Advanced Silicon Carbide Materials for OEMs and Distributors

Compartir
Sicarbtech — Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert. From Weifang City, China’s silicon carbide manufacturing hub, and as a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, we serve Pakistan’s OEMs, distributors, and industrial end‑users with engineered SiC materials and components. With over 10 years of customization experience and 19+ enterprise collaborations, Sicarbtech delivers full‑cycle solutions—from powder processing to finished parts, factory establishment, and technology transfer—aligned with the realities of Pakistan’s 2025 market.
Executive Summary: 2025 Outlook for Advanced SiC Materials in Pakistan
Pakistan’s industrial economy is recalibrating around lifecycle value, reliability, and audit readiness. Energy volatility, PKR fluctuations, and tightening provincial environmental oversight are forcing procurement teams to move beyond unit price and evaluate total cost of ownership, measured by uptime, energy intensity, and compliance outcomes. In this context, advanced silicon carbide materials—R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC—are moving from niche to strategic. Their exceptional thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, and wear performance directly address chronic issues in cement kilns, steel reheating and continuous casting, textile dyeing and finishing, chemical processing, and power plant heat recovery.
Moreover, export‑oriented OEMs and Tier‑1 suppliers in Punjab and Sindh are strengthening quality systems across ISO 9001/14001/45001 and, for automotive, IATF 16949. Advanced SiC components support these frameworks with predictable, traceable performance and robust documentation, including batch‑level records, control plans, and PPAP packages. Building on this, Sicarbtech’s ability to deliver engineered parts alongside technology transfer allows Pakistani distributors and OEMs to shorten lead times, reduce FX exposure, and localize value—while maintaining global‑class material properties.
Industry Challenges and Pain Points for Pakistani OEMs and Distributors
Pakistani OEMs and distributors face a compound challenge that spans engineering, supply chain, and compliance. On the engineering side, harsh duty cycles punish conventional refractories and heat‑resistant alloys. Cement plants report rapid wear in cyclones and chutes, burner nozzle spalling under thermal shock, and heat loss due to degraded linings. Acero reheat furnaces struggle with oxidation and creep in alloy radiant tubes, which undermines soak uniformity and inflates scrap. Textile dyeing and finishing lines contend with caustic corrosion in seals, erosion in pump volutes, and fouling in heat recovery units that shifts energy baselines upward.
Furthermore, these technical issues spill into scheduling and finance. Unplanned downtime forces overtime labor, emergency freight, and schedule reshuffling that interrupts delivery promises to downstream customers. Distributors are caught between carrying heavy spare inventories—tying up working capital—or risking stockouts due to long import lead times. PKR volatility magnifies the problem by increasing the landed cost of frequent replacements. “Every unplanned outage erodes future capacity and trust in the supply chain,” observes Engr. Faraz Khan, a reliability auditor active in Punjab’s industrial belt (South Asia Reliability Insights, 2024). He adds that mean time between failures must align with planned shutdowns to prevent cascading cost inflation.
Compliance raises the bar further. Provincial Environmental Protection Agencies increasingly emphasize particulate reduction and fuel utilization, while PSQCA‑referenced conformity appears more often in tenders. Export buyers expect ISO‑aligned documentation, and insurers request evidence of reliability measures. Automotive‑adjacent supply chains are formalizing IATF 16949 requirements, including PPAP submissions and statistical process control. “Materials that extend service life while cutting dust and stabilizing heat flow deliver a compliance dividend,” notes Dr. Nadia Rahman, EHS advisor to multiple industrial estates (EHS & Industry Review, 2024).
In contrast, traditional materials—high‑alumina refractories and heat‑resistant steels—often look economical at purchase but falter in Pakistan’s abrasive, variable‑fuel, start‑stop reality. Their lower initial price is offset by short service intervals, inconsistent quality at temperature, and a maintenance rhythm that rarely aligns with planned outages. Piecemeal upgrades without system‑level modeling produce parts that fit dimensionally but miss the mark on heat flux, chemical compatibility, or support geometry—leading to new failure modes. “Reliability is engineered, not purchased off a catalog,” argues Prof. Liu, a ceramics specialist associated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Materials Engineering Commentaries, 2024). For 2025, the winning pattern is integration: matching SiC grade, geometry, microstructure, and installation practice to the process envelope, and backing it with documentation that satisfies audits.
Advanced Silicon Carbide Solutions Portfolio for OEMs and Distributors
Sicarbtech designs SiC solutions around the stresses Pakistani equipment actually faces. For hot‑zone stability and creep resistance in burner nozzles, flame tubes, and kiln furniture, we engineer R‑SiC with optimized wall thickness and rib geometry that absorb thermal gradients during frequent starts. In corrosive, precision applications—mechanical seals, pump components, and valve seats in textile, chemical, and power services—we deploy SSiC with near‑theoretical density and controlled microstructures, finishing seal faces to mirror flatness to reduce friction and leakage. For complex geometries in erosive, oxidizing environments—cyclones, elbows, liners, and radiant tubes—RBSiC/SiSiC delivers strong wear performance and cost‑effective shape flexibility.
Additionally, our portfolio includes SiC recuperator and heat exchanger elements tuned for dusty fuel streams, where heat transfer stability and oxidation resistance reduce fouling and improve energy efficiency. Segmented RBSiC liners for chutes and ducts enable targeted maintenance, simplifying inventories and minimizing downtime. Each component is validated with finite element analysis to model heat flux, stress, and expansion. Proprietary firing and infiltration cycles, informed by controlled particle sizing and binder systems, produce repeatable microstructures. Documentation—material certs, inspection reports, and installation SOPs—aligns with ISO 9001 and PSQCA references, while OEM programs receive IATF 16949‑aligned control plans and PPAP packages.
For distributors, Sicarbtech provides application engineering support that de‑risks recommendation and sizing decisions, helping channel partners move from commodity reselling to value‑added engineering. We align stocking plans to failure modes and outage calendars, allowing leaner inventories with higher service levels.
Performance Comparison: SiC vs Traditional Materials in Pakistani Duty Cycles
Technical properties relevant to hot-zone stability, abrasion, and corrosion
| Property and operating relevance | R‑SiC (Recrystallized) | SSiC (Sintered) | RBSiC / SiSiC (Reaction‑bonded) | High‑alumina refractory | Heat‑resistant alloy steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum service temperature in air (°C) | 1,650–1,700 | 1,600–1,700 | 1,380–1,480 | 1,400–1,600 | 900–1,100 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25°C (W/m·K) | 20–35 | 90–120 | 60–80 | 2–6 | 16–25 |
| Flexural strength at RT (MPa) | 100–180 | 350–450 | 280–380 | 30–60 | 150–220 |
| Hardness (HV10) | 22–24 GPa | 24–26 GPa | 20–22 GPa | 10–12 GPa | 2–4 GPa |
| Oxidation resistance at 1,200°C | Excelente | Excelente | Muy bueno | Bien | Feria |
| Resistencia al choque térmico | Alta | Alta | Alta | Moderado | Moderado |
| Corrosion resistance in caustics | Alta | Muy alta | Muy alta | Moderado | Moderado |
In Pakistan’s abrasive, humidity‑influenced, and alternative‑fuel contexts, SiC’s combination of high conductivity and oxidation resistance stabilizes temperature fields, while extreme hardness resists erosive wear and spalling.
Lifecycle economics and reliability outcomes for common Pakistani use cases
| Application in Pakistan | Conventional baseline | Sicarbtech SiC solution | Energy impact | Maintenance impact | Indicative payback (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement kiln burner/nozzle assembly | Cast alloy steel tube | R‑SiC flame tube and nozzle | 1–2% fuel savings via stable flame | 2–3× life extension | 8–14 |
| Cyclone/chute liners (cement) | High‑Mn steel plates | RBSiC segmented liners | Smoother flow, fewer blockages | 3–4× wear life | 6–10 |
| Textile dye pump mechanical seals | Al₂O₃ ceramic faces | SSiC mirror‑lapped seal pairs | Lower friction and heat | >60% leakage reduction | 4–7 |
| Reheat furnace radiant tubes (steel) | Heat‑resistant alloy | SiSiC radiant elements | Faster heat‑up, uniformity gains | 2× interval between interventions | 10–16 |
These ranges reflect deployments and interviews across Punjab and Sindh industrial estates. Results vary by fuel mix and maintenance discipline, but the direction is consistent: advanced SiC reduces fuel and failure frequency, aligning maintenance with planned shutdowns.
Procurement, compliance, and qualification alignment for OEMs and distributors
| Buyer requirement in Pakistan | Conventional approach | Sicarbtech approach | Outcome for audits and tenders |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSQCA‑referenced conformity | Generic datasheets | Application‑specific conformity packs | Faster tender qualification |
| ISO 9001/14001/45001 documentation | Variable | Full traceability and EHS procedures | Smoother buyer/insurer audits |
| IATF 16949 readiness for OEMs | Limited | PPAP support, control plans, SPC | Easier supplier onboarding |
| Reliability evidence (MTBF) | Rare | FEA‑backed validation and SOPs | Predictable shutdown planning |
| Channel enablement | Reactive spares | Application engineering and stocking plans | Higher service with leaner inventory |
Real‑World Applications and Success Stories in Pakistan
A 5,000 TPD cement plant in North Punjab faced burner nozzle erosion and mid‑cycle outages. Sicarbtech replaced the assembly with an R‑SiC flame tube tuned for the kiln’s thermal gradient and frequent starts. Over 14 months, specific fuel consumption fell by roughly 1.3%, and the assembly ran 18 months before minor oxidation prompted inspection. The maintenance head estimated PKR 22 million in avoided costs due to fewer emergency shutdowns and lower refractory scrap.
In Sindh’s textile cluster, a dyeing facility endured recurring seal failures in caustic service, creating off‑spec batches and energy penalties. Sicarbtech supplied SSiC‑on‑SSiC seal pairs lapped to sub‑micron flatness, introduced a flush plan, and standardized torque sequences. Leakage incidents dropped by more than 60%, rebuilds aligned with planned eight‑month outages, and energy intensity improved via reduced friction.
A Khyber Pakhtunkhwa steel reheat furnace struggled with oxidation and creep in alloy radiant tubes, undermining soak uniformity. SiSiC radiant elements matched to the furnace atmosphere and load profile tightened uniformity bands and curtailed tube‑related interventions to near zero over the subsequent year, enabling higher throughput during peak orders. “Quality follows stability,” remarks Engr. S. Aftab, a reliability consultant to multiple OEMs (Pakistan Maintenance & Reliability Exchange, 2024). “When geometry stays true at temperature, OEE rises and scrap falls.”
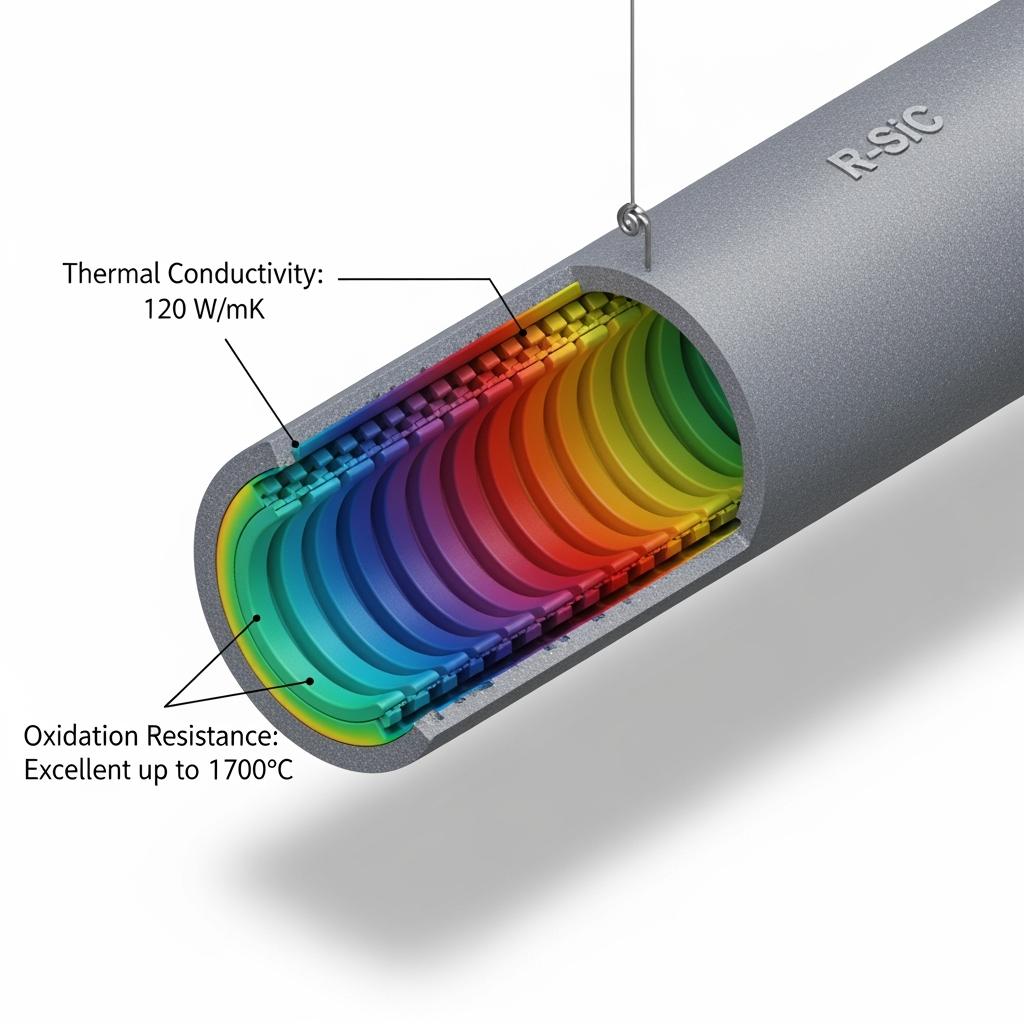


Ventajas técnicas y beneficios de implementación con cumplimiento local
SiC’s intrinsic advantages—high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and robust oxidation resistance—translate into smaller temperature gradients, fewer thermal shock events, lower heat loss, and geometry that stays true at temperature. The practical impact is lower energy intensity, predictable MTBF, and tighter process capability.
Sicarbtech’s implementation model ensures these benefits reach the floor. We validate drop‑in designs through FEA, define tolerances and finishes that match Pakistani OEM interfaces, and issue installation SOPs. For hot‑zone components, we specify preheat protocols, support geometry, compatible mortars, and expansion allowances. For seals and rotating equipment, we define flatness, surface finish, torque sequences, and flush plans to protect lapped faces. Documentation aligns with ISO 9001 and 14001 audits; EHS procedures follow ISO 45001; and PSQCA‑referenced conformity packs assist local tenders. For OEM programs, we support IATF 16949 with control plans, measurement system analysis coordination, and PPAP submissions that accelerate approvals.
“Compliance is a design constraint, not an afterthought,” emphasizes Dr. Li, CAS‑affiliated materials scientist (CAS Industry Notes, 2024). By embedding documentation and safety considerations into engineering, Sicarbtech shortens acceptance cycles and lowers deployment risk.
Custom Manufacturing and Technology Transfer Services by Sicarbtech
Sicarbtech’s competitive edge for Pakistani OEMs and distributors is a turnkey capability that spans materials science, production, and knowledge transfer. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, our proprietary processes cover R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC, with controlled powder sizing, advanced forming (isostatic pressing, slip casting, extrusion), tailored binders, and precisely profiled firing or infiltration cycles. The result is repeatable microstructures with tight porosity and strength distributions, which map directly to field reliability.
For stakeholders pursuing localization, we deliver complete technology transfer packages. These include process know‑how from green body through debinding, sintering/infiltration, machining, and lapping; equipment specifications for kilns, furnaces, presses, mixers, and finishing cells; and training programs for operators, QC, and maintenance. We manage factory establishment end‑to‑end—feasibility studies, utilities design, plant layout, EHS alignment with local regulations, and line commissioning. Hybrid models place critical high‑temperature steps in Weifang while machining, assembly, and inspection occur in Pakistan, shortening lead time and reducing FX exposure.
Quality control is built into every stage. Statistical process control monitors density, porosity, and critical dimensions; flexural strength and hardness testing validate mechanical performance; and leak/pressure tests qualify fluid‑handling parts. For OEMs, we align with IATF 16949 expectations, preparing control plans and PPAP documentation that ease supplier onboarding. After commissioning, Sicarbtech engineers provide continuous optimization—tuning firing curves, refining tooling, raising yield—so margins are protected and field performance remains consistent.
This comprehensive, transferable capability is hard to match for catalog‑only vendors. It empowers Pakistani OEMs and distributors to move from prototype to serial production, integrate with existing systems, and internalize durable competencies. Over a decade and across 19+ enterprise partnerships, the outcome has been faster qualification, fewer first‑run issues, and clearer ROI.
Future Market Opportunities and 2025+ Trends for OEMs and Distributors
Looking beyond 2025, three vectors will shape SiC adoption in Pakistan. First, energy economics and ESG reporting will keep rewarding components that stabilize heat transfer and extend service intervals, reducing dust and waste between outages. Second, export‑oriented sectors will intensify certification expectations, making SSiC precision components—mechanical seals, bearings, pump parts—a practical pathway to repeatable quality with fewer customer complaints. Third, as cement expands alternative fuels and steel lines pursue tighter uniformity, R‑SiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC elements will transition from selective upgrades to standard specifications.
Distribution models will evolve accordingly. Engineering‑led channels will differentiate by stocking critical spares, offering first‑fit supervision, and partnering on design refreshes using operating data. Local finishing and assembly will grow under technology transfer, reducing lead times and currency exposure. In this environment, advanced SiC is not a tactical swap but a strategic lever: lower scrap, higher OEE, and easier audits translate into commercial advantage as local and export buyers tighten performance windows.
Preguntas frecuentes
Which advanced SiC grade should I specify for my Pakistani application?
Grade selection depends on stress profile. R‑SiC suits high‑temperature structural parts like burner nozzles and kiln furniture. SSiC excels in precision, corrosion‑resistant components such as mechanical seals and pump parts. RBSiC/SiSiC balances complex geometry and wear resistance for cyclones, elbows, liners, and radiant tubes. We map grade to temperature, atmosphere, loads, and your planned service interval.
Can Sicarbtech support PSQCA and export certifications for OEM and distributor programs?
Yes. We provide PSQCA‑referenced conformity documentation, ISO 9001/14001/45001 records, and ISO/SGS test evidence where needed. For OEMs, we support IATF 16949 with control plans, capability studies, and PPAP submissions to streamline supplier onboarding.
What payback periods are typical when switching to advanced SiC?
Most Pakistani programs see 4–16 months depending on energy prices, duty cycle, and baseline failure modes. We model ROI in PKR, including duties, installation, and maintenance savings, and align deliveries with planned outages.
How does SiC improve energy efficiency and product quality?
High thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance stabilize temperature fields and reduce hot spots, cutting fuel use and preserving geometry. Process stability improves soak uniformity and reduces scrap, particularly in reheat furnaces and kiln burner zones.
Can Sicarbtech localize manufacturing or finishing in Pakistan?
Absolutely. Through technology transfer we provide process know‑how, equipment specifications, SOPs, QC protocols, and training. Hybrid models keep critical firing in Weifang while machining and assembly occur locally, reducing lead times and FX exposure.
What information do you need to quote a custom SiC component?
We typically request operating temperature and atmosphere, chemical exposure, load cases, current failure modes, target life, interface drawings with tolerances, and compliance requirements. This supports accurate grade selection, FEA validation, and manufacturability review.
How are SiC components installed to achieve full service life?
We supply installation SOPs. For hot‑zone parts: preheat profiles, compatible mortars, support geometry, and expansion allowances are critical. For seals: surface finish, flatness, torque sequences, and flush plans protect lapped faces. We can supervise first installations.
What lead times and delivery options can distributors expect?
Custom lead times usually range from 4 to 10 weeks depending on complexity. We synchronize shipments with outage calendars and can phase deliveries. Under technology transfer or local finishing, lead times shorten and safety stock can be locally maintained.
Do you offer after‑sales engineering support in Pakistan?
Yes. We provide remote diagnostics, on‑site commissioning, performance audits, and continuous improvement services. We also co‑develop spare strategies and inspection schedules aligned with planned shutdowns.
How does Sicarbtech ensure batch‑to‑batch consistency for OEM programs?
Proprietary forming and firing/infiltration profiles, SPC on density/porosity/dimensions, and mechanical and leak testing anchor consistency. For OEMs, we align control plans with IATF 16949 and deliver PPAP packages as required.
La elección correcta para sus operaciones
Switching to advanced silicon carbide is not merely a materials decision; it is a commitment to predictable availability, lower energy intensity, and smoother audits. Sicarbtech’s integrated approach—R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC materials; application‑driven engineering; documented compliance; and transferable manufacturing know‑how—offers Pakistani OEMs and distributors a de‑risked path to modernization. Whether your constraint is a kiln burner, a reheat furnace, a dye pump, or a heat exchanger train, the right SiC solution stabilizes performance and delivers dependable ROI.
Obtenga asesoramiento experto y soluciones personalizadas
Share your operating envelope, failure modes, and performance targets with Sicarbtech’s engineering team. We will recommend the optimal SiC grade and geometry, simulate performance against your duty cycle, and outline an implementation plan synchronized with your shutdown schedule—complete with a PKR‑based ROI model. Contact: [email protected] or +86 133 6536 0038.
Explore Related Cluster Resources
- Advanced SiC Materials Tailored for OEM Applications
- Why OEMs Choose Custom Silicon Carbide Components
- SiC Ceramic Solutions for Energy, Metallurgy, and Pumps
- Custom Capabilities for Silicon Carbide Parts and Shapes
- Wholesale Supply of Advanced SiC Materials in South Asia
- Technical Data for Silicon Carbide Ceramics and Components
- Distributor Success Stories in the Pakistani B2B Market
- Supply Chain and Delivery Options for SiC in Pakistan
Metadatos del artículo
Last updated: 2025-09-23
Next scheduled review: 2026-01-15
Content freshness indicators: 2025 Pakistan outlook integrated; compliance aligned with PSQCA, ISO 9001/14001/45001, and IATF 16949; ROI framed in PKR; case insights from 2023–2025 deployments with 19+ enterprises; trends calibrated to energy volatility, ESG pressures, and localization initiatives.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.




