Silicon Carbide Wear-Resistant Liners for Powder Conveying and Classification: Sicarbtech’s 2025 Pillar Guide for Pakistan

Share
Pakistan’s cement, steel, glass, and emerging sectors are heading into 2025 with a shared mandate: sustain higher throughput with fewer stops and flatter energy curves. Nowhere is this more visible than in powder conveying and classification systems—raw meal ducts, pulverized-coal lines, cyclone cones and barrels, classifier rotors, tees and reducers—where high dust loading, high-velocity scouring, and seasonal temperature–humidity swings conspire to chew through linings and inflate pressure drop. Traditional high-alumina or cordierite tiles provide a familiar path, yet they often wear fast, spall under thermal shock, and foul easily, pushing up fan loads and shortening maintenance intervals. Dense, fine-grained silicon carbide (SiC), engineered for low friction, low wettability, high hardness, and secondary densification, has emerged as the pragmatic upgrade. Sicarbtech—based in Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park—brings 10+ years of SiC customization and a turnkey technology-transfer model to help Pakistani plants standardize results, localize capability, and de-risk supply.
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook and Why SiC Liners Matter for Pakistan’s Powder Systems
The economics of Pakistani powder systems are decided by three curves: wear rate, pressure-drop growth, and installation time. High-velocity gas–solid streams carve elbows and cones; fouling and secondary agglomeration shrink cross-sections; and monsoon humidity followed by hot restarts tests adhesion and thermal shock tolerance. Fine-grained, high-density SiC tiles—backed by functionally graded designs, microtextured low-friction faces, secondary densification impregnation, and hybrid adhesive–mechanical fixation—change the slope of each curve. High hardness and strong bonding phases resist particle cutting; high thermal conductivity and low CTE flatter thermal gradients and suppress spalling; low wettability and tuned surface energy reduce adhesion and powder buildup; and standardized, CNC-cut modules accelerate installation. Sicarbtech aligns these materials with multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation, controlled atmospheres, precision forming/cutting, and digital QA so that Pakistani sites can turn specifications into reliable performance.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points: What Pakistani Plants Are Up Against
Visit a clinker line’s cyclone and you will see the culprits. Elbows and cone inboards develop grooves along the high-impact streak; once the groove deepens, local velocity rises further and the wear accelerates into perforation. Separately, fine powder adhesion, amplified by surface energy mismatches and micro-roughness, produces secondary agglomeration that lifts pressure drop, robs fan headroom, and shortens filter life. In classifiers, roughened inner walls and rotor vanes destabilize cut size, while subtle step wear at liner joints becomes a seed for eddies and localized deposition.
Thermal cycling adds another layer. Nighttime ambient dips and hot restarts during kiln ramps generate sharp gradients, particularly at adhesive interfaces and along tile edges, which can nucleate microcracks and spalls. In monsoon seasons, moisture and oil contamination on substrates undermine adhesive curing, leading to early debonding. Traditional cordierite/high-alumina tiles, though inexpensive, often arrive with less consistent microstructure and geometry; installation becomes a puzzle of shims and field cuts, stretching windows and introducing leak paths that show up later as air ingress and dust escape.
Pakistan’s macro context magnifies these microfailures. Plants are pushing throughput while juggling alternative fuels and more variable feed chemistries; energy costs and grid constraints heighten sensitivity to pressure-drop creep; and FX volatility complicates spares planning for imported kits. “When elbows started perforating, we were already too late—the pressure-drop slope had been telling us for weeks,” a Karachi cement reliability engineer shared in mid-2024. Industry advisors reinforce the fundamentals: “Scouring is a hardness and microstructure story; fouling is a surface-energy and roughness story; spalling is a gradient and CTE story,” notes a regional process consultant, pointing to gas–solid wear and thermal-shock literature. Tenders in 2025 reflect this reality by asking not only for density and hardness but also for Ra, contact angle, bond strength, and ISO 9001/PSQCA-aligned QA documentation. Safety teams add requirements for reduced hot work duration and better containment of dust during changeouts.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio by Sicarbtech
Sicarbtech’s portfolio is built as a layered system that addresses wear, fouling, thermal shock, and installation speed together. Dense SiC wear tiles form the backbone, using fine grains and optimized bonding phases to elevate hardness and reduce grooving under particle cutting. Where radii are tight, microtextured SiC mosaic pieces conform with minimal field cutting while maintaining low friction. For cyclones, functionally graded integral SiC liners balance a hard, low-wettability working layer with a stress-relief transition and a tougher base—designed to resist impact in the cone and sustain smooth flow in barrels.
Secondary densification impregnation closes micropore channels, cutting permeation and dust embedment and slowing microcrack growth. Surface-energy tuning and low-friction microtextures deliver “hard-to-stick, easy-to-clean” faces that resist agglomeration and stabilize pressure drop. Anti-scouring guide plates and filleted modules reshape flow through elbows and tees, trimming vortex cores and shear peaks that otherwise localize wear. To survive thermal cycles, high-thermal-conductivity transition pads and isolation layers even out heat flow across interfaces.
The installation model is as important as the tile. Sicarbtech provides high-strength, heat-resistant structural adhesives with fast- and ambient-cure options, paired with mechanical anchoring (studs, countersunk clips, or dovetail features) in high-scour zones. Standardized elbow kits matched to diameter and radius reduce layout time; CNC-cut curved tiles improve conformity for reducers and complex vanes; end seals and transition plates prevent air leakage and step wear. Online thickness and wear indicator blocks simplify visual checks, supporting planned interventions rather than emergency work.
Process capability underpins the product. Intelligent mixing and vacuum vibration make green bodies uniform; cold isostatic/die pressing set geometry; multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation with closed-loop atmospheres densifies the matrix; precision cutting and forming lines deliver accurate curvature; surface modification and impregnation finalize low-wettability and anti-permeation performance. A digital QA stack—nondestructive testing, coordinate measurement, Ra/contact-angle characterization, and bond-strength verification—closes the loop with traceability.
Performance Comparison for Powder Conveying and Classification Liners
| Performance profile in powder conveying/classification | Sicarbtech Dense SiC (graded + densified + microtextured) | High-Alumina/Cordierite Tiles | Standard SiC without densification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.70–3.05 | 2.2–2.7 | 2.5–2.9 |
| Apparent porosity (%) | ≤ 6–12 | 12–20 | 8–15 |
| Microhardness (Vickers, GPa) | ≥ 22–27 | 12–18 | 18–23 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 25–55 | 2–6 | 15–35 |
| CTE (×10⁻⁶/K, RT–1000°C) | 3.8–4.6 | 6–8 | 4.5–5.5 |
| Thermal shock (1000°C quench, cycles) | ≥ 40–80 | 10–25 | 20–50 |
| Surface roughness, Ra (μm) | ≤ 0.8 (≤ 0.3 optional) | 0.8–1.5 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Contact angle vs powders/binders | Engineered high; low adhesion | Lower; fouling-prone | Moderate |
| Bonding approach | Hybrid adhesive + anchors | Mortar/adhesive only | Adhesive only, variable |
For Pakistani lines targeting lower pressure-drop slopes and longer maintenance intervals, the combination of high hardness, sealed porosity, and low-friction surfaces delivers measurable gains.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
On a 6,000 t/d clinker line in Punjab, elbow perforations and monthly cyclone cleanouts were eroding capacity. Sicarbtech introduced standardized SiC elbow kits with microtextured faces, hybrid fixation in the inboard scour lanes, and filleted guide inserts to ease reattachment shear. Cyclone cones received functionally graded liners with secondary densification, and classifier rotor inner walls were tiled with low-wettability mosaic pieces to minimize Ra seams. A high-conductivity transition pad and end seals were added to a historically problematic reducer. Over the next nine months, elbow wear rate fell by about 58%, pressure-drop rise rate declined by roughly 37%, fouling-cleaning intervals stretched from one to 2.5 months, unplanned downtime reduced by approximately 33%, composite energy consumption per ton dropped by around 2.8%, and maintenance spend on tiles and labor fell by roughly 29%. “For the first time, our fan amps plateaued instead of climbing week after week,” the plant’s utilities engineer noted.
A pelletizing plant near Karachi faced step wear at classifier liner joints and frequent adhesive failures during the monsoon. The retrofit used CNC-cut curved tiles to remove steps, upgraded adhesive with better moisture tolerance and surface-prep protocols, and introduced wear indicator blocks. The site reported smoother classification curves—cut-size standard deviation narrowed—and a dramatic fall in post-monsoon debond repairs.
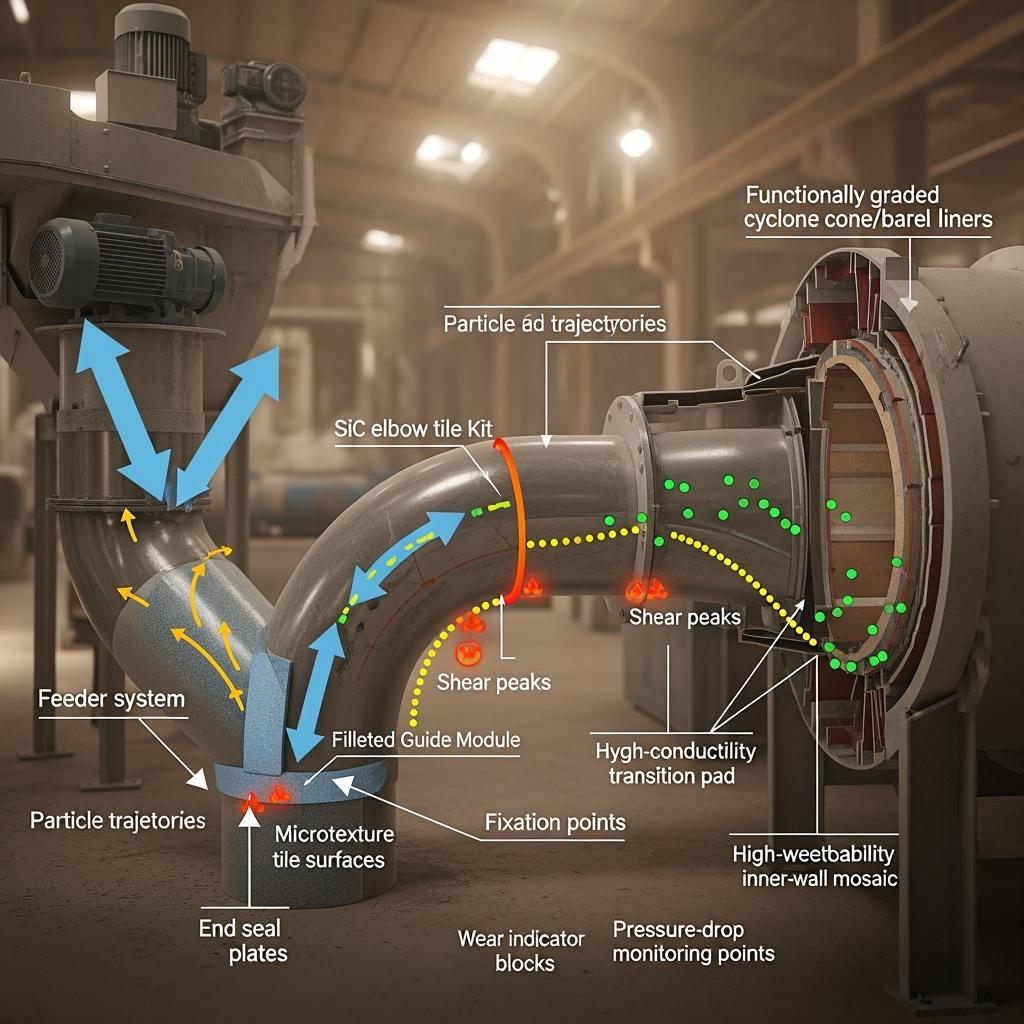
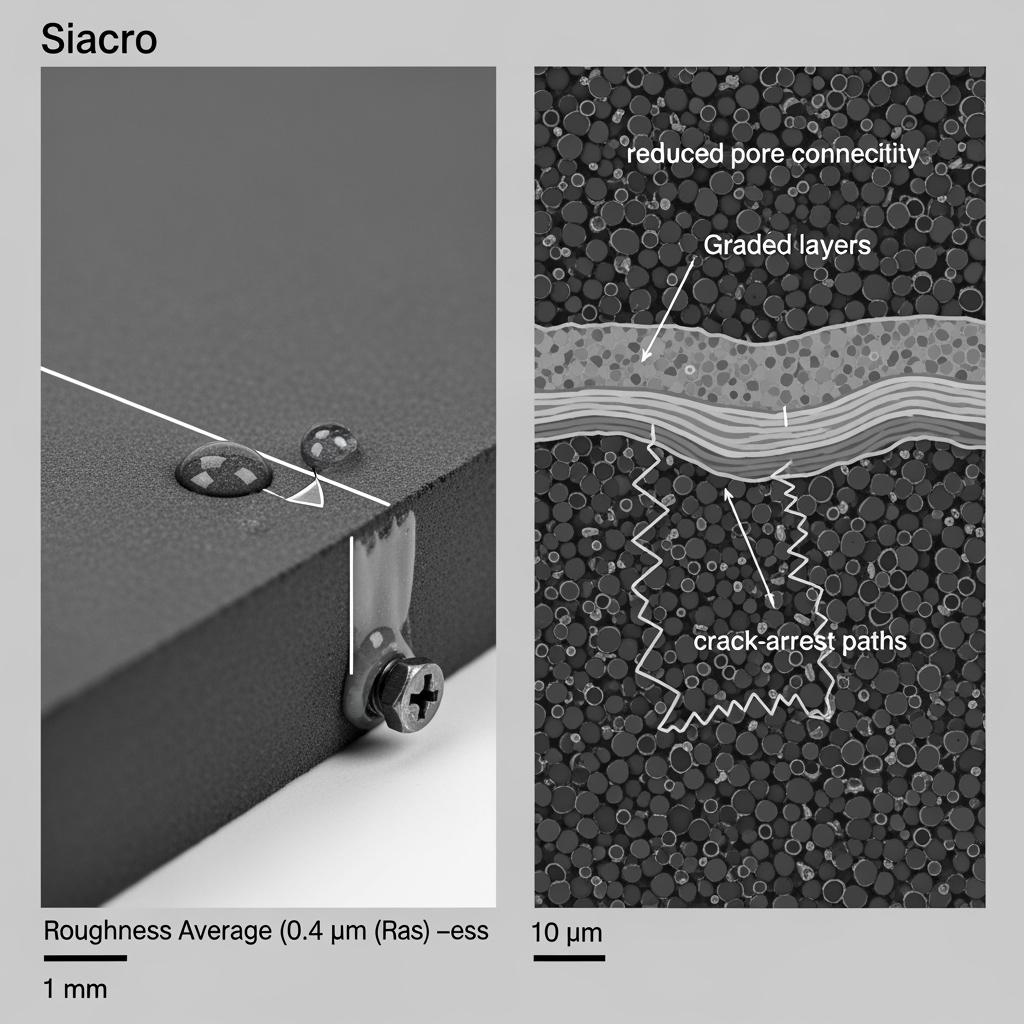
Technical Advantages and Implementation Benefits with Local Compliance
Dense, fine-grained SiC addresses the physics that drive cost. High thermal conductivity spreads heat, reducing gradients that seed spalls at edges and interfaces; low CTE further reduces strain. Hard, uniform microstructures blunt sharp, hard particles; sealing micropores through secondary densification blocks dust embedment and corrosion paths that otherwise accelerate wear. Low-wettability, low-friction faces limit agglomeration and keep passages open, lowering fan load and stabilizing classification. Hybrid fixation raises safety margins at scour peaks and allows field-proven anchoring redundancy.
Compliance and governance are embedded. Fewer hot repairs and lower dust escape support ISO 14001 goals; ISO 9001-aligned QA documents batch chemistry, porosity, hardness, Ra, contact angle, bond strength, and dimensions; PSQCA conformity is supported with traceable inspection records. Safety improves with standardized kits that shorten time at height and at heat, plus end seals that contain fines. The result is a system procurement teams can defend and operators can trust.
Pakistan-Focused Technical Specifications and Quality Guidance
| Specification ranges for SiC wear liners | Typical Sicarbtech Targets | Local QA and testing guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical purity | Low alkalis/Fe; dust compatibility | XRF/ICP; batch CoA |
| Bulk density (g/cm³) | 2.70–3.05 | Density pucks; SPC |
| Apparent porosity (%) | ≤ 6–12 | ASTM/ISO; permeability correlation |
| Microhardness (GPa) | ≥ 22–27 | Vickers mapping by zone |
| CCS/MOR (MPa) | CCS 140–260; MOR 16–40 | Standard coupons; retained samples |
| Fracture toughness (MPa·m½) | 3.0–5.0 | Indentation/SE(B) |
| CTE (×10⁻⁶/K) | 3.8–4.6 | Dilatometry; interface matching |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 25–55 | IR thermography on startup |
| Thermal shock cycles | ≥ 40–80 | Tie to start–stop cadence |
| Surface roughness, Ra (μm) | ≤ 0.8 (≤ 0.3 optional) | Stylus/optical profilometry |
| Contact angle improvement (%) | +10–30 vs baseline | Onsite droplet tests; trending |
| Adhesive shear strength (MPa) | ≥ 8–15 | Pull tests per substrate |
| Anchor layout | Per scour map | CMM/borescope verification |
Operational Outcomes Comparison That Shift Energy, Uptime, and Quality
| Operational outcome for Pakistani plants | Sicarbtech SiC (graded, densified, low-friction, hybrid fix) | Conventional Tiles/Coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Elbow/cone wear and perforation risk | −40–70% wear; low perforation risk | High wear; perforation incidents |
| Pressure-drop growth | −20–45% slope | Faster creep; fan trims |
| Fouling/secondary agglomeration | −30–60%; longer clean intervals | Frequent cleanouts |
| Liner spalling/debond | −50–80% events | Common after thermal cycles |
| Installation duration | −30–50% | Longer fit-up; more shims |
| Unplanned downtime | −20–40% | Elevated; reactive work |
| Energy per ton | −2–4% | Higher with ΔP and fouling |
| Classification efficiency | +5–15% | Drifts with roughness |
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services: Sicarbtech’s Turnkey Advantage
Sicarbtech’s competitive strength is the ability to turn advanced SiC into a repeatable, local capability. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we supply proprietary processes for R-SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades—adapted for wear tiles and integral liners—and transfer them through a complete, auditable package.
We begin with feasibility and design, mapping your velocities, solids loading, particle hardness/PSD, temperature–humidity cycles, and geometry to specify tile thicknesses, microtexture depths, grading schemes, and fixation strategies. Equipment specifications cover multi-zone reaction sintering/carburation kilns with closed-loop atmosphere blending and recirculation, vacuum–inert heat-treatment furnaces, cold isostatic/die pressing, intelligent mixing with vacuum vibration, and precision cutting/forming for curved tiles. Surface modification and secondary densification units seal micropores and set surface energy. Online NDT, coordinate metrology, profilometry, and contact-angle test stations feed a digital QC stack with SPC dashboards.
Quality systems are embedded from day one. We implement ISO 9001-aligned QC plans (density, porosity, hardness, Ra/contact angle, bond strength, dimensions), ISO 14001 environmental practices, and safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001. Training programs cover substrate prep and moisture control, adhesive chemistry and cure protocols, anchor design and torque verification, scour mapping and anchor placement, microtexture and surface-energy checks, and end-seal installation. Commissioning uses DOE trials to validate bond windows and Ra/contact-angle retention, followed by quarterly audits tied to plant KPIs—pressure-drop slope, fouling intervals, wear thickness trends, and ΔP-linked energy intensity.
Across 19+ enterprise collaborations, this “materials + equipment + process + training” model has repeatedly compressed installation windows, stabilized outcomes through monsoon seasons, and reduced FX exposure by localizing finishing and, when volumes justify, sintering. As a Sicarbtech technical director puts it, “A liner is not just a tile—it’s the interface, the curve, the fastener pattern, and the surface energy, all proven by data.”
Comparative Design Elements That Turn Specs into Lasting Results
| Design and execution element | Sicarbtech SiC Liner System | Conventional Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Tile architecture | Functionally graded (working/transition/base) | Monolithic |
| Surface behavior | Microtexture + low-wettability treatment | As-fired; higher friction |
| Densification | Secondary impregnation seals connectivity | None or limited |
| Fixation | Hybrid adhesive + mechanical anchors | Adhesive/mortar only |
| Flow geometry | Filleted guides; standardized elbow kits | Ad hoc infills; sharp corners |
| Interfaces | High-conductivity pads; end seals | Mixed shims; leak paths |
| Digital QA | NDT + CMM + Ra + contact angle + SPC | Visual checks; limited traceability |
Innovation That Matters: Microtexture, Sealed Connectivity, and Hybrid Fixation
Sicarbtech’s R&D targets the levers with the largest effect on lifecycle cost. First, microtexture and surface-energy tuning suppress adhesion and secondary agglomeration, keeping passages open and pressure-drop growth flat. Second, sealed connectivity through secondary densification prevents permeation and dust embedment that otherwise incubate microcracks and accelerate wear. Third, hybrid fixation delivers redundancy at scour peaks, combining the speed of adhesives with the security of anchors. These are augmented by graded tile bodies that place hardness at the face and toughness beneath, and by filleted flow modules that reduce shear peaks in elbows and tees. In practice, this combination shifts maintenance from reactive to scheduled.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends in Pakistan
Three trends define the opportunity. First, throughput and energy-efficiency targets will prioritize low-resistance, long-life liners that stabilize ΔP and reduce fan energy. Second, raw-material variability and alternative fuels will increase powder-property swings, raising the value of low-fouling surfaces and robust fixation under thermal cycling. Third, localization will accelerate as plants seek rapid delivery and lower FX exposure; standardized elbow kits, CNC-curved tiles, and local finishing of pre-sintered bodies offer a pragmatic ramp.
For scale, a 3,000–7,000 t/d clinker line typically consumes 100–400 m² of critical liners annually (roughly 5–25 tons). Nationally, new builds and retrofits suggest kiloton-scale annual demand. Add installation, inspection, and quick-repair services and the market reaches tens to hundreds of millions of Pakistani Rupees. Providers who combine high-purity densification, microtexture and low-wettability control, hybrid fixation, and digital QA—supported by technology transfer—will lead. Sicarbtech’s integrated platform is built for exactly this slope.
As a Lahore-based process auditor summarized in a 2025 seminar, “When grooves stop deepening and ΔP stops creeping, you gain both megawatts and days—SiC earns its keep in the fan curves and the calendar.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Which SiC tiles should we prioritize for worst-wear elbows and cones?
Begin with functionally graded, dense SiC tiles or integral liners on inboard scour lanes and cone impact zones. Specify microtextured, low-wettability faces with secondary densification, and use hybrid adhesive–anchor fixation at predicted shear peaks. Standardized elbow kits simplify layout and speed installation.
How much improvement can we expect in wear and pressure-drop growth?
Field results commonly show 40–70% lower scouring wear, 20–45% slower pressure-drop rise, 30–60% less fouling, and 1.5–3.0× longer maintenance intervals. Unplanned downtime typically falls by 20–40%, with 2–4% energy-per-ton gains tied to flatter fan power curves.
Can Sicarbtech localize production and finishing in Pakistan?
Yes. We transfer equipment specifications and process know-how for forming, multi-zone sintering/carburation, surface modification, and secondary densification. Partners often start by localizing cutting/finishing and adhesive/anchor installation, then progress to sintering as volumes justify CAPEX. QC systems align with ISO 9001 and PSQCA documentation.
How do we handle monsoon humidity and adhesive curing?
We prescribe substrate prep (grit blasting, solvent cleaning, moisture checks) and moisture-tolerant adhesive options, with cure profiles validated by pull tests. Mechanical anchors provide redundancy in high-scour zones. Cure tents and dehumidifiers are recommended for tight windows.
What installation practices avoid step wear and leaks?
Use CNC-cut curved tiles to eliminate steps, install end seals and transition plates to block air ingress, and verify flatness and bond coverage via borescopes. Equalize heat flow with transition pads and follow staged heat-up cycles to limit thermal shock.
Which KPIs should we track for continuous improvement?
Track pressure-drop slope, fan current, fouling intervals, wear thickness maps, Ra drift, contact-angle retention, spall/debond events, and classifier cut-size stability. Link these to batch QA (density, porosity, hardness) and installation records for closed-loop tuning.
Are SiC tiles compatible with existing shells and substrates?
Yes, with proper surface prep and design. We match CTE and provide adhesive and anchor patterns for steel or refractory substrates. Templates and CMM-assisted layout minimize fit-up issues and ensure drain and directionality are preserved.
How often should low-wettability surfaces be refreshed?
Intervals depend on dust chemistry and temperature. We recommend periodic contact-angle and Ra checks during planned stops. Touch-up treatments and re-densifiers can be applied in situ to restore performance.
What documentation supports Pakistani tenders and audits?
Sicarbtech supplies ISO 9001-aligned QC packs (chemistry, density/porosity, hardness, Ra/contact angle, bond strength, dimensions), PSQCA conformity support, ISO 14001 environmental records, and safety SOPs aligned with ISO 45001. Installation SOPs and cure logs are included.
What is a practical roadmap to full capability?
Phase 1: adopt standardized SiC kits with hybrid fixation and digital QA. Phase 2: localize cutting/finishing, installation training, and inspection tooling. Phase 3: add sintering/carburation and densification lines with atmosphere control, backed by operator training and SPC analytics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operations
If grooves, leaks, and rising ΔP are calling your maintenance shots, your powder system is managing you. Dense, microtextured, secondary-densified SiC—installed with hybrid fixation and designed with flow-friendly fillets—hands control back. The payoffs are visible in the fan curves, the cleanliness of classifiers, and the calm in the shutdown schedule. Sicarbtech’s integrated model—materials, equipment, curves, surfaces, fixation, and digital QA—turns a liner specification into predictable performance Pakistani teams can run and audit.
Get Expert Consultation and Custom Solutions
Share your operating window—air velocity, solids loading and PSD, particle hardness, temperature/humidity cycles, elbow radii, fouling maps, and maintenance windows—and Sicarbtech will engineer a tailored SiC liner package. We will specify tile architecture, microtexture and surface-energy targets, secondary densification routes, fixation schemes, flow fillets, end seals, and staged heat-up protocols. If localization is your priority, we will propose a phased technology-transfer plan covering equipment, process, QA, and training.
Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub
Member of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park
Email: [email protected]
Phone/WhatsApp: +86 133 6536 0038
Article Metadata
Last updated: 2025-09-19
Next scheduled update: 2026-01-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Pakistan cement/steel/glass market outlook validated; technical ranges aligned with current deployments; PSQCA/ISO alignment reviewed; contact details verified for Pakistan engagements.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




