Mastering Precision and Durability: A Guide to Silicon Carbide Extrusion Equipment

Share
Silicon carbide (SiC) stands as a cornerstone material in high-performance industrial applications, prized for its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear and chemical attack. For manufacturers aiming to produce complex SiC components like tubes, rods, and custom profiles with consistent quality and precision, silicon carbide extrusion equipment is indispensable. This advanced machinery is pivotal in shaping SiC paste into desired forms before the critical sintering process, enabling the production of robust parts for demanding environments. As industries from semiconductors to aerospace increasingly rely on the superior properties of SiC, understanding the intricacies of its extrusion process and the equipment involved becomes crucial for engineers, procurement managers, and technical buyers. This blog post delves into the world of SiC extrusion equipment, exploring its applications, advantages, design considerations, and how to select the right supplier for your manufacturing needs.
Introduction to Silicon Carbide Extrusion Equipment: Shaping a High-Performance Future
Silicon carbide extrusion is a specialized manufacturing process used to produce continuous, uniform shapes from SiC-based ceramic pastes. The core of this process lies in silicon carbide extrusion equipment, which typically includes a high-pressure extruder, precision dies, and often, integrated control systems. This equipment is engineered to handle the abrasive nature of SiC powders mixed with binders and plasticizers, forcing the mixture through a specifically designed die to create green bodies with precise cross-sectional profiles. These green parts are then subjected to drying and high-temperature sintering to achieve their final, exceptionally hard and durable state.
The importance of specialized SiC extrusion technology cannot be overstated. Unlike conventional metal or polymer extrusion, ceramic extrusion, particularly with a material as hard as SiC, presents unique challenges. These include managing the high abrasiveness of the SiC feedstock, ensuring uniform density in the extruded part to prevent defects during sintering, and achieving tight dimensional tolerances. Modern ceramic extrusion equipment designed for SiC often incorporates wear-resistant components, sophisticated pressure and speed controls, and die designs optimized for complex geometries. These features are essential for industries that demand high-quality SiC components such as silicon carbide tubes, rods, and custom profiles for applications in high-temperature furnaces, chemical processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Key Industrial Applications for Extruded SiC Components
The versatility and exceptional properties of silicon carbide make its extruded components highly sought after across a spectrum of demanding industries. The ability of silicon carbide extrusion equipment to produce complex and precise shapes efficiently opens doors to numerous applications where performance under extreme conditions is paramount.
Here are some key industrial sectors and their applications for extruded SiC components:
- High-Temperature Furnaces and Kilns:
- Rollers and Beams: Extruded SiC rollers and beams are extensively used in industrial furnaces for their high hot strength, excellent thermal shock resistance, and ability to withstand high loads at elevated temperatures (up to $1600^\\circ C$ for certain grades). They ensure stable and reliable support for products during heat treatment processes in industries like ceramics, glass, and metallurgy.
- Burner Nozzles and Radiant Tubes: SiC’s high-temperature stability and thermal conductivity make it ideal for burner nozzles and radiant tubes, offering efficient combustion and heat distribution while resisting oxidation and corrosion.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Process Chamber Components: Extruded SiC components are used in semiconductor etching and deposition equipment due to their chemical inertness, high purity, thermal stability, and plasma erosion resistance. This ensures minimal contamination and longer component lifetimes in aggressive processing environments.
- Wafer Handling Components: Precision SiC rods and custom profiles are used for wafer handling, where dimensional stability and wear resistance are critical.
- Aerospace and Defense:
- Heat Exchangers and Recuperators: The high thermal conductivity and strength of SiC are beneficial for compact and efficient heat exchangers in aerospace applications, operating under demanding thermal cycles.
- Rocket Nozzles and Armor Components: While often produced by other methods for intricate shapes, certain simpler geometries or pre-forms for these applications can leverage extrusion.
- Chemical Processing Industry:
- Mechanical Seals and Pump Components: Extruded SiC rings and sleeves are used in mechanical seals and pumps handling corrosive and abrasive fluids. Their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and chemical inertness lead to extended service life and reduced maintenance.
- Heat Exchanger Tubes: For corrosive environments where metallic tubes would fail, SiC tubes offer superior performance.
- Energy Sector (including Power Generation and Renewable Energy):
- Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) Substrates: Porous SiC, often formed through extrusion, is a key material for DPFs in diesel engines, effectively trapping soot particles due to its high-temperature resistance and thermal shock capabilities.
- Solar Energy Components: SiC is used in components for concentrated solar power (CSP) systems and in the production of photovoltaic (PV) cells.
The table below highlights common extruded SiC components and their primary industrial uses:
| Extruded SiC Component | Primary Industries | Key Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Tubes & Pipes | Chemical Processing, Furnaces, Energy | Corrosion Resistance, High-Temperature Strength |
| Rods & Bars | Furnaces, Mechanical Engineering, Semiconductor | Stiffness, Wear Resistance, Thermal Stability |
| Beams & Profiles | Kiln Furniture, Structural Supports | Hot Strength, Creep Resistance |
| Honeycomb Structures/Substrates | Automotive (DPFs), Catalysis | Porosity Control, High Surface Area, Thermal Shock |
| Custom Profiles | Semiconductor, Aerospace, Specialized Industrial | Design Flexibility, Specific Functionality |
The consistent demand for high-performance technical ceramics production equipment that can reliably manufacture these parts underscores the importance of advanced SiC extrusion machinery.
Advantages of Using Dedicated SiC Extrusion Equipment
Investing in dedicated silicon carbide extrusion equipment offers significant advantages for manufacturers aiming for high-quality, consistent, and cost-effective production of SiC components. Standard extrusion machinery often falls short due to the unique challenges posed by SiC’s hardness and abrasiveness. Specialized equipment, however, is engineered to address these issues directly.
Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Component Quality and Consistency:
- Uniform Density: Dedicated SiC extruders are designed to apply consistent pressure and ensure homogenous mixing of the SiC paste, leading to uniform density in the green body. This is critical for preventing warping, cracking, or dimensional inaccuracies during the subsequent drying and sintering stages.
- Precise Dimensional Control: Specialized die designs and sophisticated control systems on high-performance ceramic extrusion machines allow for tighter tolerances on extruded profiles, reducing the need for extensive and costly post-machining.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency:
- Higher Throughput: Equipment optimized for SiC can often operate at higher speeds without compromising quality, leading to increased output.
- Reduced Downtime: Components in SiC extruders, such as barrels, screws, and dies, are typically made from highly wear-resistant materials. This extends their lifespan and reduces the frequency of maintenance and replacement, minimizing costly downtime. Standard equipment would wear out rapidly when processing abrasive SiC.
- Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run:
- Lower Material Waste: Precise control over the extrusion process minimizes defects and rejects, leading to less wasted SiC material, which is a significant cost factor.
- Reduced Machining Costs: Achieving near-net shapes through precision extrusion reduces the reliance on diamond grinding and other expensive post-sintering machining processes.
- Capability for Complex Geometries:
- Advanced SiC extrusion die design capabilities, coupled with powerful extrusion forces, enable the production of more intricate and complex profiles that might be difficult or impossible with generic equipment. This opens up new application possibilities and design freedom for engineers.
- Improved Safety and Operability:
- Equipment designed specifically for ceramic powders often incorporates better dust containment and handling features, improving workplace safety. User-friendly interfaces and automation can also simplify operation and reduce the need for highly specialized labor.
For companies looking to establish or upgrade their industrial SiC parts manufacturing capabilities, the choice of extrusion equipment is a critical decision. While the initial investment in specialized machinery may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of quality, efficiency, and reduced operational costs make it a worthwhile endeavor. Sicarb Tech , with its deep understanding of SiC processing, emphasizes the importance of utilizing equipment tailored to the material’s unique properties to achieve optimal results in custom SiC component production.
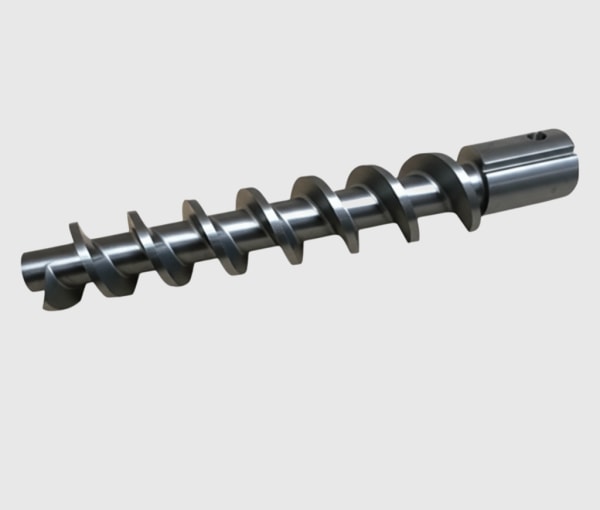

Critical Components and Technologies in SiC Extrusion Lines
A successful silicon carbide extrusion line is more than just an extruder; it’s an integrated system of critical components and technologies working in concert to produce high-quality SiC green bodies. Understanding these elements is crucial for optimizing the process and ensuring reliable output.
Key components and technologies include:
- Material Preparation System:
- Mixers/Kneaders: Before extrusion, SiC powder must be intimately mixed with binders (e.g., methylcellulose), plasticizers (e.g., water, glycols), and other additives to form a homogeneous, extrudable paste or dough. The choice of mixer (planetary, sigma blade, etc.) depends on batch size and paste rheology. Consistent mixing is paramount for defect-free extrusion.
- Extruder Unit:
- Barrel and Screw/Piston: This is the heart of the silicon carbide extrusion machine.
- Screw Extruders: Commonly used for continuous production of simpler profiles. The screw conveys, compacts, and forces the SiC paste through the die. Both single and twin-screw designs exist, with twin-screws offering better mixing and conveying for some formulations. Wear-resistant materials for the screw and barrel liner (e.g., hardened tool steels, or even SiC-lined components for extreme wear) are essential.
- Piston/Ram Extruders: Often preferred for high-viscosity pastes, larger cross-sections, or when extremely high pressures are needed. They operate in a batch or semi-batch mode.
- De-airing System: Entrapped air in the SiC paste can lead to voids and defects in the final product. Most industrial SiC extruders incorporate a vacuum de-airing system (typically a vacuum chamber between an initial conveying screw and the final extrusion screw/ram) to remove air before the paste enters the die.
- Barrel and Screw/Piston: This is the heart of the silicon carbide extrusion machine.
- Extrusion Die and Tooling:
- Die Design: The SiC extrusion die design is critical for achieving the desired profile and dimensional accuracy. Dies are typically made from hardened tool steels, tungsten carbide, or even advanced ceramics for extended life due to the abrasive nature of SiC. Complex internal features in the die control the flow of the paste to ensure uniform velocity across the die exit, preventing distortion.
- Die Material: Must be highly wear-resistant and capable of being machined to very fine tolerances.
- Quick-Change Systems: Some modern equipment features quick-change die systems to minimize downtime when switching between different profiles.
- Downstream Handling Equipment:
- Cutters: Automated cutters (e.g., wire cutters, blade cutters) are used to segment the continuous extrudate into desired lengths. Precision and clean cuts are important to avoid deformation of the green body.
- Conveyors and Transfer Systems: Gentle handling systems are required to move the soft, deformable green extrudates to drying areas without causing damage.
- Control and Monitoring Systems:
- PLC/HMI: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) with Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) allow for precise control of extrusion parameters such as screw speed, ram pressure, temperature (if applicable for paste conditioning), and cutting frequency.
- Sensors: Pressure transducers, temperature sensors, and motor load sensors provide real-time feedback for process monitoring and control, ensuring consistency and allowing for early detection of potential issues.
- Data Logging: Advanced systems offer data logging capabilities for quality assurance and process optimization.
The integration and proper functioning of these components are vital for any turnkey SiC extrusion line. Companies like Sicarb Tech , drawing on their extensive experience in Weifang, China’s SiC hub, understand the nuances of these technologies. Their expertise extends to advising on or even supplying specialized equipment tailored for specific SiC grades and product requirements, ensuring clients can achieve robust and efficient silicon carbide processing equipment setups.
Design and Operational Considerations for SiC Extrusion Processes
Successfully extruding silicon carbide components requires careful consideration of both the equipment design and the operational parameters. The inherent properties of SiC—its hardness, abrasiveness, and the specific rheology of SiC pastes—dictate many of these considerations. Optimizing these factors is key to achieving high-quality products, minimizing wear on silicon carbide extrusion equipment, and ensuring an efficient manufacturing process.
Material Formulation and Preparation:
- Particle Size Distribution (PSD) of SiC Powder: The PSD significantly affects paste rheology, packing density, and sintering behavior. A well-controlled PSD is crucial for consistent extrusion.
- Binder System: The choice and amount of binders, plasticizers, and other additives (e.g., lubricants, dispersants) are critical. This system must provide:
- Sufficient plasticity for extrusion without excessive pressure.
- Adequate green strength to handle the extruded parts.
- Clean burnout during sintering without leaving detrimental residues.
- Mixing Uniformity: Inhomogeneous paste leads to variations in density, shrinkage, and potential defects. Thorough and consistent mixing is essential.
- Paste Viscosity and Rheology: The paste must flow smoothly under pressure but retain its shape after exiting the die. Rheological properties must be tailored to the specific SiC extrusion technology (screw vs. ram) and die design.
Equipment Design and Setup:
- Wear Resistance: Components in direct contact with the SiC paste (barrel, screw, die) must be made from highly wear-resistant materials. This is a primary concern for industrial SiC parts manufacturing equipment.
- Example Materials: Nitrided steels, tool steels, tungsten carbide inserts, advanced ceramics.
- De-airing Efficiency: Entrapped air is a common source of defects. The vacuum de-airing system must be adequately sized and maintained.
- Die Design and Material:
- Flow Balancing: Dies for complex profiles require careful design to ensure uniform flow velocity across the entire cross-section, preventing warping or cracking. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling can be beneficial here.
- Land Length: The length of the parallel section of the die (land) influences surface finish and back pressure.
- Entry Angle: A gradual entry angle into the die can promote smoother flow and reduce defects.
- Temperature Control: While SiC extrusion is often a cold or warm process, some temperature control of the paste or die can help stabilize viscosity and improve consistency.
Operational Parameters:
- Extrusion Speed/Pressure: These must be carefully controlled. Too high a speed can lead to defects like tearing or shark-skinning, while too low a pressure may result in poor compaction. The optimal parameters depend on the paste formulation and die geometry.
- Cutting and Handling: Green SiC extrudates are fragile. Cutting mechanisms must be precise and non-deforming. Handling systems should minimize stress on the parts.
- Drying Process: Controlled drying is crucial to remove moisture/solvents from the binder system without causing cracking or warping. The drying schedule (temperature, humidity, airflow) must be tailored to the part geometry and paste formulation.
- Maintenance Schedule: Regular inspection and maintenance of the silicon carbide extrusion machine, particularly wear parts and de-airing systems, are vital for consistent performance and longevity.
Key Engineering Tips for SiC Extrusion:
- Start with a well-characterized and consistent SiC powder.
- Develop a robust paste formulation with optimal rheology for your specific equipment and desired product.
- Invest in high-quality, wear-resistant dies and extruder components.
- Implement stringent process control for mixing, extrusion parameters, and drying.
- Regularly monitor for wear and tear on critical equipment parts.
By addressing these design and operational factors, manufacturers can significantly improve the quality and yield of their extruded SiC components. Sicarb Tech often assists clients in optimizing these aspects, leveraging their comprehensive knowledge of SiC materials and processing technologies, including material, process, design, measurement & evaluation technologies.
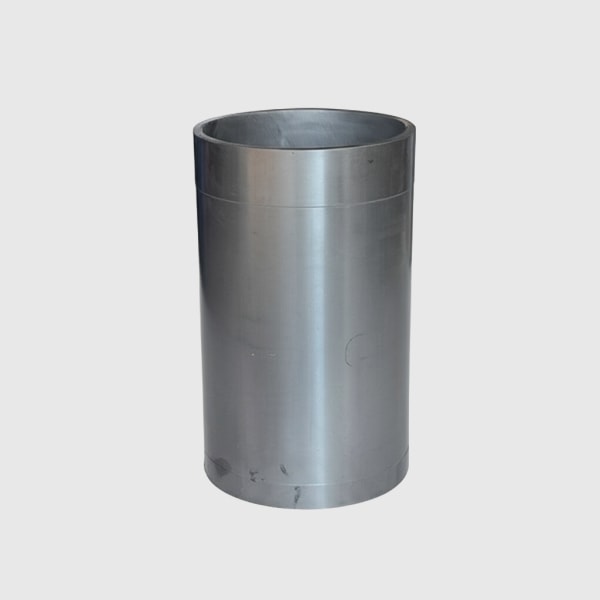

Optimizing Output: Quality Control, Tolerances, and Post-Extrusion Processing
Achieving optimal output from silicon carbide extrusion equipment involves more than just the extrusion process itself. It encompasses rigorous quality control measures, understanding achievable tolerances, and implementing necessary post-extrusion processing steps to meet final product specifications. These elements are critical for ensuring that the custom SiC profiles and components meet the demanding requirements of industries like semiconductors, aerospace, and high-temperature processing.
Quality Control in SiC Extrusion:
Effective quality control (QC) starts with raw material inspection and continues through each stage of production.
- Raw Material Inspection:
- Verification of SiC powder properties (particle size, purity, morphology).
- Consistency checks for binders and other additives.
- Paste Consistency Monitoring:
- Regular checks of viscosity, plasticity, and homogeneity of the SiC paste.
- Moisture content analysis.
- Green Body Inspection:
- Dimensional Checks: Measuring critical dimensions of the green extrudate immediately after extrusion and after cutting. This helps in adjusting die design or extrusion parameters if deviations occur.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects like cracks, tears, lamination, or inclusions.
- Density Measurement: Ensuring uniform green density, as this impacts shrinkage during sintering.
- Sintered Part Evaluation:
- Final dimensional accuracy and tolerance checks.
- Density and porosity measurements.
- Mechanical strength testing (e.g., flexural strength).
- Microstructural analysis (grain size, phase composition) if required.
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) like X-ray or ultrasonic inspection for critical components.
Achievable Tolerances and Surface Finish:
The achievable tolerances and surface finish for extruded SiC components depend on several factors:
- Type of SiC Grade: Different SiC formulations (e.g., SSiC, RBSC) have varying shrinkage rates and machining characteristics.
- Complexity of the Profile: Simpler shapes like rods and tubes can generally achieve tighter tolerances than complex custom profiles directly from extrusion.
- Quality of Extrusion Equipment and Tooling: Precision of the SiC extrusion machine and die is paramount.
- Control over Sintering Process: Uniform sintering is crucial for predictable shrinkage.
| Parameter | Typical As-Extruded (Green) Tolerance | Typical As-Sintered Tolerance (Without Grinding) | Typical Ground Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter | pm1 | pm0.5 | As low as pm0.01textmm |
| Wall Thickness | pm2 | pm1 | As low as pm0.02textmm |
| Length | pm0.5textmmtopm1textmm | Dependent on overall length | As low as pm0.05textmm |
| Surface Finish (R_a) | 1textmumtextto5textmum (Green) | 0.8textmumtextto3textmum (Sintered) | Down to 0.1textmum |
Note: These are general guidelines; specific values can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above.
Post-Extrusion Processing:
While the goal is often to achieve near-net shape through extrusion, some post-processing is usually required.
- Drying: A critical step to remove moisture or solvents slowly and uniformly to prevent cracking or warping before sintering. Controlled humidity and temperature dryers are used.
- Green Machining: Minor modifications or feature additions can sometimes be performed on the green body before sintering when it is relatively soft. This is more cost-effective than machining fully sintered SiC.
- Sintering: This high-temperature process densifies the SiC green body, giving it its final mechanical and thermal properties. Precise control of temperature profiles and atmosphere is essential.
- Sintered Machining (Grinding/Lapping/Polishing): Due to SiC’s extreme hardness, sintered parts requiring very tight tolerances or fine surface finishes must be machined using diamond tooling. This includes:
- Grinding: For achieving precise dimensions and flat/cylindrical surfaces.
- Lapping: For achieving very flat surfaces and fine finishes.
- Polishing: For optical-grade or ultra-smooth surfaces.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Final cleaning to remove any machining residues, followed by comprehensive final inspection.
- Coatings or Sealing (Optional): For specific applications, coatings (e.g., CVD SiC for ultra-high purity) or sealing (to reduce porosity in some RBSC grades) might be applied.
Optimizing these QC and post-processing steps is vital for delivering high-quality technical ceramics. Sicarb Tech , with its integrated approach from materials to products and robust measurement and evaluation technologies, ensures that clients receive components that meet the most stringent specifications, whether produced through their partner network in Weifang or by implementing their technology transfer solutions.
Choosing the Right Silicon Carbide Extrusion Equipment Supplier: A Buyer’s Guide
Selecting the right supplier for silicon carbide extrusion equipment is a critical decision that can significantly impact your manufacturing capabilities, product quality, and overall operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, technical procurement professionals, and OEMs, this choice goes beyond just the initial purchase price. It involves evaluating a vendor’s technical expertise, the robustness and adaptability of their machinery, their after-sales support, and their understanding of advanced ceramics machinery.
Here’s a guide to help you evaluate and choose the right supplier:
- Technical Expertise and Experience in SiC:
- Specialization: Does the supplier specialize in ceramic extrusion equipment, specifically for abrasive materials like SiC? Generic extrusion machine manufacturers may lack the nuanced understanding required for SiC.
- Track Record: Look for a supplier with a proven track record and case studies or references from other companies processing SiC or similar technical ceramics.
- Material Knowledge: A good supplier should understand the challenges associated with different SiC grades (RBSiC, SSiC, etc.) and how their equipment can handle various formulations.
- Equipment Design and Manufacturing Quality:
- Robustness and Durability: Given the abrasive nature of SiC, the equipment must be built with high-quality, wear-resistant materials for critical components (barrels, screws, dies). Inquire about the materials used and expected lifespan of wear parts.
- Precision and Control: Evaluate the precision of the extrusion mechanism, the sophistication of the control system (PLC, HMI, sensors), and the ability to maintain tight operational parameters.
- De-airing System Efficiency: A reliable and efficient de-airing system is crucial for void-free extrudates.
- Customization Capabilities: Can the supplier tailor the equipment (e.g., extruder size, die design, handling systems) to your specific product requirements and throughput needs for custom SiC profile extrusion?
- Range of Equipment and Turnkey Solutions:
- Complete Lines: Does the supplier offer complete turnkey SiC extrusion lines, including material preparation (mixers), extruders, cutting systems, and basic handling? An integrated solution from a single supplier can simplify setup and ensure component compatibility.
- Scalability: Consider if the equipment allows for future scaling of production.
- After-Sales Support and Service:
- Technical Support: Availability of prompt and knowledgeable technical support for troubleshooting and process optimization.
- Spare Parts: Ensure availability and reasonable lead times for critical spare parts, especially wear components.
- Training: Does the supplier offer comprehensive training for your operators and maintenance staff on the silicon carbide processing equipment?
- Warranty: Understand the warranty terms and conditions.
- Process Support and Technology Transfer:
- Process Know-How: Some suppliers, particularly those deeply embedded in the SiC industry, may offer valuable process know-how beyond just the machinery.
- Technology Transfer: For companies looking to establish new SiC production facilities, suppliers like Sicarb Tech offer unique advantages. Leveraging their position within the Chinese Academy of Sciences Innovation Park and their role in developing the Weifang SiC industry hub, SicSino provides not only access to customized silicon carbide components but also comprehensive technology transfer for professional silicon carbide production. This includes factory design, procurement of specialized equipment, installation, commissioning, and trial production – a full turnkey project service.
- Cost vs. Value:
- While initial cost is a factor, focus on the total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes the purchase price, maintenance costs, expected lifespan, efficiency, and the impact on product quality and yield. A cheaper machine that wears out quickly or produces inconsistent products will be more expensive in the long run.
Evaluating Suppliers – Key Questions to Ask:
| Category | Questions to Ask |
|---|---|
| Experience | How many years have you been making SiC extrusion equipment? Can you provide references? |
| Technology | What wear-resistant materials do you use? What are the typical tolerances achievable with your equipment? |
| Customization | Can you design custom dies for our specific profiles? Can the machine capacity be tailored? |
| Support | What does your after-sales support include? What is the lead time for spare parts? Do you offer process support? |
| Integration | Do you offer full extrusion lines including mixers and cutters? |
| Innovation | What R&D are you doing to improve your SiC extrusion technology? |
Choosing a partner like Sicarb Tech offers a distinct advantage. Their domestic top-tier professional team specializes in customized SiC production, backed by a wide array of technologies including material, process, design, and evaluation. They not only facilitate the production of higher-quality, cost-competitive custom SiC components in China but also empower businesses globally by assisting in establishing specialized factories. This commitment to comprehensive service and technological advancement makes them a strong candidate for companies serious about excelling in SiC component production.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about SiC Extrusion Equipment
Q1: What are the primary challenges in extruding silicon carbide, and how does specialized equipment address them?
A1: The primary challenges in extruding silicon carbide stem from its inherent properties: * High Abrasiveness: SiC particles are extremely hard and cause rapid wear on standard extrusion equipment components like screws, barrels, and dies. Specialized silicon carbide extrusion equipment uses highly wear-resistant materials (e.g., hardened tool steels, tungsten carbide, advanced ceramics) for these parts, significantly extending their life and reducing downtime. * Paste Rheology: Achieving a SiC paste with the right flow characteristics (plasticity, viscosity) for uniform extrusion without defects can be difficult. Dedicated equipment often features optimized screw designs or ram configurations for better paste conveyance and pressure control, along with sophisticated de-airing systems to remove trapped air that can cause voids. * Die Design Complexity: Creating dies that produce precise profiles and maintain dimensional stability despite the abrasive flow and high pressures is challenging. Suppliers of specialized SiC extrusion technology invest in advanced die design, often using CFD modeling, and robust die materials. * Green Strength: Extruded SiC green bodies can be fragile. The equipment must handle them gently, and the process parameters must be controlled to maximize green strength.
Q2: What types of SiC materials can be processed using extrusion equipment?
A2: Silicon carbide extrusion equipment can process various types of SiC formulations, provided they can be made into a suitable paste. Common types include: * Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSiC): Fine SiC powder mixed with sintering aids and binders. * Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RBSiC or SiSiC): A mixture of SiC powder and carbon, which is then infiltrated with molten silicon during firing. The initial extrusion forms the porous carbon-SiC preform. * Nitride-Bonded Silicon Carbide (NBSC): SiC grains bonded by a silicon nitride phase. * Recrystallized Silicon Carbide (RSiC): High purity SiC that is sintered at very high temperatures. The paste formulation (SiC powder characteristics, binders, plasticizers) will need to be adapted for each specific SiC type and the capabilities of the ceramic extrusion equipment. Some equipment might be better suited for certain formulations due to pressure capabilities or de-airing efficiency. Sicarb Tech has experience with various SiC grades and can advise on suitable equipment and process parameters.
Q3: Can silicon carbide extrusion equipment be used to produce very complex or hollow SiC profiles?
A3: Yes, silicon carbide extrusion equipment, particularly when coupled with advanced die design, can produce a wide range of complex and hollow profiles. * Hollow Shapes (e.g., tubes, multi-channel elements): This is achieved using dies with one or more mandrels (pins) held in the center of the die opening. The paste flows around the mandrel(s) and fuses back together before exiting the die, forming the hollow structure. This is common for producing silicon carbide tubes and honeycomb-like structures. * Complex Solid Profiles: Intricate solid shapes can be produced, but the complexity is limited by factors such as paste flow dynamics, the ability to maintain uniform density, and the structural integrity of the green extrudate. * Limitations: Extremely thin walls, very sharp internal corners, or features with high aspect ratios can be challenging. The design of the SiC extrusion die is critical, and often requires specialized expertise. For highly complex 3D shapes beyond the capabilities of extrusion, other forming methods like injection molding or additive manufacturing might be considered. However, for continuous profiles, extrusion remains a highly efficient method.
Q4: What is the typical lead time and cost range for industrial SiC extrusion equipment?
A4: The lead time and cost for industrial SiC extrusion equipment can vary significantly based on several factors: * Equipment Size and Capacity: Larger extruders with higher throughput capacity will generally cost more and may have longer lead times. * Complexity and Customization: Standard machines will be less expensive and quicker to deliver than highly customized custom SiC profile extrusion lines tailored to specific needs, including specialized dies, automation, and downstream handling. * Level of Automation: Fully automated lines with advanced PLC controls, sensors, and data logging will be at the higher end of the cost spectrum. * Materials of Construction: The extent of use of highly wear-resistant materials (e.g., tungsten carbide vs. hardened steel) for critical components will influence cost. * Supplier Reputation and Origin: Established brands or suppliers offering extensive service and technology packages may have different pricing structures.
* **Cost Range:**
* Smaller, basic laboratory or pilot-scale extruders might range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand USD.
* Industrial-scale production extruders or more complete **turnkey SiC extrusion lines** can range from several hundred thousand to over a million USD.
* **Lead Time:**
* For standard or smaller units, lead times might be a few months (e.g., 3-6 months).
* For large, customized, or fully integrated lines, lead times can extend to 6-12 months or even longer, depending on the supplier's backlog and the complexity of the project.
It’s crucial to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers, clearly specifying your requirements. Companies like Sicarb Tech can assist in defining these requirements and even in the procurement of specialized equipment as part of their technology transfer services for setting up SiC production plants, ensuring a cost-effective and technologically sound investment.
Conclusion: Partnering for Excellence in SiC Component Manufacturing
The journey from raw silicon carbide powder to high-performance industrial components is complex, with the extrusion process playing a pivotal role for many shapes and applications. Investing in the right silicon carbide extrusion equipment is not merely a capital expenditure but a strategic decision that underpins manufacturing quality, efficiency, and innovation. As industries continue to push the boundaries of performance, the demand for precisely engineered SiC parts—from intricate custom SiC profiles for semiconductor tools to robust silicon carbide tubes for high-temperature furnaces—will only escalate.
Successfully navigating this landscape requires more than just machinery; it demands expertise in materials science, process engineering, and equipment technology. Suppliers who offer not only state-of-the-art advanced ceramics machinery but also comprehensive support, including customization, process optimization, and even broader technology transfer, become invaluable partners.
Sicarb Tech exemplifies such a partner. Rooted in the heart of China’s SiC manufacturing hub in Weifang and backed by the formidable scientific capabilities of the Chinese Academy of Sciences , SicSino offers a unique blend of deep material knowledge, process innovation, and a commitment to client success. Whether you are seeking high-quality, cost-competitive custom SiC components or aiming to establish your own specialized SiC production facility, SicSino’s domestic top-tier professional team and integrated technological solutions provide a reliable pathway to achieving your goals. By choosing an expert partner, businesses can confidently leverage the exceptional properties of silicon carbide, driving progress and performance in the world’s most demanding industrial environments.

About the Author: Sicarb Tech
We provide clear and reliable insights into silicon carbide materials, component manufacturing, application technologies, and global market trends. Our content reflects industry expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to helping readers understand the evolving SiC landscape.