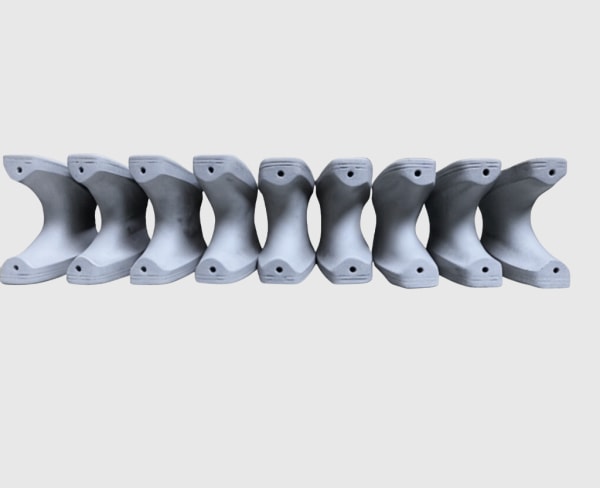
SiC Burner Nozzles for Optimized Combustion

Share
SiC Burner Nozzles for Optimized Combustion
Introduction: The Critical Role of SiC Burner Nozzles in Industrial Combustion
In the demanding world of industrial combustion, efficiency, longevity, and performance are paramount. Traditional materials often falter under extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, and abrasive conditions, leading to frequent downtime and increased operational costs. This is where custom silicon carbide (SiC) products, particularly SiC burner nozzles, emerge as a game-changer. Engineered for superior thermal resistance, exceptional hardness, and chemical inertness, SiC burner nozzles are revolutionizing high-temperature processing across a multitude of industries. From semiconductor manufacturing to aerospace, power generation to metallurgical furnaces, these advanced ceramic components are essential for achieving optimized combustion, reduced emissions, and extended equipment lifecycles. For engineers, procurement managers, and technical buyers, understanding the transformative potential of SiC burner nozzles is key to unlocking new levels of industrial performance and efficiency.
Main Applications: Where SiC Burner Nozzles Excel
The unique properties of silicon carbide make SiC burner nozzles indispensable in a diverse range of high-temperature industrial applications. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions ensures reliable and efficient combustion processes, directly impacting productivity and operational costs. Key industries benefiting from these advanced ceramic components include:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In highly sensitive processes requiring precise temperature control and minimal contamination, SiC burner nozzles contribute to uniform heating and long-term stability in diffusion furnaces and rapid thermal processing equipment.
- Aerospace: For components exposed to intense heat and corrosive gases, SiC burner nozzles provide critical performance in jet engine components, rocket propulsion systems, and thermal protection systems, ensuring durability and safety.
- Power Electronics: As power demands grow, SiC’s thermal conductivity and electrical properties make it ideal for high-power density applications, including heat sinks and power modules.
- Renewable Energy: In concentrated solar power (CSP) systems and biomass combustion, SiC burner nozzles offer excellent thermal shock resistance and high-temperature stability, improving efficiency and reliability.
- Metallurgy & High-Temperature Furnaces: From steel production to non-ferrous metal smelting, SiC burner nozzles are crucial for enhancing combustion efficiency, reducing fuel consumption, and extending the lifespan of industrial furnaces.
- Defense: For demanding military applications requiring extreme durability and performance under harsh conditions, SiC components are vital in ballistic protection, aerospace components, and propulsion systems.
- Chemical Processing: In environments with corrosive chemicals and high temperatures, SiC burner nozzles provide exceptional chemical inertness and wear resistance, crucial for reactors, incinerators, and heat exchangers.
- LED Manufacturing: Precision heating elements and components in LED production benefit from SiC’s thermal stability and purity, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Industrial Machinery & Equipment: General industrial furnaces, kilns, and dryers leverage SiC burner nozzles for improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance in a variety of manufacturing processes.
- Telecommunications: While less direct for burner nozzles, SiC’s broader applications in high-frequency and high-power electronics contribute to the backbone of telecommunications infrastructure.
- Oil & Gas: In refining and petrochemical processes, where high temperatures and corrosive gases are common, SiC components offer robust solutions for burners and process heaters.
- Medical Devices: Precision heating and high-purity requirements in some medical device manufacturing processes can utilize SiC technology for controlled thermal environments.
- Rail Transportation: Components requiring high wear resistance and thermal stability, such as braking systems or propulsion elements in specialized rail applications, can benefit from SiC.
- Nuclear Energy: In critical applications demanding extreme durability and radiation resistance, SiC is being explored for fuel cladding and structural components due to its superior properties.
Why Choose Custom Silicon Carbide for Burner Nozzles?
The decision to opt for custom SiC burner nozzles is driven by a compelling set of advantages that standard materials simply cannot match. Customization ensures that the components are precisely tailored to the specific operational demands of each application, maximizing performance and longevity.
- Superior Thermal Resistance: SiC maintains its structural integrity and performance at temperatures exceeding 1,600°C (2,900°F), far surpassing the limits of conventional metals and ceramics.
- Exceptional Wear Resistance: With a hardness approaching that of diamond, SiC burner nozzles resist abrasion from high-velocity gas streams and particulate matter, significantly extending their operational life.
- Outstanding Chemical Inertness: SiC is highly resistant to corrosive acids, alkalis, and oxidizing atmospheres, making it ideal for harsh chemical processing and combustion environments.
- Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance: The material’s low thermal expansion coefficient and high thermal conductivity enable it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or degradation.
- High Strength and Stiffness: SiC offers remarkable mechanical strength, even at elevated temperatures, ensuring the structural integrity of burner nozzles under operational stresses.
- Optimized Combustion Efficiency: The precise design and material properties of custom SiC nozzles facilitate more efficient fuel-air mixing and combustion, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions.
- Reduced Downtime and Maintenance: The extended lifespan and robust performance of SiC components translate directly into less frequent replacements and lower maintenance costs, boosting overall productivity.
Recommended SiC Grades and Compositions for Burner Nozzles
The performance of SiC burner nozzles is heavily influenced by the specific grade and composition of the silicon carbide used. Selecting the right material is crucial for optimizing properties like thermal conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance for a given application. Here are some commonly recommended SiC grades:
| SiC Grade/Type | Key Properties | Typical Applications for Burner Nozzles |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RBSiC/SiSiC) | High strength, excellent wear resistance, good thermal shock resistance, relatively lower cost. Contains free silicon. | Industrial kilns, metallurgical furnaces, incinerators, chemical process burners. |
| Sintered Alpha SiC (SSiC) | Extremely high purity, superior corrosion resistance, high strength, excellent creep resistance, no free silicon. | Semiconductor processing, aggressive chemical environments, high-purity applications, precision burners. |
| Nitride-Bonded SiC (NBSiC) | Good strength, excellent thermal shock resistance, good oxidation resistance, porous structure. | Thermal processing, refractory applications, less demanding combustion environments. |
| Recrystallized SiC (ReSiC) | High purity, good thermal shock resistance, lower mechanical strength than SSiC. | Furnace linings, setter plates, less mechanically stressed burner components. |
For specialized applications, custom compositions can be developed to fine-tune properties such as thermal conductivity, electrical resistivity, or specific chemical resistance.
Design Considerations for SiC Burner Nozzles
Designing SiC burner nozzles requires a deep understanding of both the material’s properties and the specific operational environment. Careful design ensures optimal performance, manufacturability, and longevity of the component. Key considerations include:
- Geometry Limits: While SiC offers excellent strength, complex geometries with sharp corners or abrupt changes in cross-section can introduce stress concentrations during firing or operation. Designs should favor smooth transitions and generous radii.
- Wall Thickness Uniformity: Consistent wall thickness is crucial for uniform heating and cooling during manufacturing (sintering) and operation, minimizing internal stresses and potential cracking.
- Stress Points and Load Bearing: Identify areas of the nozzle that will experience the highest thermal and mechanical stresses. Reinforce these areas or design them to distribute loads effectively. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is often employed here.
- Mounting and Sealing: Consider how the nozzle will be mounted and sealed within the combustion system. Designs should account for differential thermal expansion between SiC and mating components, often incorporating flexible gaskets or compliant mounting strategies.
- Flow Dynamics: The internal geometry of the burner nozzle directly impacts fuel-air mixing and flame stability. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations can optimize flow patterns for efficient combustion.
- Weight and Thermal Mass: While SiC is lighter than many metals, its density and specific heat impact the overall thermal mass of the nozzle, which can influence system warm-up times and thermal response.
- Surface Area for Heat Exchange: For indirect heating applications, the surface area exposed to the flame and process gases needs to be optimized for efficient heat transfer.
Tolerance, Surface Finish & Dimensional Accuracy
Achieving tight tolerances and a precise surface finish in SiC components is critical for their performance, especially in precision applications. While SiC is a hard material, advanced machining techniques enable high levels of accuracy.
- Achievable Tolerances:
- As-fired/Sintered: Typically, tolerances for as-fired SiC components range from $pm 0.5%$ to $pm 1.0%$ of the dimension, with a minimum of $pm 0.1$ mm to $pm 0.2$ mm. This is suitable for many industrial applications.
- Ground/Lapped: For high-precision applications, SiC can be ground and lapped to achieve much tighter tolerances, often down to $pm 0.01$ mm or even finer, depending on geometry and size.
- Surface Finish Options:
- As-fired: The surface finish is generally matte to semi-glossy, with a roughness (Ra) typically ranging from $1.6 mu m$ to $6.3 mu m$.
- Ground: Grinding can achieve surface finishes with Ra values from $0.4 mu m$ to $1.6 mu m$.
- Lapped/Polished: For extremely smooth surfaces, such as those required for sealing or minimal friction, lapping and polishing can achieve Ra values as low as $0.05 mu m$ or even finer.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Consistent dimensional accuracy is crucial for proper fitment and performance within an assembly. Factors influencing accuracy include raw material consistency, sintering control, and post-processing capabilities. Utilizing advanced metrology and quality control processes is essential for meeting stringent requirements.
Post-Processing Needs for Enhanced Performance
While SiC boasts exceptional inherent properties, certain post-processing steps can further enhance the performance, durability, and specific functionalities of burner nozzles. These processes are typically chosen based on the application’s unique demands.
- Grinding and Lapping: For components requiring high dimensional accuracy, tight tolerances, and superior surface finishes (e.g., sealing surfaces, critical flow paths), diamond grinding and lapping are essential.
- Honing: Used to refine the internal bore of nozzles, improving flow characteristics and reducing friction.
- Surface Coating: In highly corrosive or erosive environments, or for specific catalytic properties, thin film coatings (e.g., CVD SiC, nitrides, or specialized ceramics) can be applied to the nozzle surface.
- Sealing/Impregnation: For certain porous SiC grades (e.g., NBSiC), impregnation with resins or glasses can reduce porosity and improve resistance to gas permeation or liquid absorption.
- Heat Treatment: While SiC is already stable at high temperatures, specific post-sintering heat treatments can sometimes be applied to optimize microstructure or relieve residual stresses.
- Joining and Assembly: SiC components can be joined to other SiC parts or dissimilar materials using advanced brazing, active metal bonding, or mechanical fastening techniques.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them in SiC Manufacturing
Working with silicon carbide presents unique manufacturing challenges due to its extreme hardness and high sintering temperatures. However, experienced manufacturers have developed sophisticated techniques to overcome these hurdles, ensuring high-quality, reliable products.
- Brittleness: Like most ceramics, SiC is inherently brittle, making it susceptible to chipping or fracture during machining and handling. Overcoming this involves careful design to avoid sharp corners, controlled grinding parameters, and robust handling procedures.
- Machining Complexity: The extreme hardness of SiC makes conventional machining nearly impossible. Advanced techniques such as diamond grinding, ultrasonic machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM – for electrically conductive SiC grades), and laser machining are employed.
- High Sintering Temperatures: Producing fully dense SiC requires very high sintering temperatures (above 2000°C), demanding specialized furnaces and precise atmosphere control. This is addressed through advanced furnace technology and proprietary processing techniques.
- Thermal Shock Sensitivity (during processing): During the manufacturing process, rapid heating or cooling cycles can induce thermal shock. Controlled temperature ramps and cooling rates are critical during sintering and subsequent heat treatments.
- Cost of Raw Materials and Processing: High-purity SiC powder and the energy-intensive manufacturing processes contribute to the cost. Optimization of material usage, efficient processing, and economies of scale help manage costs.
- Size Limitations: Manufacturing very large, monolithic SiC components can be challenging due to sintering constraints and machining limitations. This is often addressed by designing complex parts as assemblies of smaller, precisely machined components.
How to Choose the Right SiC Supplier for Burner Nozzles
Selecting a reliable supplier for custom SiC burner nozzles is paramount to the success of your project. A capable partner will not only provide high-quality components but also offer invaluable technical expertise and support. When evaluating potential vendors, consider the following critical factors:
- Technical Capabilities & Expertise: Does the supplier possess a deep understanding of SiC material science, design for manufacturability, and advanced processing techniques? Look for a team that can provide engineering support from concept to production.
- Material Options and Customization: Can they offer a range of SiC grades (e.g., RBSiC, SSiC, NBSiC) and tailor compositions to meet your specific application requirements? The ability to provide truly custom solutions is a key differentiator.
- Quality Control & Certifications: What quality management systems are in place (e.g., ISO 9001)? Request information on their inspection procedures, statistical process control (SPC), and material characterization capabilities.
- Experience in Your Industry: A supplier with a proven track record in your specific industry (e.g., semiconductors, aerospace) will have a better understanding of your unique challenges and performance needs.
- Production Capacity & Scalability: Can they meet your current volume requirements and scale up production as your needs grow?
- References and Case Studies: Ask for references from satisfied clients or review case studies that demonstrate their success in similar projects.
- Geographic Location and Supply Chain Reliability: Consider the stability and reliability of their supply chain. This is where Sicarb Tech stands out. As you are aware, the hub of China’s silicon carbide customizable parts manufacturing is situated in Weifang City of China. Now the region has been home to over 40 silicon carbide production enterprises of various sizes, collectively accounting for more than 80% of the nation’s total silicon carbide output.
Cost Drivers and Lead Time Considerations for SiC Burner Nozzles
Understanding the factors that influence the cost and lead time of custom SiC burner nozzles is essential for effective project planning and budgeting. While the initial investment in SiC can be higher than conventional materials, the long-term benefits often far outweigh the upfront costs.
Cost Drivers:
- Material Grade: Sintered SiC (SSiC) is generally more expensive than Reaction-Bonded SiC (RBSiC) due to higher purity requirements and more complex sintering processes.
- Design Complexity: Intricate geometries, thin walls, and tight tolerances increase manufacturing difficulty and, consequently, cost. Designs requiring extensive post-processing (e.g., grinding, lapping) will also incur higher costs.
- Volume: As with most manufactured goods, higher production volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale in material procurement and processing.
- Size of Component: Larger SiC components require more raw material and longer sintering cycles, impacting cost.
- Surface Finish Requirements: Achieving a very smooth surface finish (e.g., lapping or polishing) adds significant processing time and cost.
- Testing and Certification: Specific testing requirements (e.g., non-destructive testing, specific material property verification) can add to the overall cost.
Lead Time Considerations:
- Design and Prototyping: Initial design iterations, simulations, and prototype manufacturing can take several weeks to months, depending on complexity.
- Material Procurement: Sourcing high-purity SiC powder and other raw materials can sometimes have lead times, especially for specialized grades.
- Manufacturing Process: The SiC manufacturing process itself, including forming, sintering, and post-processing, is time-intensive. Sintering cycles alone can take several days.
- Post-Processing: Grinding, lapping, and other finishing operations add to the overall lead time, particularly for precision components.
- Batch Size and Production Schedule: Larger batch sizes might have longer overall production times but a shorter per-unit processing time. A supplier’s current production schedule also plays a role.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Thorough quality checks and final inspections are crucial steps that contribute to the lead time.
Early engagement with your chosen supplier is recommended to get accurate cost estimates and realistic lead time projections. Companies like Sicarb Tech offer transparent pricing and project timelines, working closely with clients to optimize solutions for both cost and delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about SiC Burner Nozzles
Here are some common questions we receive regarding silicon carbide burner nozzles:
- Q1: How long do SiC burner nozzles typically last compared to metallic nozzles?
- A1: SiC burner nozzles can last significantly longer, often 5 to 10 times, or even more, than metallic nozzles in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Their superior wear, thermal, and chemical resistance drastically extends their operational lifespan, leading to reduced replacement cycles and lower maintenance costs.
- Q2: Can SiC burner nozzles be repaired if damaged?
- A2: Due to the extreme hardness and monolithic nature of SiC, traditional repair methods like welding are not feasible. Minor surface damage might be addressed by grinding in some cases, but typically, damaged SiC burner nozzles are replaced. Proper design and material selection, along with careful handling, are crucial to prevent damage.
- Q3: Is SiC electrically conductive, and does this affect its application in burners?
- A3: The electrical conductivity of SiC varies significantly depending on its grade and doping. Some grades, like Sintered SiC (SSiC), can be semi-conductive, while others are more resistive. For burner nozzles, this electrical property is generally not a concern unless specific electrical insulation is required within the combustion system itself, in which case appropriate SiC grades or design modifications would be necessary.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Value of Custom SiC Burner Nozzles
In today’s demanding industrial landscape, where efficiency, longevity, and performance dictate success, custom silicon carbide burner nozzles are not just an alternative—they are an indispensable solution. Their unparalleled properties in extreme temperature, abrasive, and corrosive environments offer a definitive edge over traditional materials. For engineers, procurement managers, and technical buyers across the semiconductor, aerospace, power electronics, and various manufacturing sectors, investing in SiC burner nozzles translates directly into optimized combustion, reduced operational costs, minimized downtime, and a significant improvement in overall system reliability.
By partnering with a knowledgeable and experienced supplier like Sicarb Tech, you gain access to not only superior custom SiC products but also deep technical expertise, robust manufacturing capabilities rooted in China’s silicon carbide hub, and comprehensive support throughout your project. We are committed to delivering high-quality, cost-competitive solutions that meet your precise needs, and even offer technology transfer services for those looking to establish their own manufacturing capabilities. Embrace the future of high-performance combustion with custom SiC burner nozzles – a strategic investment that delivers long-term value and operational excellence.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.