Industrial Silicon Carbide Solutions for Pakistan’s Energy and Manufacturing Economy (2025 Outlook)

Share
Executive Summary: Why Silicon Carbide Now
Pakistan’s industrial core—textile, cement, and steel—faces a decisive moment. Rising electricity tariffs, grid volatility on 11–33 kV feeders, and pressure to decarbonize are driving accelerated adoption of high-efficiency power conversion. Battery energy storage system PCS, medium-voltage photovoltaic inverters, and high-performance drives are converging on silicon carbide (SiC) as the enabling platform for 2025–2030.
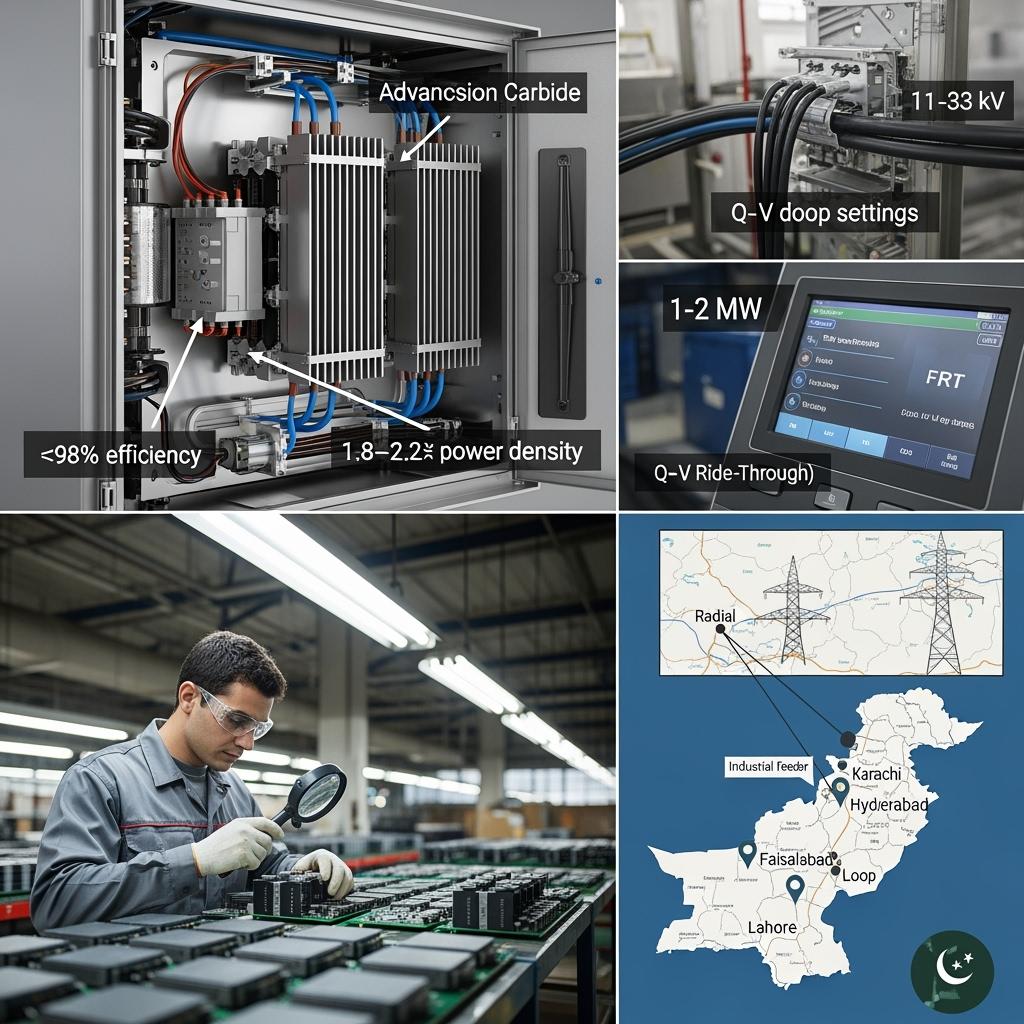
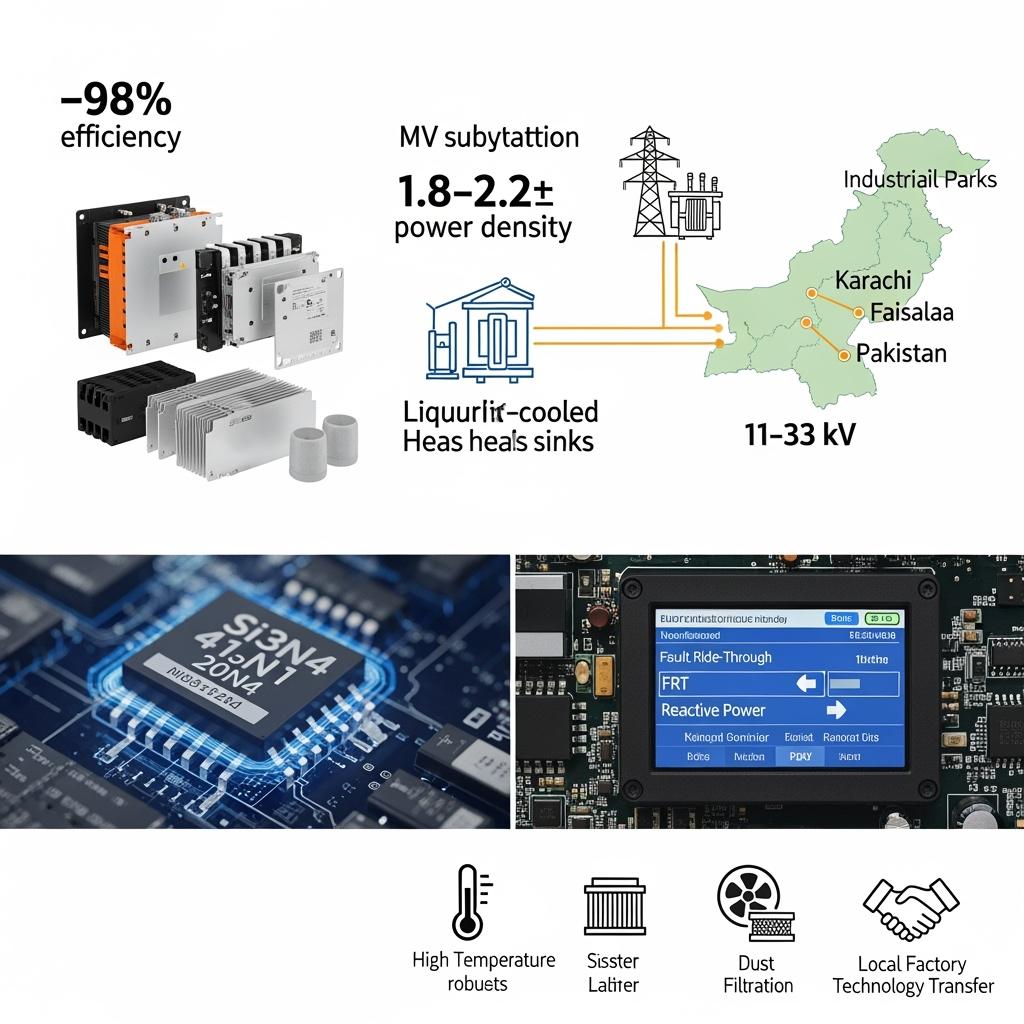
Sicarb Tech, based in Weifang City’s SiC manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, delivers a full-cycle SiC offering: advanced R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC materials; custom epitaxy; high-voltage power devices and modules; packaging and cooling; plus turnkey factory establishment and technology transfer. With 10+ years of customization experience and support for 19+ enterprises, Sicarb Tech helps Pakistani OEMs and integrators achieve ≥98% conversion efficiency, 1.8–2.2× power density, and MTBF targets near 200,000 hours—even in 45–50°C, dusty operating environments common across Sindh, Punjab, and Balochistan.
Key 2025 market signals:
- C&I and grid-side storage expected to add 3–5 GWh in five years, unlocking a PCS market of USD 400–600 million and a significant TAM for SiC modules, drivers, and boards.
- MV interconnection (11–33 kV) increasingly requires fault ride-through (FRT), reactive power, and frequency support; SiC control and protection excellence is now a must-have.
- Localization priority: speed-to-market and lifecycle economics favor partners who can transfer technology, stand up local lines, and sustain long-term engineering support.
Expert perspective:
“SiC’s high-frequency switching and thermal headroom can shrink power conversion hardware while improving efficiency—critical in regions with constrained grids and high ambient temperatures.” — IEEE Power Electronics Magazine (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org)
Industry Challenges and Pain Points in Pakistan
Pakistan’s market presents a distinctive mix of environmental, regulatory, and operational constraints that legacy silicon technologies struggle to address.
- Harsh environmental envelope
- High ambient temperatures (regularly 45–50°C in southern regions) drive thermal stress and require oversized cooling in conventional designs.
- Dust ingress in industrial parks blocks heat exchangers and clogs filters, elevating junction temperatures and accelerating wear-out.
- Cost implication: Overbuilt cooling adds capex and parasitic consumption; frequent maintenance cycles disrupt production and inflate opex.
- Grid volatility on MV feeders
- Voltage sags/swells and harmonic pollution are common on 11–33 kV networks connected via distribution transformers to industrial parks.
- MV interconnection codes used by local utilities increasingly require FRT behavior, reactive support (Volt/VAR), and frequency response (P–f) while maintaining low THD.
- Cost implication: Nuisance trips, rejected commissioning, and penalties for power quality breaches extend project schedules and erode ROI.
- Energy economics and payback pressure
- Retail tariffs and cross-subsidy dynamics create a strong case for peak shaving, valley filling, and backup power through BESS.
- PCS must surpass 98% to meaningfully lower round-trip losses; silicon platforms often plateau at 95–96% in ruggedized configurations.
- Reliability and serviceability
- Dispersed industrial sites and import lead times demand robust, remotely diagnosable systems with predictive maintenance.
- Dust, heat, and humidity shorten lifespan unless materials, packaging, and thermal design are re-optimized.
- Localization and capacity-building gaps
- Local suppliers excel in conventional silicon but face competency gaps in SiC epitaxy, device processing, packaging, and reliability testing.
- International solutions can be cost-prohibitive with long service chains; local manufacturing and technology transfer are strategic priorities.
Expert perspective:
“Grid-support capabilities—ride-through, reactive power, and fast frequency response—must be integrated with converter controls and protection, especially where feeder strength is limited.” — CIGRE Technical Insights on Converter-Grid Interactions (https://e-cigre.org)
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for Pakistan
Sicarb Tech’s portfolio directly targets these pain points with high-performance products and deployment services tailored to local conditions.
- High-voltage SiC power modules (1200V–3300V)
- Low-inductance layouts, Si3N4/AlN substrates, Ag-sinter die attach, and liquid-ready baseplates withstand thermal cycles and dust-induced airflow variability.
- Field benefit: ≥98% PCS efficiency, 30–40% reduction in cooling volume, and stable operation at +175°C junction ratings.
- SiC MOSFET gate-drive and main control boards
- Active Miller clamp, negative gate bias, high CMTI isolation, DESAT and two-level turn-off; FRT/Q–V/P–f algorithms with grid-forming/grid-following modes and active LCL damping.
- Field benefit: Fewer nuisance trips on weak MV feeders, faster commissioning, and compliance with power quality requirements.
- Custom epitaxial wafers and wafer processing
- Large-diameter epi with engineered doping and low defectivity; SiC-specific thinning/dicing for robust edges and uniform backside metallization.
- Field benefit: Consistent breakdown voltages, lower leakage drift, and better thermal paths in compact modules.
- High-thermal-conductivity ceramic substrates and modular cooling
- Si3N4 for superior cycling strength; AlN for maximal conductivity; modular liquid/air coolers with dust-tolerant design.
- Field benefit: Maintains ΔTj targets despite dust and ambient heat, extending lifetime and reducing service calls.
- Reliability and test platforms
- HTGB/HTRB, power cycling (ΔTj control), and thermal shock rigs to qualify devices/modules for 45–50°C ambient and industrial dust scenarios.
- Field benefit: Predictable lifetimes and lower warranty risk.
- Technology transfer and local factory establishment
- Process know-how, equipment specs, training, and certification support to enable localized packaging and test, shortening delivery cycles and creating local value-add.
Performance Comparison for Pakistan’s MV and C&I Storage Use Cases
Converter Performance and Lifecycle Metrics in Hot, Dusty Environments
| Criterion | Silicon carbide solution | Traditional silicon solution |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion efficiency (PCS/inverter) | ≥98% at 50–200 kHz | 95%–96% at lower frequency |
| Power density | 1.8–2.2× higher | Baseline |
| Cooling hardware | Compact; liquid cooling optional | Large air-cooling systems |
| Junction temperature capability | -40°C to +175°C | Lower thermal headroom |
| Uptime in dusty environments | High (robust thermal stack; coatings) | Lower; frequent cleaning |
| Expected MTBF | Toward 200,000 hours | Lower under heat/humidity |
Grid Interconnection and Commissioning Outcomes
| Requirement | SiC solution with integrated algorithms | Legacy silicon approach |
|---|---|---|
| Fault ride-through | Built-in FRT curves; robust PLL/GFM | Custom, slower tuning |
| Reactive and frequency support | Q–V and P–f droops; virtual inertia | Limited setpoints |
| THD control | Active damping for smaller LCL filters | Larger filters required |
| Commissioning timeline | Parameter packs; remote diagnostics | Longer on-site trials |
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
- Punjab industrial park energy storage (2 MW/4 MWh)
- Challenge: High tariffs and feeder sags caused curtailed operation and poor ROI.
- Solution: SiC-based PCS with integrated FRT and reactive support; modules on Si3N4 substrates and liquid cooling.
- Result: Efficiency up to 98.2%; equipment volume down 35%; stable operation; subsequent expansion orders.
- Textile drives in Sindh
- Challenge: Dust and heat triggered thermal trips and derating during peak seasons.
- Solution: SiC modules with Ag-sinter attach and optimized cooling; gate-drive upgrades with negative bias and clamp.
- Result: Reduced trips; improved uptime; lower maintenance intervals.
- MV PV in southern Pakistan
- Challenge: Weak feeders and EMC challenges inflated commissioning time.
- Solution: 100 kHz SiC inverters with dv/dt control, active damping, and pre-validated FRT profiles.
- Result: ≥98.5% efficiency; ~40% cooling volume reduction; faster grid acceptance.

Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Local Compliance
- Thermal and mechanical robustness
- Si3N4/AlN and Ag-sinter stacks resist thermal fatigue under dust-constrained cooling, keeping ΔTj within limits even during 45–50°C heatwaves.
- Grid code readiness for MV feeders
- FRT ride-through curves, reactive power priority, and frequency droops tailored to utility practices; low THD via active damping aligns with power quality expectations.
- EMC and power quality excellence
- dv/dt shaping, common-mode suppression, and Kelvin-source layouts reduce emissions and enable smaller filters—simplifying compliance and reducing footprint.
- Reliability proven by accelerated testing
- HTGB/HTRB stress for gate oxide and leakage stability; ΔTj-controlled power cycling validates packaging endurance for long MTBF.
Expert perspective:
“Converter platforms that combine wide bandgap devices with grid-support control strategies are better suited for modern distribution networks with variable conditions.” — IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org)
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services
Sicarb Tech provides a comprehensive, de-risked pathway to localized SiC capability in Pakistan.
- Advanced R&D with institute-backed innovation
- Collaboration within the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park accelerates material, epitaxy, and packaging advancements across R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC.
- Proprietary manufacturing processes
- Detailed process windows for epitaxy (doping profiles, uniformity), implantation/anneal (activation and surface recovery), die attach (Ag sinter optimization), and dicing/thinning (edge integrity for high breakdown).
- Complete technology transfer packages
- Transfer documents, SOPs, process FMEAs, equipment specifications, acceptance protocols, and spare parts plans.
- Multi-tier training: engineering, technicians, and maintenance staff, plus certification support to align with IEC/IEEE performance and safety standards.
- Factory establishment and ramp
- Feasibility studies, facility design (HVAC, clean zones, ESD/ESHV safety), procurement support, installation and SAT/FAT, pilot runs, and ramp to target OEE.
- MES/SCADA integration for traceability, SPC, and audit-ready records.
- Quality and compliance enablement
- Guidance for EMC, environmental, and electrical safety; documentation for tenders and financing; alignment with local utility interconnection practices and test labs.
- Ongoing optimization and service
- Yield improvement, cost-down programs, design-for-reliability updates, and rapid-response field engineering across Pakistan’s industrial centers.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends
- PCS SiC penetration rising to >35% by 2028
- Capital and operating savings plus higher reliability favor SiC adoption as costs decline.
- Grid-forming and synthetic inertia at MV
- As renewables and storage grow, advanced control modes (VSM, virtual oscillator) will become standard for resiliency.
- Predictive maintenance and digital twins
- Telemetry from gate drivers and thermal nodes feeding analytics for RUL estimation, optimizing service schedules.
- Localized ecosystems
- Partnerships to establish packaging and test capacity in Pakistan, shrinking lead times and building domestic competency.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Which standards apply to PCS and MV inverters in Pakistan?
Systems typically align with IEC converter, EMC, and safety standards and IEEE grid-interconnection practices. Utilities impose MV feeder requirements for FRT, reactive and frequency support, and THD limits. Project documentation should demonstrate compliance, test results, and commissioning procedures. - Can SiC solutions handle 45–50°C ambient and dust?
Yes. Conformal coating, corrosion-resistant finishes, dust-tolerant cooling, and Si3N4/AlN substrates with Ag-sinter attaches maintain performance. Reliability screening (HTRB/HTGB, ΔTj cycling) validates durability. - What efficiency and density improvements are realistic?
PCS efficiency at ≥98% and power density improvements of 1.8–2.2× are typical, enabling ~30–40% reductions in cooling size and cabinet volume. - How long does local production setup take?
With technology transfer and coordinated equipment sourcing, pilot production can start in 6–9 months; full ramp typically completes in 12–18 months, contingent on facility readiness and workforce training. - Will SiC integrate with existing systems?
Yes. Sicarb Tech provides integration engineering, parameter packs for control boards and drivers, and EMC strategies to minimize redesign and accelerate commissioning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operations
The combination of high-frequency operation, high voltage capability, and thermal resilience makes SiC the pragmatic upgrade for Pakistan’s PCS, MV inverters, and industrial drives. When paired with robust packaging, grid-ready control libraries, and proven reliability testing, SiC delivers measurable gains: ≥98% efficiency, 1.8–2.2× power density, rapid commissioning, and strong uptime in harsh conditions. Choosing a partner with vertically integrated materials-to-systems expertise and technology transfer capability ensures faster ROI and sustainable local capability.
Get Expert Consultation and Custom Solutions
Sicarb Tech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
- Weifang City SiC hub; member of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park
- 10+ years of customization; supporting 19+ enterprises
- Full-cycle solutions from materials (R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, SiSiC) to devices, packaging, testing, and controls
- Proprietary processes, quality systems, and international certification support
- Complete technology transfer and factory establishment services—from feasibility to commissioning
- Application engineering, integration, and continuous improvement for Pakistan’s market
Contact for a free consultation, feasibility assessment, and tailored roadmap:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Secure 2025–2026 co-development and localization slots now to accelerate compliance, commissioning, and ROI across PCS, MV inverters, and industrial drives.
Article Metadata
Last updated: 2025-09-10
Next scheduled update: 2026-01-15

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




