Industrial Silicon Carbide Solutions for Pakistan: Sicarbtech’s 2025 Guide to Dustproof, Anti‑Corrosion, High‑Reliability Packaging and Thermal Management

シェア
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook for High‑Reliability Silicon Carbide Packaging in Pakistan’s Harsh Environments
From Karachi’s salt‑laden coastal air to the dust corridors around cement and steel plants in Lahore and Faisalabad, Pakistan’s real‑world operating conditions are unforgiving. Electric two‑ and three‑wheelers, light commercial vehicles, and compact industrial platforms must deliver stable performance despite heat, humidity, dust, and chemical exposure during monsoon seasons and daily wash‑downs. In 2025, the differentiator is no longer device efficiency alone; it is the marriage of silicon carbide (SiC) devices with dustproof, anti‑corrosion, high‑reliability packaging and thermal management that preserves performance over years, not months.
Sicarbtech—Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert—based in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, brings more than a decade of SiC customization and supports 19+ enterprises with full‑cycle capabilities. From materials (R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC) and devices to power modules, busbars, thermal stacks, coatings, and reliability validation, Sicarbtech has system‑level playbooks for harsh‑environment packaging. For the Pakistan market, turnkey technology transfer and factory establishment enable local packaging, screening, and after‑sales—compressing lead times, raising consistency, and improving PKR‑denominated lifecycle returns.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points: Why High‑Reliability Packaging Defines Uptime
The foremost constraint is environmental ingress. Dust and sand around cement and construction routes accumulate on exposed fins and inside housings, steadily raising thermal resistance and forcing derating during heat waves. Monsoon rains and daily wash‑downs—often with detergents—drive water droplets and chemical agents into micro‑gaps, while salt mist along coastal routes accelerates galvanic corrosion on aluminum and copper parts. Over months, conformal coatings that are poorly specified or applied crack, and potting that is too stiff introduces stress that delaminates interface layers. The combined effect is a slow march toward higher junction temperatures, intermittent faults, and early failures.
Thermal path degradation is the second enemy. Single‑sided cooling with commodity interface materials suffers from pump‑out, voiding, and thickness drift under vibration and thermal cycling. Hotspots form around die clusters and bond feet, while particulate fouling blocks airflow channels, increasing fan loads and acoustic noise. As junction‑to‑case resistance creeps up, control algorithms reduce output to survive, but the vehicle’s daily range and hill‑climb capability suffer precisely when ambient temperatures are highest.
Electrical susceptibility compounds these issues. Parasitic inductance in busbars and enclosure wiring can trigger ringing and overvoltage during high current transients; when combined with moisture and contamination, partial discharge risk rises. Insulation creepage distances that were acceptable in laboratory conditions fall short after months of dust caking and salt deposition. Nuisance trips spread through fleets, and maintenance teams spend hours diagnosing intermittent leakage currents or corrosion‑driven voltage offsets.
The business impact is stark. Every derating event shortens trip capacity, while unscheduled maintenance erodes revenue and SLA performance. Tenders and financing are increasingly explicit about environmental endurance: IEC 60068 test profiles for damp heat, salt spray, dust ingress, vibration and shock; documentation of insulation, creepage, and leakage current control; and quality systems aligned with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 principles. As Dr. H. Rehman, an industrial reliability advisor, notes, “Efficiency gets you shortlisted; environmental reliability wins the contract and keeps it profitable.” [Source: Regional Reliability and Power Electronics Workshop, 2024]
In contrast, SiC combined with engineered packaging flips the script. Double‑sided cooling shortens thermal paths and spreads heat evenly. Low‑inductance busbars reduce electrical stress at the root. Breather‑balanced sealing and high‑adhesion coatings maintain protective envelopes through temperature swings. With online monitoring of junction temperature estimation, interface health, and leakage trends, maintenance shifts from reactive to predictive—cutting downtime and protecting margins.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio: Sicarbtech for Dustproof, Anti‑Corrosion, High‑Reliability Packaging
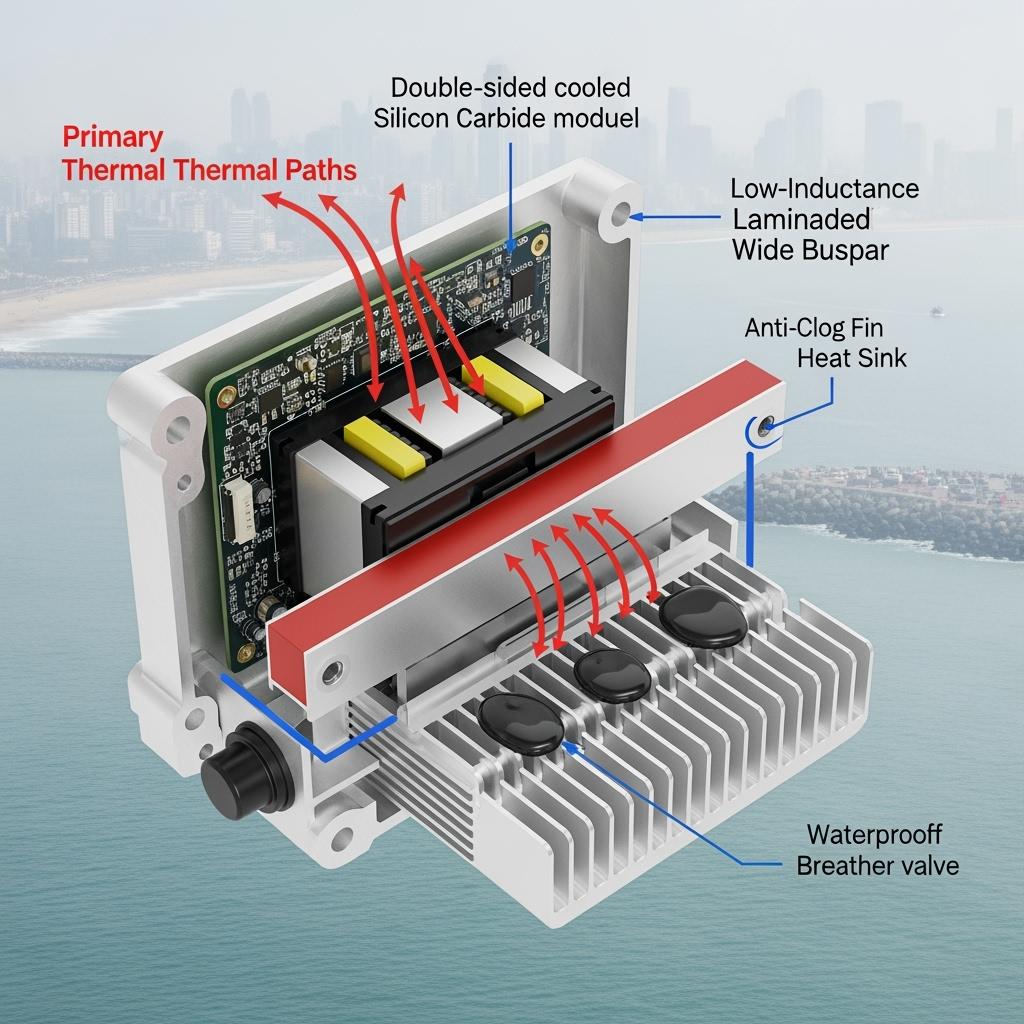
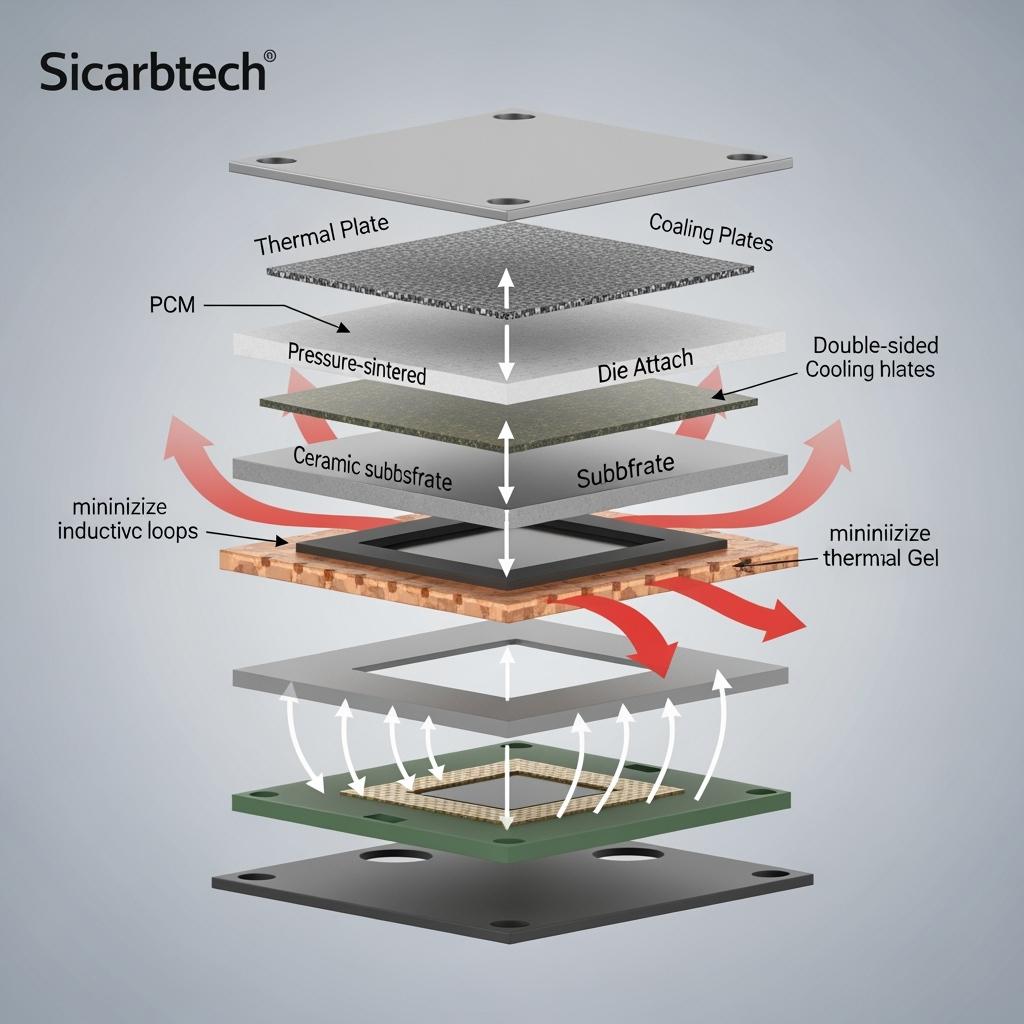
Sicarbtech’s harsh‑environment stack is designed end‑to‑end. At the device level, automotive‑grade 650 V and 1200 V SiC MOSFETs provide low loss and high junction temperature headroom. Power modules are double‑sided cooled on high‑thermal‑conductivity ceramic substrates with pressure‑sintered die attach, delivering low thermal resistance and robust fatigue life under thermal cycling. Low‑inductance busbars and shielding structures minimize loop area, suppressing spikes and ringing.
Thermal management is treated as a system. High‑conductivity interface material kits—phase‑change pads, thermal gels, and gap fillers—are matched to assembly pressure and thickness windows to prevent pump‑out and voiding. Cold‑plate channels are optimized for anti‑fouling and corrosion resistance, while modular heat sinks use anti‑clog fin geometries and self‑clean surfaces to maintain airflow with low‑pressure washing. Protective enclosures achieve high protection grades with standardized seals and quick‑release service features.
Environmental protection integrates conformal coating with high‑adhesion primers, selective potting with low‑stress, thermally conductive formulations, and anodic or conversion coatings for aluminum and copper parts. Breather valves manage pressure equalization and humidity to prevent condensation while maintaining sealing integrity. Isolated sensing kits are selected for stable behavior in humidity and salt mist, with creepage/clearance enhancements for pollution‑resistance classes relevant to Pakistan’s dust and coastal exposure.
Validation and O&M close the loop. Online health modules estimate junction temperature, track interface thermal resistance drift, measure leakage currents, and monitor corrosion indicators. Accelerated life testing—salt mist, dust, rain, temperature–humidity cycling; power cycling; thermal shock—establishes life models and derating rules. Together with local packaging and screening—vacuum brazing, pressure sintering, and in‑country environmental testing—Sicarbtech turns harsh‑environment reliability into a repeatable process.
Performance Comparison: Harsh‑Environment SiC Packaging vs Conventional Designs
Thermal, Environmental, and Electrical Reliability Under Pakistan’s Conditions
| 属性 | Sicarbtech SiC Double‑Sided Cooled, Sealed Package | Conventional Single‑Sided, Limited Protection | パキスタンにおける事業インパクト |
|---|---|---|---|
| Junction temperature peak at equal load | −5 to −12 °C | ベースライン | Higher summer output, fewer derates |
| Continuous output at 40–50 °C ambient | +10%–20% | Frequent derates | Stable vehicle range and torque |
| Salt‑mist endurance (relative time to failure) | ×2–×4 | ベースライン | Longer life in Karachi coastal zones |
| Dust/ingress impact on cooling | Low (anti‑clog fins, self‑clean) | High fouling | Longer cleaning intervals, lower OPEX |
| Busbar parasitic inductance | Low (optimized loops) | より高い | Less ringing/overshoot, improved EMC |
| Early failure rate (post burn‑in) | Reduced via screening | Higher variability | Fewer returns, predictable fleets |
By lowering thermal resistance and protecting against ingress, the system buys thermal headroom and reduces the frequency of nuisance trips that plague fleets during monsoon seasons and heat waves.
Real‑World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
A coastal two‑wheeler fleet near Karachi deployed Sicarbtech’s double‑sided‑cooled, conformal‑coated controller modules with breather‑balanced sealing. Under accelerated salt‑mist testing, failure rates dropped by roughly 60% compared with prior designs, while field maintenance intervals more than doubled. Drivers reported fewer mid‑route derates during humid nights, stabilizing delivery schedules.
In Lahore’s dust‑heavy distribution zones, a light commercial platform switched to high‑conductivity interface materials and anti‑clog fin heat sinks. Peak junction temperature at equivalent load fell by about 8 °C, and annual derating events declined by approximately 35%. Cleaning routines were simplified to low‑pressure washing, cutting service time and water use.
A sanitation fleet in Faisalabad introduced low‑stress potting and corrosion‑treated busbars. Online monitoring flagged a gradual rise in interface thermal resistance on a subset of vehicles, prompting proactive re‑torque and TIM refresh during scheduled service. Downtime dropped by double‑digit percentages, and warranty claims for thermal faults fell noticeably.

Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Local Regulatory Compliance
Engineering for Pakistan’s climate requires co‑optimization across thermal, electrical, and environmental domains. Double‑sided cooling with high‑thermal‑conductivity substrates lowers junction‑to‑case resistance and spreads heat evenly, preventing hotspot‑driven fatigue. Low‑inductance busbars and shielded loops reduce dv/dt stress and ringing, which protects devices and eases EMC compliance. Breather‑balanced sealing preserves protection grades without pressure‑induced seal failure, while low‑stress potting mitigates CTE mismatch that can crack joints during temperature swings.
Compliance is designed in from the start. Sicarbtech aligns device behavior with IEC 60747 and validates environmental endurance via IEC 60068 for damp heat, salt spray, dust, vibration, and shock. Insulation and leakage behavior are documented with creepage/clearance strategies appropriate for high‑pollution environments. EMC targets align with expectations similar to IEC 61800‑3 for adjustable speed systems, ensuring compatibility with nearby drives in textile and 鉄鋼 plants. As Engr. S. Khan remarks, “When coatings, sealing, and busbar geometry are treated as first‑class design elements, EMC and endurance stop being ‘test lab surprises’ and start being predictable outcomes.” [Source: EV Systems Roundtable, 2024]
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Edge for Harsh Environments
Sicarbtech’s competitive advantage is transferring capability, not only shipping parts. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, the company brings proprietary processes across R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC into thermally stable substrates and corrosion‑resistant assemblies.
The technology transfer package covers full process know‑how: pressure‑sintered die attach profiles; vacuum brazing parameters; metallization/passivation stacks; busbar and bonding rules for low inductance; gate‑drive tuning for soft turn‑off and active clamping; and validated conformal coating and potting formulations for damp‑heat and salt‑mist endurance. Equipment specifications include vacuum brazing furnaces, pressure sintering presses, inline electrical testers, power cycling rigs, HTRB/HTGB setups, and IEC 60068 environmental chambers—with acceptance tests, calibration procedures, and vetted vendor lists.
Training programs build operator and QA capability in reliability screening (power cycling, temperature–humidity cycling, salt‑mist), failure analysis, SPC‑driven yield improvement, and PPAP‑like control plans aligned with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 principles. Factory establishment services span feasibility, facility layout and utilities, line installation and commissioning, pilot runs, and capability validation. After SOP, Sicarbtech sustains quarterly audits, yield sprints, and roadmap co‑development to match Pakistan’s ambient profiles, cleaning practices, and duty cycles.
Across 19+ enterprise collaborations, outcomes include faster time‑to‑market, higher first‑pass yield, and lower field failure rates. In Pakistan, localized packaging and screening compress spare turnaround from months to days or weeks, while online burn‑in and pre‑compliance raise batch consistency. The result is predictable uptime during peak seasons—an advantage import‑only models rarely match.
Comparative Engineering Choices and Lifecycle Economics
Packaging and Cooling Choices That Survive Heat, Dust, and Salt Mist
| Design Area | Sicarbtech High‑Reliability Implementation | Conventional Implementation | Practical Outcome in Pakistan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling architecture | Double‑sided cooling, high‑k substrates | Single‑sided, commodity TIM | Lower Tj, fewer derates in 40–50 °C |
| Interface materials | Phase‑change + gel/gap fillers with pressure window control | Grease with pump‑out risk | Stable thermal resistance over life |
| 環境シール | Breather‑balanced, standardized seals | Rigid sealing, no pressure relief | Less condensation, longer seal life |
| Busbars & loops | Low‑inductance, shielded loops | Long leads, higher parasitics | Less ringing, improved EMC margins |
| Coatings & potting | High‑adhesion coats, low‑stress potting | Thin coat, rigid potting | Lower crack/leak risk, better endurance |
Localization and Total Cost of Ownership Benefits
| Business Factor | With Sicarbtech Technology Transfer | Import‑Only Approach | Outcome for Fleets and OEMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spare lead time | Days–weeks via local screening | Weeks–months | Higher availability, fewer canceled routes |
| Batch consistency | In‑country burn‑in and environmental screens | Variable incoming quality | Lower warranty claims, smoother ramps |
| Cleaning and service | Anti‑clog fins, quick‑release cold plates | Fixed fins, disassembly required | Shorter maintenance windows |
| Energy and cooling OPEX | Lower Tj, smaller fans/pumps | Higher thermal resistance | Lower PKR OPEX, quieter operation |
| Capability growth | Domestic process and QA maturity | Vendor dependency | Stronger ecosystem and skilled jobs |
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends: Reliability as a Revenue Strategy
Electrification in Pakistan’s logistics and passenger segments is set to intensify, and with it the premium on uptime. Procurement language will increasingly reward demonstrated environmental endurance alongside efficiency, while ESG‑linked financing will scrutinize failure rates and maintenance logs. Data‑driven O&M will extend from powertrains to packaging health, turning interface thermal resistance and leakage current trends into scheduled service actions. Meanwhile, coastal urbanization and expansion of routes across saline‑alkali districts will elevate anti‑corrosion from “nice‑to‑have” to “must‑have.”
Technically, double‑sided cooling will become mainstream in compact drives, while anti‑fouling cold‑plates and fin geometries will cut cleaning costs. Breather‑balanced sealing and composite shielding will reduce both condensation and EMI coupling. Sicarbtech’s integrated stack—devices, packaging, materials, validation, and technology transfer—aligns with these trends, enabling Pakistani partners to lead not only in initial efficiency, but in sustained reliability and low OPEX—core elements of 2025 tenders and multi‑year service contracts.
Extended Technical Specifications and Local Standards Alignment
Sicarbtech’s high‑reliability SiC packages support 48–120 V platforms for two‑/three‑wheelers and extend to 400–800 V for light commercial vehicles. Typical power ranges span 2–10 kW for smaller platforms and 10–60 kW for light commercial. Devices support operating junction temperatures up to 175 °C. System switching frequencies of 10–40 kHz are selected to balance electrical loss and acoustics while preserving thermal headroom.
Environmental protections target dust, moisture, salt mist, rain, and chemical exposure, with vibration and shock robustness tailored to local road conditions. Monitoring includes junction temperature estimation, interface thermal resistance trend, leakage current, and corrosion indicators. Documentation maps to IEC 60747 (devices) and IEC 60068 (environmental test batteries), with EMC expectations similar to IEC 61800‑3 for adjustable speed systems. Sicarbtech coordinates third‑party testing in Karachi and Lahore and supports ISO 9001/IATF 16949‑aligned quality documentation for tenders and financing.
よくある質問
How much thermal improvement can double‑sided cooling and high‑conductivity interfaces deliver?
Field and lab data typically show 5–12 °C lower junction temperature at equal load, which often converts into 10%–20% higher continuous output at 40–50 °C ambient.
Will sealing and coatings survive Karachi’s humidity and saline conditions?
Yes. Breather‑balanced sealing, high‑adhesion conformal coatings, and selective potting are validated under IEC 60068 damp‑heat and salt‑spray profiles, maintaining insulation and limiting corrosion pathways.
How often will we need to clean anti‑clog fins and cold plates?
Anti‑clog fin geometries and self‑clean surfaces support low‑pressure wash intervals that are 50%–100% longer than conventional fins in dusty corridors, depending on duty and road conditions.
Can low‑inductance busbars really improve EMC and reliability?
Reducing loop area and adding shielding lowers ringing and overshoot, improving device stress margins and conducted/radiated behavior—shortening EMC remediation cycles and preventing nuisance trips.
How do you monitor interface aging before failures occur?
Online estimation tracks interface thermal resistance via temperature–power modeling, paired with leakage current trends. Thresholds trigger planned service before overheating or insulation faults emerge.
What is the typical design‑to‑pilot timeline with local screening?
With standardized modules and process kits, pilots commonly launch in 8–12 weeks, accelerated by in‑country environmental screens and burn‑in to stabilize early life performance.
How do coatings and potting avoid cracking over time?
Low‑stress potting formulations and controlled CTE matching, combined with high‑adhesion primers and application windows, prevent brittle failures during thermal cycling and vibration.
Are these solutions compatible with textile and steel plant EMC requirements?
Yes. Low‑inductance packaging and shielding, combined with filtering strategies, are engineered to meet EMC expectations similar to IEC 61800‑3, reducing coupling with nearby drives and PLCs.
What quality systems back Sicarbtech’s technology transfer?
Quality plans align with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 principles, including PPAP‑like validation, SPC, power cycling, and IEC 60068 environmental screening—delivered with full documentation for tenders.
How does localization change our total cost of ownership?
Local packaging, screening, and spares reduce lead times to days–weeks, lower warranty rework, and improve batch consistency—cutting PKR OPEX and increasing fleet availability.
オペレーションに適した選択
When heat, dust, humidity, and corrosive exposure define reality, reliability is not a bolt‑on—it is the architecture. Sicarbtech’s silicon carbide solutions join double‑sided cooling, low‑inductance busbars, and engineered sealing and coatings into a cohesive system that keeps torque, range, and uptime intact through Pakistan’s harshest seasons. With technology transfer and local validation, you convert design intent into sustained field performance and superior PKR economics.
専門家によるコンサルテーションとカスタムソリューション
Work with Sicarbtech’s engineering team to specify device ratings, packaging geometry, interface materials, sealing strategies, and cooling architectures tailored to your duty cycles and cleaning practices. Explore factory establishment and process transfer to localize packaging, environmental screening, and spares—building a resilient in‑country capability for scale.
Sicarbtech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
Eメール:[email protected]
Phone: +86 133 6536 0038
Headquarters: Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub
“Efficiency earns attention; reliability earns trust; localization earns market share.” — Sicarbtech Applications Team
記事のメタデータ
Last updated: 2025-09-18
Next update scheduled: 2025-12-15
Content freshness indicators: integrates 2025 Pakistan market outlook; aligns with IEC 60747 and IEC 60068 environmental profiles; references EMC expectations similar to IEC 61800‑3; reflects Sicarbtech’s current SiC portfolio, high‑reliability packaging, technology transfer, and factory establishment services.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




