering and high-temperature densification kilns with documented curves; cold isostatic and die-press forming for uniform green bodies; precision classification and demagnetization to stabilize PSD and purity; and intelligent mixing with vacuum vibration for rheology and packing density control. CNC cutting, forming, and grinding/polishing ensure dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Non-destructive testing—ultrasonic/acoustic emission, rebound, and adhesion pulls—plus coordinate metrology and online flatness inspection create traceable QA.
Quality systems are embedded on day one. We implement ISO 9001-aligned QC with SPC on bulk density, apparent porosity, CCS/MOR, thermal shock performance, contact-angle indices, flatness, thickness, and mass; ISO 14001 environmental practices; and safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001 principles. Training modules cover operator skills, furnace curve management, forming orientation to control residual stress, adhesion protocols, staged bake-out, and seasonal adjustments for humidity. Commissioning includes live curve tuning and supervised installations, followed by quarterly audits and formulation/geometry iteration tied to site KPIs—energy per cycle, takt time, flatness yield, cleaning hours, and downtime frequency.
Across more than 19 enterprise collaborations, this “materials + equipment + process + training” stack has shortened lead times from months to weeks, stabilized batch-to-batch quality through weather swings, and reduced inventory buffers even under FX volatility. As a Sicarbtech technical director remarks, “Owning the powder is not the same as owning the outcome. When Pakistani teams own the curves, the topology, and the inspection gates, fixtures stop scheduling your plant—you do.”
Pakistan-Focused Technical Specification Ranges and QA Guidance
| Specification ranges for kiln cars/setter plates/roller kilns | Typical SiC Targets | Local QA and testing guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.60–3.05 | Verify per ISO/ASTM equivalents; SPC by batch/season |
| Apparent porosity (%) | 6–15 (dense ≤ 6; honeycomb tuned) | Correlate with permeability and oxidation tests |
| Cold crushing strength (MPa) | 120–240 (dense ≥ 260) | ISO 10059/ASTM C133 equivalents; coupon traceability |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 14–35 (ribbed +20–40%) | Bend tests; orientation documented |
| Thermal shock (1000°C quench) | ≥ 30–60 cycles | Cross-check vs cycle count and takt |
| Max service temperature (°C) | 1500–1650 | Confirm vs volatiles and O2 potential |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 20–55 | Validate with IR thermography across plates |
| Linear change at temperature (3 h) | ≤ 0.5% | Dimensional checks pre-/post-exposure |
| Surface contact angle (relative) | 10–30% better than oxide systems | Track vs sticking/cleaning hours |
| Flatness tolerance (mm/1000 mm) | ≤ 0.5–1.0 | 3D coordinate and online flatness logs |
| Thickness tolerance (mm) | ±0.5–1.0 | Gauge control and SPC charts |
Operational Outcomes Comparison That Drive Energy, Throughput, and Yield
| Operational outcomes central to Pakistani kilns | SiC Honeycomb/Thin-Rib + Coatings + Graded Layers + Modular Locks | High-Alumina/Mullite or Dense Plate Baselines |
|---|---|---|
| Fixture mass/heat capacity | −20–45% mass; −15–35% heat capacity | Higher; slow heat/cool |
| Cycle time (heating/cooling) | −10–25% | Longer; energy-intensive |
| Thermal shock/warpage | −30–60% warpage; +50–120% shock life | Higher warpage and chipping |
| Flatness yield | Higher; plane stability | Lower; rework/scrap risk |
| Sticking/cleaning man-hours | −30–55% | Frequent cleaning cycles |
| Energy per load | −5–10% typical | Baseline or rising |
| 계획되지 않은 가동 중단 | −20–40% | Elevated due to defects |
| 리드 타임 및 FX 노출 | Localizable via tech transfer | Import-dependent; volatile |
Innovation That Matters: From Lightweight Topology to Residual-Stress Control
Sicarbtech’s innovation program bridges design, materials, and process. Honeycomb and ribbed lightweight topology is tuned for strength-to-mass and heat-flow, with cell size, rib thickness, and orientation optimized to resist buckling and manage conduction. Functionally graded structures place a high-SiC, high-hardness working face over a low-modulus transition layer and supportive backing to diffuse stress. Composite bonding systems—sol, micropowder, and ultrafine powder—lift post-firing strength and minimize connected porosity that invites penetration. Low-wettability coatings and microtextures reduce molten-phase adhesion. Forming orientation and sintering curve design address residual stress and warpage at the source, while digital QC—acoustic emission/ultrasonic, 3D coordinate checks, and online flatness inspection—keeps batch quality inside tight corridors. Finally, modular locking and locating systems with flexible shims translate design intent into fast, reliable, and repeatable field assembly.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Pakistan
Three forces will drive adoption. First, energy and throughput pressures will favor fixtures that cut heat capacity and shorten cycles; SiC honeycomb and thin-rib designs are tailor-made for this shift. Second, the move toward larger, more complex bodies will elevate the value of high flatness and anti-warpage fixtures, pushing demand for functionally graded designs and residual-stress control. Third, localization will accelerate as producers seek to stabilize supply and budgets; many will phase in mixing, classification, prefabrication, and coatings first, then add reaction sintering for high-value parts as volumes justify.
Sizing the opportunity, a medium-to-large roller kiln or pusher kiln line typically consumes 80–200 tons of fixtures annually, depending on product mix and firing regimes. With Pakistan’s upgrades and retrofits, national SiC fixture demand plausibly reaches several thousand tons per year. When prefabs, coatings, installation services, and enabling equipment are included, the addressable market extends into the tens to hundreds of millions of Pakistani Rupees, contingent on adoption speed and capital access. Providers who can demonstrate raw-material stability, densification and topology design capability, onsite service, and fast delivery will earn durable positions. Sicarbtech’s integrated “materials + equipment + process + training” platform is tuned to this trajectory.
As a South Asia-focused kiln technologist summarized in a 2025 briefing, “When the heat budget shrinks and the flatness chart stays flat, you’ve stopped paying for your fixtures twice—once in energy and again in defects.”
자주 묻는 질문
Which Sicarbtech SiC fixtures should we prioritize to lower energy and improve flatness?
Start with reaction-sintered SiC honeycomb setter plates to cut mass and heat capacity, and migrate kiln car top decks to SiC honeycomb to slash the heat budget. For large bodies, use high-density thin-rib plates with functionally graded layers to stabilize flatness. Add low-wettability coatings where sticking is recurrent.
How much improvement can we expect in cycle time and yield?
Typical results include 10–25% shorter heating/cooling phases, 8–18% higher per-furnace turnaround efficiency, 30–60% less warpage, 50–120% higher thermal shock life, and 30–55% fewer cleaning hours. Energy per load often drops by 5–10% depending on the process window.
Can Sicarbtech help us localize production and reduce FX exposure?
Yes. We deliver full technology transfer: recipes, equipment specifications, plant layout, operator training, ISO 9001/14001 QA frameworks, safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001 principles, and commissioning. Most partners start with mixing, classification, prefabrication, and coatings, then add reaction sintering as volumes grow.
How do SiC fixtures perform under alkali–sulfur–chlorine volatiles?
Dense, low-connected porosity and grain-boundary purification resist oxidation-induced porosity and volatile-induced reactions. Low-wettability coatings reduce adhesion and bottom sticking, stabilizing quality and reducing cleaning frequency.
What installation practices ensure flatness and longevity?
Use modular locks and locating pieces with flexible shims to control planarity; follow staged bake-out curves tuned to ambient humidity; manage moisture and venting carefully; and validate with 3D coordinate measurements and online flatness checks. Record forming orientation to manage residual stress.
Which KPIs should we track to verify benefits?
Track cycle time segments (heat-up/cool-down), energy per load, flatness yield, warpage distributions, sticking events and cleaning man-hours, fixture mass/heat capacity trends, and unplanned downtime. Correlate with fuel mix, humidity, and loading patterns.
Are honeycomb setters strong enough for heavy loads?
Yes—when cell size, rib thickness, and orientation are engineered for the span and load. Sicarbtech designs topology using strength-to-mass targets and validates through CCS/MOR testing, acoustic emission checks, and finite element simulations tied to your kiln curve.
How do we manage repairs between campaigns?
Keep SiC gunning and repair mortars for edge/corner fixes, and stock modular replacement pieces for high-wear zones. With standardized interfaces, many swaps can be completed within one shift, preserving production windows.
What documentation supports Pakistani tenders and audits?
Sicarbtech supplies ISO 9001-aligned QC records, ISO 14001 environmental documentation, safety SOPs aligned to ISO 45001 principles, PSQCA conformity packs, and SPC dashboards for density, porosity, CCS/MOR, thermal shock, contact angle, flatness, and dimensions.
What is a phased roadmap to full local capability?
Phase 1: classification/mixing, prefabrication, coatings, and repair materials with digital QC. Phase 2: cold isostatic/die pressing and densification kilns for select components. Phase 3: reaction sintering for dense, high-value parts. We align CAPEX, staffing, training, QA gates, and commissioning to your targets.
운영에 적합한 선택하기
If your fixtures are dictating your cycle time, your energy budget, and your flatness yield, materials are managing your plant. Silicon carbide changes that balance. With higher conductivity, lower expansion, lightweight strength, and anti-fouling surfaces—delivered through engineered honeycomb and rib topologies—SiC fixtures convert heat into throughput and stability. Sicarbtech’s integrated approach—materials, topology design, densification, coatings, installation playbooks, and localizable manufacturing—turns “better parts” into a documented, predictable performance system for Pakistani kilns.
전문가 상담 및 맞춤형 솔루션 받기
Share your process window—kiln curves, load mass and distribution, product dimensions, volatile chemistry, gas-flow profiles, flatness/yield data, and failure maps—and Sicarbtech will design a tailored SiC package with modeled cycle-time and energy gains, topology and grading selections, surface and joint strategies, and staged bake-out protocols. If localization is your priority, we will map a phased technology transfer that fits your CAPEX, staffing, and schedule.
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub
Member of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park
이메일: [email protected]
전화/왓츠앱: +86 133 6536 0038
문서 메타데이터
Last updated: 2025-09-19
다음 예정 업데이트: 2026-01-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Pakistan kiln and thermal processing outlook validated; technical ranges aligned with current field data; PSQCA/ISO alignment reviewed; contact details verified for Pakistan engagements.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.